Coonhounds: historical background
Coonhounds are a group of breeds native to America. The Coonhound group is divided into seven breeds:
- black and tan coonhound;
- English American (red speckled) coonhound;
- red coonhound;
- Plott's coonhound (plotthound);
- mottled blue coonhound;
- Walker's arboreal coonhound;
- leopard hound.
Coonhounds - breed group
The history of coonhounds began during the colonization of America in the 18th century. At that time, dogs began to be imported to America from France and the British Isles for the favorite pastime of the aristocracy - hunting. These were Foxhounds, as well as French hounds and other breeds. But it turned out that these dogs, accustomed to hunting mainly burrowing animals, could not effectively track down American game, since most of the animals were hiding in the trees (hunting for possums, raccoons, bears, lynxes, pumas, foxes, etc. was practiced in America. ). Thus began the history of the Coonhound.
Each breed arose differently, so their history must be considered individually. Thus, the Black and Tan Coonhound (the only variety recognized by the FCI) is related to Bloodhounds, which gives it extraordinary olfactory abilities. The second progenitor was the black and tan foxhound. The Black and Tan variety was recognized by the FCI in 1945 and the official valid standard was published in 1991. Other coonhounds are considered only a variety of black and tan and are not allowed for exhibitions.
Coonhounds hunt small and large game
The Red Coonhound is descended from red foxhounds brought to Georgia in the mid-19th century. In 1840, the blood of Irish Foxhounds and Bloodhounds was added to this breed. The name of the breed (in the original Redbone Coonhound) was given by the name of the first breeder - Peter Redbone. Red Coonhounds were bred to hunt tree climbers and large game. They were recognized by the AKC (American Kennel Club) in 1902.
The book Where the Red Fern Grows, written by Wilson Rowles, tells the story of two red coonhounds and their 10-year-old owner.
The Plotta Coonhound is somewhat different from its counterparts. Its origins are related to Spanish, German, French and Native American dogs and has nothing to do with Bloodhounds and Foxhounds. In the mid-18th century, the German Johann Plott settled in North Carolina. He brought with him several Hanoverian hounds, bred for hunting bear and wild boar. He, and subsequently his son Henry, worked to improve the breed without crossing it with others. As a result, Plott's hounds became famous.
Coonhounds were bred for the so-called tree hunting - they drive the animal into a tree and control it until the hunter arrives.
One hunter who bred leopard hounds borrowed a male from Plott's pack to improve his breed, but later abandoned this idea, giving Plott the puppies. The influx of leopard hound blood had a good effect on the breed. At the beginning of the 20th century, in addition to the Plotts, Ferguson was involved in the breed. It is possible that Plott Hounds were crossed with other breeds at that time, but this is an undocumented fact. Plotthounds were recognized in 1946 by the United American Kennel Club and in 2006 by the AKC.
Directly related to the Plott Hound, the Leopard Hound (not to be confused with the Catahoula Leopard Dog!) is the rarest of the Coonhound group. It appeared as a result of crossing the dogs of the Spanish conquistadors and the dogs of the Indians. There is also a version that Beaucerons and even wolves took part in the formation of the breed. This breed became the ancestor of the Plotthound in the 19th century. The Leopard Hound is currently regulated by the AKC as a rare breed.
The Coonhound group includes seven breeds.
The Blue Speckled Coonhound is the result of a cross between the Foxhound and the French Blue De Gascogne Hound. This breed also has a variant, the American Blue Gascony Hound. She is often called the Old Type Blue Coonhound. It is distinguished by greater massiveness, cold color and a more restrained style of tracking prey. The Blue Coonhound was recognized in 1946 by the United American Kennel Club and in 2007 by the AKC.
The English Coonhound is a descendant of Virginia hounds, which were bred from foxhounds and other dogs brought to America by George Washington and other US politicians. In 1905 he was recognized by the United American Kennel Club.
Coonhounds can hunt in the most difficult terrain
The Walker Coonhound is descended from Foxhounds. Two breeders under the auspices of the US government were breeding strong, hardy dogs capable of hunting in American conditions. In 1800, a black and tan dog of unknown origin was crossed with future Walker Coonhounds to strengthen the gene pool. Perhaps later the blood of French tricolor hounds was added to the breed. Walker Coonhounds were recognized in 1945 by the United American Kennel Club and in 2012 by the AKC.
Description of the breed
There are several varieties of coonhound: red, blue speckled, black and tan, red speckled and Walker coonhound. The Red-Speckled Coonhound (another name is the English Coonhound) is a light and slender, hardy and strong dog. Height at the withers is 52-68 cm, weight up to 29 kg. The description is enshrined in the standard. The head is massive, elongated. The transition from forehead to muzzle is clearly pronounced. The ears are large and hanging. The eyes are medium-sized, widely set, dark in color. The body is square, slightly elongated, with well-developed muscles. The chest is wide, the back is straight. The tail is long and set low. The legs are straight and muscular, movements are easy.
The Redbone Coonhound (red dog) was bred in Georgia (USA) in the 19th century as a hunting dog (hunts in any terrain and in any weather). This is not only an excellent hunter, but also a companion. The dog is strong and swims well, as it has webbed paws. The eyes are large, the ears are long. The dog is active, smart, affectionate. Despite the fact that he gets along with children, he should not be left with children. Due to its highly developed hunting instinct, it is not recommended to keep it with other pets. The peculiarity of this species is that the redbone does not distinguish its own from strangers, so it will not make a watchman.
The Black and Tan Coonhound is the only officially recognized species (FCI #300).
Colors and coat
Coonhounds have short, moderately coarse, and shiny fur. It shimmers beautifully in the sun. Doesn't shed much. The color is red-chestnut (red-speckled), there are white spots. Other colors are allowed: blue-speckled (blue), black, yellow, red, tri-color.
Character
Although the dog is a hound, it can be affectionate and treats all family members with tenderness. Devoted, strongly attached to family, loves children. Expresses his emotions violently. Loves to play and walk outdoors. It is patient with other pets, but can sometimes mistake them for prey. The character is independent, slightly aggressive, obedient, strong-willed. The peculiarity of the dog is that it behaves with restraint under any circumstances. He cannot stand it when his freedom is restricted, so it is not recommended to keep him at home all the time.
The Red Coonhound is a universal hunter, catches any animal (small and large animals), an attentive watchman, and a good companion. Active and energetic. Loves to run at high speed without rest and compete with other dogs. Brave, fearless, flexible and hardworking. He barks loudly, which may not please the neighbors.
The dog needs socialization, in this case it will behave friendly and politely with other people. Some representatives of the breed are shy and timid. They also need to undergo a socialization course.
Appearance and breed standard
Each variety has its own standard, since the appearance of the breeds is somewhat different. There is an FCI standard only for the Black and Tan Coonhound.
Table: Black and Tan Coonhound Standard
| Purpose of the breed | Beagle | |
| Classification |
| |
| general description | A large dog, capable of working in the most difficult conditions, intended for hunting mainly raccoons, but coping with bears, cougars, lynxes, etc. Strong, dexterous, vigilant. The muscles are well developed, the bones are of medium weight, males are more massive than females. | |
| Proportions |
| |
| Head | Folded harmoniously. Length for males - 22.5–25.5 cm, for females - 20.5–23 cm. Friendly, impatient expression, skin without folds. | |
| Skull area | The outline is rather oval. In profile, the line of the skull is parallel to the line of the nose. The transition of the forehead to the nose (stop) is pronounced, in line with the occipital tubercle. | |
| Muzzle area |
| |
| Neck | Muscular, sloping, medium length. The skin is not folded, without dewlap. | |
| Body | Back | Powerful, smooth. |
| Breast | Medium depth, reaches the level of the elbows. | |
| Ribs | Full, round, without flatness. | |
| Tail | Strong, base just below the level of the sacrum. Standing freely, in motion it should rush high. | |
| Limbs | Front |
|
| Rear |
| |
| Feet | Compact, with thick, strong pads and well-curved toes. | |
| Movements |
| |
| Wool | Short, but thick and dense to protect against mechanical injuries during hunting. | |
| Color | Jet black with deep tan markings above the eyes, on the sides of the muzzle, chest, legs, covering the lower part (from the hock) of the legs with slate markings on the toes. | |
| Dimensions |
| |
| Faults and Disqualifications | Flaws:
Disqualification:
| |
Standards for other varieties are provided by the AKC and the United American Kennel Club. Coonhounds differ not only in color, but also in some aspects of appearance, so we will consider the general and individual characteristics of the breeds.
Common features:
- legs are straight, long, with medium heavy bones and developed muscles;
- drooping ears reaching to the tip of the nose when extended;
- short and smooth, but thick and dense fur, protecting the dog in wooded areas;
- the chest is deep enough, reaching the elbows;
- the tail is held high when standing and in motion, the head is held proud;
- massive head with a moderately wide skull;
- long muzzle;
- there are no folds of skin on the muzzle, and no dewlap on the neck;
- body length from shoulders to buttocks is approximately equal to height at withers;
- drooping lips typical of hounds;
- The eyelids do not droop under any circumstances.
Each Coonhound has its own characteristics
Individual characteristics:
- Red Coonhound:
- pleading expression of the muzzle;
- massive feet;
- brown eyes;
- clearly defined withers;
- sharp transition from forehead to nose;
- the line of the back is smoothly inclined towards the base of the tail;
- the bottom line is almost flat;
- the occipital tubercle is pronounced;
- the contours of the muzzle profile are not perfectly smooth;
- the back is straight;
- movements are proud, stable, with good space coverage;
- color - dark rich red, a small amount of white on the paws and lips is allowed, as well as black pigment on the muzzle near the ears.
- Plotthound:
- more elegant, thin;
- eyes brown or hazel;
- the line of the back is not perfectly straight: the withers are slightly higher than the hips, the line from the withers to the lower back bends slightly, then noticeably slopes towards the base of the tail;
- the eyes are slightly narrower and closer set;
- the profile lines of the muzzle are smooth, the transition of the forehead to the nose is softer;
- the muzzle is a little narrower, the cheekbones are more pronounced;
- movements are graceful, dexterous, rhythmic, at all trot speeds the legs move the same;
- The color must be brindle or black solid, white spots on the chest and a slight slate tint on the face and paws are permissible.
- Mottled Blue Coonhound:
- the muzzle is more square, massive, somewhat shorter;
- dark brown eyes;
- lips droop a little more;
- the line of the back is smoothly curved from the withers to the base of the tail;
- the belly is even leaner, and the chest is deeper, which makes the legs appear longer;
- deeper-set eyes;
- the line of the skull is perfectly rounded;
- movements are active, energetic, with a well-raised head and a soft back line;
- The color is black and white, maybe with red tan, it seems blue due to the abundant black speckling.
- Walker Coonhound:
- muzzle in profile is wide and long;
- there are no breaks in the line from the back of the head to the base of the tail;
- the line of the back gently descends to the tail;
- the body is somewhat shorter than that of other breeds;
- the tail is thicker and shorter, more curved;
- the belly line is straight;
- movements are smooth, without tension;
- color - tricolor: white, black, tan. White and black may be dominant, and the dominant color may have markings of other color colors.
- English American Coonhound:
- the back is straight;
- paws are more massive;
- the head is proportionally larger, the lines are clear, not smoothed;
- smooth curve of the back, which is repeated by the lower line of the body;
- the body as a whole is thinner, so the legs appear longer;
- color - white with red, on white - red specks;
- when moving, the tail is carried high, swaying from side to side, the movements are smooth and energetic.
- Leopard hound:
- slightly curved, the belly line is straight;
- the skin on the neck is thicker, denser and lies looser;
- the coat is slightly longer;
- the skull is perfectly rounded;
- eyes can be blue, heterochromic, yellowish and brown;
- color - leopard (possible with brindle), there are also solid colors.
Photo gallery: varieties of coonhounds:
The Black and Tan Coonhound is the only one recognized by the FCI.
Plotthound can only be brindle or black
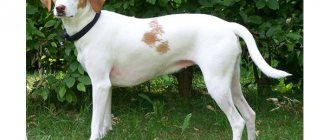
The American English Coonhound looks a bit like a Pointer
The Walker Coonhound is the most popular of the coonhounds.
The mottled blue coonhound is an excellent hunter.
The Red Coonhound was probably related to Irish Setters
The Leopard Hound is a descendant of Spanish and Mexican dogs.
Disadvantages of each breed:
- Red Coonhound:
- white spots on legs and chest;
- white markings;
- flat feet;
- hips higher than withers;
- undershot and undershot;
- any pigment on the face and ears except black;
- pointed skull.
- Plotthound:
- heavy bones;
- sad expression of the muzzle;
- Ears that are too long or too short (disqualification);
- the skull is sharp or too flat;
- square muzzle;
- feet pointing outwards, flat, front legs arched (disqualification).
- Mottled blue:
- overshot and undershot (disqualification);
- too short or long coat;
- disqualification - deviation from color;
- disqualification - deviation from size.
- Walker Coonhound:
- nose of any color except black;
- short, high-set ears;
- narrow skull;
- short neck;
- excessively curved tail;
- flat feet;
- disqualification - deviations from color.
- English American:
- narrow skull;
- disqualification - overshot and undershot;
- neck set too high or low;
- protruding shoulders;
- hairless or plumed tail;
- disqualification - tricolor color, brindle, lack of markings, solid color without markings.
AKC standards are much softer than FCI standards
Coonhounds: general characteristics
All Coonhounds are energetic, strong and hardy dogs of above medium or large size, strongly built with well-developed muscles, short or medium-length hair.
They are balanced in character, not aggressive, quite intelligent with a pronounced hunting nature. They love long walks and value freedom of movement. Not suitable for apartment living. They require serious education and competent training. Without the opportunity to hunt or engage in other work, they acquire various behavioral problems.
At home they are calm and friendly, not aggressive towards strangers. They get along with children and other animals. Without appropriate training, they can chase neighbors' cats, dogs and other small animals. Often prone to wandering and barking excessively. They can howl out of boredom.
They do not require complex care. Short hair needs to be brushed periodically. Somewhat more often during the molting period. The problem of a specific dog smell can be solved by regular bathing. The owner also needs to monitor the condition of the dog’s eyes, teeth and ears.
Coon hounds are relatively healthy dogs. Life expectancy is 11-13 years. There are few breed diseases. Dysplasia of the hip and elbow joint occurs. Notes predisposition to ear and eye infections. Other diseases are more often associated with improper feeding or poor living conditions.
American English Coonhound (Red Speckled Coonhound)
The American English Coonhound is believed to be a direct descendant of the English Foxhounds, which were imported to the United States in the 17th and 18th centuries. and retrained as hunters in the southeastern states. Known for his speed, endurance, intelligence and athleticism.
The American English Coonhound has a strong build, a deep chest and a strong back. Overall the dog looks balanced, without any exaggeration.
- Height: 58-66 cm;
- Weight: 20-29 kg.
The head is wide, of medium length. The eyes are dark brown, widely spaced. The ears are set quite low and drooping. The jowls cover the lower jaw. Medium length coat, hard .
Colors: red-speckled, blue-speckled, tricolor with specks, red-white, black-and-white.
The American English Coonhound is even-tempered, energetic, friendly, confident, sociable and loyal. Loves hunting and long walks. Gets along well with children if raised appropriately. Feels better in a pack of other hunting dogs. Sentry abilities are weakly expressed, security abilities are absent. Distrustful attitude towards strangers. The American English Coonhound is quite easy to train and strives to please the owner, but is not without its own opinion, perseverance and some independence.
Black and tan coonhound
The Black and Tan Coonhound was developed by crossing both the Virginia Black and Tan Foxhound and the Bloodhound. Hunts solely using instinct. Used primarily for raccoon hunting. However, courage, strength and endurance allow it to also be used for hunting deer, bear, wolf and puma.
The Black and Tan Coonhound is a fairly large, muscular dog with long ears and a noticeable double dewlap on the neck. Appearance gives the impression of strength and dexterity. Sexual dimorphism is well expressed.
- Height: 58-69 cm;
- Weight - 18-34 kg.
The Black and Tan Coonhound has a dry, strong head with low-set, long ears and friendly dark eyes. The limbs are strong and strong. The tail is set low. Square format case. The coat is short but thick. The color is jet black with rich red tan, located symmetrically above the eyes, on the sides of the muzzle, on the chest, legs, and under the tail.
By nature, the Black and Tan Coonhound is calm, gentle, good-natured and unobtrusive. Doesn't like to be left alone for a long time. We are quite tolerant with children. Able to work closely with other dogs.
Mottled Blue Coonhound
The Blue Speckled Coonhound was developed in the 20th century by crossing American, French and English hunting dogs. Like other representatives of the coonhounds, this is a hardy, energetic dog with a pronounced hunting instinct. In addition to sense of smell, he uses keen vision. It can work at any time of the day, even in impenetrable thickets.
The Blue Coonhound is a powerful, but at the same time elegant, dog with a regular physique and high adaptability. Sexual dimorphism is well expressed.
- Height: 53 69 cm;
- Weight: 20-36 kg.
The head is quite long and heavy. The muzzle is square. The ears are long, narrow, pointed at the ends. The eyes are round and dark brown. The body is strongly built, muscular, and somewhat sloping. The limbs are strong, the paws are cat-like, with well-curved toes. The coat is short but very dense. The color is tri-color, black and white with red tan. It appears “blue” because of the black specks on a white background.
The mottled blue coonhound is the mascot of the University of Tennessee.
The Mottled Blue Coonhound is energetic, resilient and active, and needs regular training, physical and mental stress. He is quite friendly not only with his own people, but also with strangers. Can become not only a hunting companion, but also a good family dog.
Plott (Plott's coonhound)
Specializes in hunting large animals: bears, boars, bobcats and cougars, but can also track raccoons, possums, coyotes and wolves. Plott is very different from other coonhounds. It descended from hunting dogs brought by the breed's originator, Henry Plott, from Germany to North Carolina in the 18th century. According to some reports, he brought several Hanoverian hounds with him and protected them from autocrosses.
The Plotta Coonhound is the national breed of North Carolina.
The Plott is an athletic and muscular hound of medium size, powerfully built with a distinct brindle coat.
- Height: 55-71 cm;
- Weight: 18-27 kg.
The coat is smooth, fine, medium texture, short to medium length, glossy. Possible colors: yellow, red, brown, black, gray, blue.
Plott works well alone and in a small pack of dogs. Sensual, reliable and patient by nature. He is a good companion and companion. Has enormous speed, strength and endurance. Courageous and strong enough to pursue and hold a large animal.
Red Coonhound
The ancestors of the red coonhound are English hounds and, possibly, Irish setters from which he could have inherited the color. Used to hunt raccoons, but can also pursue larger prey. The breed got its name from its short, shiny coat of deep red color.
The red coonhound became the main character in the Walt Disney Production film The Dog Who Thought He Was a Raccoon (1960).
The Red Coonhound has a strong build, a deep chest, straight long legs and a high-set head.
- Height: 53-69 cm;
- Weight: 25-32 kg.
Eyes as dark a color as possible. The ears are drooping and reach the nose. The paws are large, with very dense pads and webbed toes. The coat is short, smooth, lying close to the body. The color is solid red. Small white spots are allowed.
The Red Coonhound is energetic, cheerful and affectionate, he is the calmest of all the Coonhounds, which does not prevent him from being a passionate hunter. In the family circle he is loyal and friendly with a strong sense of humor. Gets along well with other animals, especially if he grew up with them. It adapts better than other Coonhounds to life in the house, but will miss long, regular walks.
Wood coonhound
Another name for the breed is the Walker Arboreal Coonhound. It becomes clear that the author of the breed is a certain person, or rather two: breeders from Kentucky John Walker and George Washington Maupin. The breed was bred to hunt raccoon, but is also used to hunt mountain lion, bear and deer. The Treehound is an American favorite among the Coonhounds.
Externally, the Arboreal Coonhound gives the impression of a working dog; it is strong, lean and agile.
- Height: 58-65 cm;
- Weight: 23-32 kg.
The skull is wide with a long muzzle and long drooping ears. The eyes are dark with a soft expression. The legs are straight and quite long. Cat paws, compact. The coat is thin, smooth, glossy. The color is three-color, but two-color dogs are also found: black and white and brown and white dogs.
The Tree Coonhound is friendly, even-tempered, intelligent and confident. Gentle around the family, enjoys the company of people and gets along well with children. In the forest he is a tireless and passionate hunter, at home he is a calm lover of comfort.
Leopard hound
The Leopard Hound is believed to be a descendant of Spanish hunting dogs crossed with Mexican ones. Early settlers brought them to America from Mexico for bear hunting.
The Leopard Hound is a powerful, agile dog of medium to large size. The body is somewhat elongated. The legs are quite long.
- Height: 53-60 cm;
- Weight: 16-34 kg.
The head is wide, the ears are hanging and long. The tail is set low, straight, and can be of any length. The coat is short. There are three possible colors: solid, leopard and brindle. Due to their color, the Leopard Hound is often confused with the Catahoula Leopard Dog.
The Leopard Hound is known for its eagerness to please its owner, making it highly trainable, easy to keep, and easy to hunt. The leopard hound can follow both a cold and a hot scent, hunt both day and night, uses scent and vision, and is very versatile in terms of use. Easily adapts to different weather conditions and navigates any terrain. They have exceptional courage, endurance and firmness.
Character and psyche of coonhounds
The character of coonhounds is generally the same. Differences arise only between dogs bred for generations for hunting and pets. The former are better able to work in a pack, are attentive, aggressive hunters, but loyal to people. The latter are excellent family dogs, playful, active and patient.
It is not for nothing that Coonhounds are one of the most popular breeds and even symbols of some states. These dogs are distinguished by a great desire to please their owner, fulfilling any of his commands. They are reserved with strangers, but never attack without reason; aggression towards people is unusual for them. But small animals, especially cats, can be attacked with pleasure. Therefore, it is not recommended to keep a Coonhound with cats or small dogs unless they were raised together.
Coonhounds are playful and sociable.
Dogs of this breed are self-confident and patient with children (puppies, children). They are distinguished by their love of affection, but at the same time they are polite - they will never suck up, they would rather wait for the owner to call them. From the outside, the Coonhound gives the impression of being a proud and independent dog, but in reality it really needs communication. The Coonhound is an excellent dog for traveling, as it is not afraid of a change of environment.
Coonhounds, like all hounds, are able to work well in a pack. Even if the dog has not been trained in a pack, it will get along well with its own kind. He responds to aggression directed at himself, but it rarely comes to a fight. Coonhounds are distinguished by their courage. These dogs can not only hunt, but also protect property and the owner. If they are in danger, the Coonhound will rush into battle without hesitation.
Coonhounds are brave and determined
Loneliness is detrimental to a social Coonhound, so it is recommended that only active people who can devote at least 5 hours a day to the dog should own one. The Coonhound needs long walks with mental and physical stimulation, otherwise it will get bored and make a big mess in the house. In addition, without activity and exercise, coonhounds will certainly develop behavioral problems and behave noisily: howl, bark, whine and spoil everything around them.
Coonhound training
If this is a family dog, then you need to pay attention to unquestioning obedience and suppression of attempts to attack small animals. Of course, suppressing a dog's hunting instinct is not the answer. Therefore, you should simply teach the puppy that hunting is prohibited on a walk without the owner’s permission.
If a Coonhound chases its "prey" it can put it in a dangerous situation. Therefore, first of all, he must learn the command “Come to me!” It is practiced until it is executed automatically, only then will the dog be safe. In general, a course of OKD will be enough for a comfortable life with a coonhound. But their intelligence and devotion to the owner will allow them to learn interesting tricks and take other training courses (UGS, agility, ZKS if desired).
Coonhounds are obedient, intelligent and easy to train.
If a dog is preparing to hunt, then you can start training it from six months. Take him out hunting with adult dogs (hounds), where the puppy will quickly learn everything he needs, accustom him to the commands “Fetch!” "To me!". Coonhounds are trained to drive prey up a tree and watch it until the owner arrives, but they can also be taught driven hunting.
Features of behavior and education of hounds
Today people also breed hounds, they are needed for various purposes, not necessarily for hunting. The breed has many characteristic features, and the owner must clearly know why he is breeding such dogs. You should pay attention to your pet. He needs long walks, but it is better not to walk him near the road.
The dog must always be on a leash, otherwise it may simply run away.
The name “hounds” comes from the word “drive”, it speaks for itself: initially people got dogs for the purpose of hunting hare, wild boar, fox
The pet needs to be controlled and raised very well. He can be trained to different commands. You need to show persistence, courage and rigor in raising these animals. They have an innate instinct to intimidate and corner their prey. Puppies and adult males run fast - this is another distinctive feature. If necessary, an adult dog can run 7 km unhindered, while maintaining the pace. The hound has developed limbs - this allows it to run for a long time and not stop.
If you are a hunter, a hound will help you in a difficult task. But to hunt on Russian territory, you need to go to a special reserve. Dogs help in hunting hare, wild boar, fox, even bear. For hunting, you can use not one dog (bitch), but two.
It is important to know: the hound loves a pack lifestyle, but you can get one individual by teaching it all the necessary commands. Experts recommend taking kids, and they should learn from adults. If you want to take not one, but 2 dogs, you need to make sure that one is the leader and the other is the follower.
Caring for Coonhounds
Caring for a Coonhound includes food, walking, maintenance and general care.
Food for a Coonhound should be high quality and balanced. The basis is animal proteins (meat) - 75%, so if you feed your dog food, pay attention to the percentage of meat. The food should be at least super-premium class; you can choose one specialized for hunting breeds or active dogs.
What common foods are suitable for a coonhound:
- Carnilove (whole line for dogs);
- Acana (entire line for dogs);
- Orijen (entire line for dogs);
- Summit for large breed dogs;
- AATU for dogs (very high meat content).
Meat is the basis of a dog’s diet
All these foods are gluten and grain free, with a lot of protein, their class is not lower than super-premium. The food is given according to the instructions on the packaging.
Natural food consists of lean meats, vegetables, and porridge. Some owners practice feeding only meat with a small addition of vegetables. This is also possible provided that the dog is given 100–150 g of low-fat cottage cheese per week and 3–4 raw eggs. Otherwise, calcium deficiency may occur. The amount of main food per day is calculated from the ratio of 40–45 g per 1 kg of dog weight.
When feeding natural food, it is a good idea to choose vitamin supplements (be sure to consult a veterinarian!).
The following should not be given to a Coonhound:
- food from the human table;
- spicy, fried, fatty foods;
- onions, garlic, potatoes, cereals, spices, seasonings;
- sweets (especially chocolate);
- pork and sea fish.
Food is the basis of a dog's health
You need to walk your coonhound at least 2 times a day for 1.5–2 hours. The walk should be active. You can optimally exercise your dog by teaching it to run next to a bicycle. But don’t forget that the dog not only needs to run, but also play with the owner and learn new things. Try, if possible, to change walking routes more often, so the dog will not get bored. It is best to keep a coonhound in a private house with a garden area. But a spacious apartment is also suitable, provided that the dog is walked a lot.
You don't need to wash your Coonhound more than 2-3 times a year. Short hair requires weekly brushing with a thick brush. Coonhound ears require special attention. They need to be examined more often so as not to miss an infection, the inner surface should be wiped daily with a napkin with a special lotion for cleaning dog ears, and the inside should be cleaned with it once every 5 days.
Since coonhounds, like all hunting breeds, love to roll around in something smelly (thus hiding their smell), frequent washing is necessary. My dog, although not a hunter, loves to give his owner “pleasant” surprises. But washing a dog with shampoo often is not very useful, so I found a very effective recipe from a breeder I know. You need to take clean sand and add a few drops of eucalyptus or lavender oil to it (not very much, just to remove the smell). Okay, but gently rub the dog, leave for 5 minutes and rinse. Sand will remove all dirt, and oil will remove unpleasant odors. It only helps those with short hair, because it is difficult to wash sand out of long hair.
Coonhounds, like all hunting dogs, love to roll around in odorous substances.
Appearance
The Black and Tan Coonhound is a large dog that belongs to the group of hounds that use their underbelly. It is worth saying that six more similar breeds have been bred in the USA, each of which can work as a raccoon and several other profiles. All four-legged animals are slightly similar to each other, but have obvious differences in color. There is only one variety recognized by the Fédération Cynologique Internationale (FCI), the Black and Tan Coonhound.
This is interesting! The youngest variety of the group is the Leopard Hound, which is not yet recognized as a breed, but is included in the provisional register. Experts are monitoring the development and establishment of the new line.
Representatives of the breed are strongly built, the body format tends to be square. Bitches are smaller and more refined than males. The height and length of the head from the nose to the back of the head are limited by the standard, the weight is proportional to:
- Males: 64–69 cm; 23–25 cm; 30–34 kg.
- Females: 58–64 cm; 20–23 cm; 25–32 kg.
Note! Exceeding the height limits is allowed, provided that the dog is proportional, but height that does not reach the standard, as well as visually short legs, is a defect that discards the dog from breeding work.
Breed standard
- Head - size is strictly proportional to height, dry build, strong structure. The forehead is quite wide, spacious, oval. The transition to the front part is pronounced, but not sharp. The length of the bridge of the nose is maximally equal and parallel to the skull. The lips are massive, slightly saggy, but neat. Loose or too thick lips are considered a defect.
- The teeth are large, well developed, aligned in a scissor bite. When assessing teeth, any, even minor, errors are unacceptable.
- The nose is very sensitive, mobile, black with wide open nostrils.
- The eyes have a wary, but at the same time gentle and intelligent expression. Small, round, planted at medium width and height, shallow. The iris ranges from light to dark in a brown palette. The irises should not be yellow, otherwise the dog will be culled.
- The ears are large, lowered to the head, set not wide and not too high. The set and line of the ears emphasize the decisive expression of the dog's muzzle. The length of the ears is measured by stretching forward; if the tips of the ears reach the nose, the dog meets the standard. Defects include high set ears.
- The body is as square as possible. The neck is well muscled, set at a medium height and inclined, not too long, free from folds (suspension is considered a defect). The scruff is barely pronounced, the withers are developed, the back is smooth, muscular, and straight. The chest is massive, deep to the level of the elbows, the ribs are well developed and convex. The groin line is straight, but free from folds and not sagging. The limbs are strong, strong with prominent, dry muscles, without folds, free to move. The shoulders are pronounced, strong, the forearms are vertical, the elbows are set parallel to the axis of the body, powerful, the pasterns are set vertically to the ground. The hind legs are more muscular than the front legs, visually strong and strong. The lower legs are elongated, with pronounced muscles, and the metatarsals are slightly shortened and vertical. The stifles and hocks are large, strong, not collapsed, not turned out. In the working stance, the front paws are placed vertically on the ground, the hind paws are extended beyond the line of the croup. The brushes are large, oval and strong. The fingers are gathered, with a slight bend. Dewclaws and splayed fingers, too long hands or straight fingers are considered a defect.
- The tail is powerful, set slightly below the back, carried freely and carried vertically.
Coonhound diseases
Coonhounds are strong, tough and healthy breeds that have not been inbred and bred from equally strong hunting breeds. The lifespan of a family dog is rarely less than 14 years; hunting dogs live 10–12 years. The breed has few diseases, but there are some predispositions.
Obesity
Many hunting breeds are susceptible to it because they need movement. If it is not enough, the dog naturally gains weight.
How to recognize obesity:
- inability to feel the ribs and spine through the layer of fat;
- it is difficult for the dog to walk, shortness of breath appears after minor exertion;
- problems with the heart and joints begin;
- The dog is rapidly gaining weight and eating more and more.
Coonhounds are prone to obesity
To prevent obesity you need to:
- Buy a scale for your dog and closely monitor weight changes. This will allow you to quickly adjust your diet.
- Watch your diet, do not feed more than normal.
- Do not feed the dog uncontrollably, do not give it treats outside of feeding and training.
- Treats are included in the daily diet and, if they are not fruits or vegetables, are deducted from the daily diet.
- Lead an active lifestyle with your dog.
Treatment is prescribed by a veterinarian. It consists of diet, exercise regimen and, in some cases, hormonal medications.
Ear infections
All dogs with floppy ears are susceptible to them, as infections thrive in enclosed, warm, humid areas. Main symptoms:
- severe scabies;
- the appearance of scratches and crusts;
- increased temperature of the ears;
- unpleasant odor;
- purulent discharge;
- negative reaction when touched;
- bending and shaking your head in a certain direction becomes especially noticeable while running.
Ear hygiene is the best prevention of ear infections
Prevention - ear hygiene, taking antiparasitic drugs. Treatment is medicinal, prescribed by a veterinarian depending on the infection.
Dysplasia
The term “dysplasia” refers to any deviation from the norm in the condition of a joint: destruction of cartilage or bone, cracks, defects, etc. Large breed dogs and dogs with a genetic predisposition are susceptible to dysplasia. Main symptoms:
- lameness or change in gait;
- decreased activity;
- swelling of the paw;
- stiffness in movements;
- inability to lean on the paw.
Treatment of dysplasia depends on the degree of neglect. Mild forms are treatable with physical therapy and medications. Severe forms can only be cured by surgery or hip replacement.
To prevent joint injuries in puppies, you need to dose the loads
Choosing a puppy
Coonhounds are practically unknown in Europe and Asia, with the exception of a couple of black and tan kennels in Europe. You can only buy a real puppy in your homeland, America. There, a puppy will cost from $500. It’s not difficult to choose a puppy - he has:
- long drooping ears;
- distinctive color;
- rather long legs;
- developed brow ridges;
- smooth line of the skull;
- tail held high while running.
You can choose a Coonhound puppy in its homeland - America
Coonhounds are rare dogs not only in origin, but also in their qualities. With proper love and upbringing, they will become wonderful pets, and if necessary, hunters. The Coonhound will allow a person to become active, teach him to understand animals and love them.
Hunting
Representatives of the breed are dogs bred for hunting. The genetics of animals include endurance, resistance to cold and heat, and the ability to work in difficult terrain. The purpose of the Black and Tan Coonhound is to track and drive prey . Taking into account the fact that according to the profile, dogs hunt raccoons, the dog drives the animal into a tree.
Note! The Black and Tan Coonhound is a rare breed whose centralized breeding is possible through fan sponsorship. According to connoisseurs of the breed, the main thing about it is not its appearance, but its working skills.
When working, Black and Tan Coonhounds rely solely on their sense of smell, meaning they do not need to see prey to chase it. In addition to hunting raccoons, representatives of the breed are used in work on large ungulates and predators. Even cougars have been known to hunt with Black and Tan Coonhouns.
Modern hunting is more of a sport or hobby than a necessity. In the United States, there is a tradition of night hunting for small fur-bearing animals, in particular raccoons, and possums. In that area, the animals are considered pests, so they do not see anything supernatural in their extermination. The night hunt involves a group of Black and Tan Coonhounds who begin their search from the outskirts of the city and follow the tracks of their prey.
During the chase, no matter where the dog is, it constantly barks. All dogs have unique voices, distinguished by hunters and other four-legged animals. The procession is accompanied by a loud bark, which serves as a sign for the movement of the hunters. As soon as the voices stop moving away, the hunters realize that the dogs have driven the game up a tree. By jumping on tree trunks and stretching towards certain branches, the four-legged animals indicate the exact location of the prey.
In America, Black and Tan Coonhounds are considered a very valuable breed. Only the best individuals are bred; puppies are raised under strict supervision, and their training begins from a very early age.