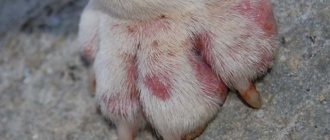
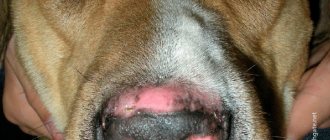
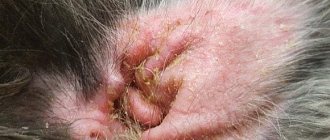
Why does this happen
It is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the pet’s stool, whether there are any bloody inclusions in it.
Clots can form due to trauma to the tissues of the intestines, stomach, infectious diseases and neoplasms.
Determining the focus by the color of the blood
If the stool contains red blood, the dog may be suffering from varicose hemorrhoids. This can happen due to frequent constipation, and in bitches a similar problem occurs after giving birth.
Black clots indicate problems with the stomach and intestines. They can be provoked by helminthic infestations and ulcerative lesions. In this case, the feces are mushy, with black streaks.
What diseases does it occur with?
Blood in the stool of dogs can appear due to many pathologies. For example, neoplasms in the digestive organs narrow the intestinal lumen as they develop.
As the food bolus moves forward, it injures the mucous membrane and causes bleeding. Blood clots appear in the stool.
Parvovirus enteritis in dogs is a disease accompanied by inflammation of the intestines. The pathology is manifested by vomiting, myocarditis, and a decrease in the level of leukocytes.
The virus that causes it is especially dangerous for puppies between 6 and 10 weeks of age. The dog develops diarrhea.
In the early stages, the stool is gray-yellow in color, later mucus and blood can be found in it, and a strong unpleasant odor appears. The animal may die within 48 hours.
Traces of blood and gastrointestinal problems
Ulcer, gastroenteritis, pancreatitis are the causes of blood discharge from the anus. An advanced ulcer is accompanied by vomiting mixed with blood, which, under the influence of intestinal enzymes, coagulates and turns black.
For helminthic infestations
Hookworms are parasites that destroy the intestinal mucosa.
During their life, helminths secrete substances that reduce blood clotting, which, after defecation, leaves the anus in small quantities. With extensive lesions, the animal develops anemia.
Parasites are especially dangerous for puppies and older animals.
My dog is bleeding from his anus, what could this be?
Intestinal or anal tumors, inflammation of the anal glands also cause a reduction in the width of the intestines and painful bowel movements.
Symptoms
Some dogs suffer from muscle degeneration in the anus, which leads to the formation of a perineal hernia (an enlarged mass in the intestine just behind the anus). This can cause stool to sink in and make it difficult to have a normal bowel movement, which puts extra strain on the muscles in the area, worsening the damage.
Diagnostics
A prolonged process of bowel movements and straining (tenesmus) may be a sign of disease in the rectum or anus.
A veterinarian wearing gloves performs a digital rectal examination, palpating the inner surface of the rectum and anus. The dog is given anesthesia or general anesthesia, especially if further tests, such as x-rays, are expected to be performed to diagnose abnormalities in the area. In this case, a sample of any tumor-like formations is taken and sent to the laboratory for examination.
Treatment
Determined by the cause of the disease. Most foods for older dogs have a high fiber content, which helps eliminate feces and restore the digestive system. Some older dogs benefit from a laxative. Some people require painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs to improve bowel mobility and normal bowel movements. Surgery may be required to remove any tumor-like formations and perineal hernia, as well as to restore normal bowel function. In some cases, surgery is necessary to remove the inflamed anal sac.
How to treat anal diseases?
Many anal tumors are benign and grow slowly. Some of them are associated with high levels of hormones in the body of unspayed male dogs and after castration they shrink or stop growing. Surgical removal is required for tumors that make defecation difficult. Blocked or inflamed anal sacs can cause pain in the anus and make it difficult to have a bowel movement. Filled anal sacs must be emptied by squeezing or rinsing under anesthesia or removed surgically.
The dog’s digestive system is a complex and at the same time delicate apparatus that instantly reacts to poor-quality food, a sudden change in food, a foreign body swallowed by the dog, and the proliferation of helminths due to deworming not carried out on time.
As a result, the animal may experience disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines, accompanied by diarrhea.
Manifestations of bloody diarrhea
This pathology often occurs with diseases of the digestive system. The problem can be caused by poisoning, including chemicals, dysbacteriosis, and foreign objects.
Frequent loose stools
The symptom is observed in cases of poisoning, infectious diseases, and dysbacteriosis. Carnivore plague is also accompanied by severe bloody diarrhea, fever, and photophobia.
Scarlet blood
Dysbacteriosis causes digestive disorders, the walls of the large intestine become inflamed. In this case, feces are released with streaks of scarlet blood. In advanced conditions, severe bleeding appears and mucus is present in the feces.
Expert opinion
Panteleeva Irina Petrovna
Breeder, 11 years experience.
Bright red discharge from the anus may indicate injuries to internal organs, in particular the rectum.
The symptom may indicate internal bleeding, hemorrhoids, the presence of tumors in the rectum, or the likelihood of rectal prolapse. Lack of stool and prolonged constipation can provoke a pathological condition.
Black feces
The symptom indicates damage to the walls of the stomach and the presence of internal ulcers. This may be an injury to the upper gastrointestinal tract or small intestine.
The cause may be chemical poisoning, such as rat poison.
Other symptoms
A small amount of blood released without diarrhea indicates minor injuries to the mucous membrane.
If severe diarrhea is accompanied by severe bleeding with scarlet spots, the animal needs urgent veterinary attention.
Other dangerous symptoms:
- poor appetite is a sign of poisoning, injury, viral and infectious diseases;
- lethargy is a manifestation of anemia, the condition develops with significant blood loss;
- stool has a pungent odor - a sign of parvovirus enteritis;
- stool mixed with mucus is a symptom of viral and intestinal infections;
- pale mucous membranes – the development of anemia, dehydration, signal a deterioration of the condition;
- rapid breathing and fever accompany all pathologies, regardless of their origin - this is a sure sign that the animal needs emergency help from specialists.
An adult dog has more vitality. In puppies, dangerous conditions leading to death develop at lightning speed. This statement also applies to mature individuals of dwarf breeds.
What does an increase in temperature mean?
This is a sign of salmonellosis, an inflammatory process. Hypothermia may indicate the presence of the rabies virus in the dog's body. With carnivore plague, the pet’s body temperature can rise to +40 °C.
Heat is also observed with inflammation of the paraanal glands. In a normal state, they are cleared during defecation, but in pathologies they become clogged, and the inflammatory process begins. The pet needs the help of a veterinarian.
Consequences of an animal refusing water
With severe diarrhea, fluid is removed from the body in large volumes.
A sick pet often refuses to eat and drink. Dehydration develops, which can lead to death.
Why does my dog's anus bleed?
If the dog has been bleeding from the mouth for quite a long time, you need to make a cotton swab and place it between the jaws. This must be done in such a way that it closes the space where the missing or damaged tooth is and puts light pressure on it. The cotton roller must be absolutely clean. For safety and greater effectiveness of the procedure, it can be moistened with Vivaton gel. In order to properly fix your pet's jaw, you will need to hold it with your hands or tighten it with a rope made from a bandage that is not too tight. If the injury is severe enough to cause severe pain, your dog may be given pain medication.
Intestinal bleeding.
- Most often it is caused by foreign bodies entering the stomach, intestinal injuries, as well as various gastrointestinal diseases. Bleeding that is not too severe can be detected by noticing that the animal's feces have become tarry. If the bleeding is heavy enough, the dog defecates much more often. In this case, the feces themselves become almost black. When trying to provide first aid to a dog, you should take into account the fact that, first of all, it needs complete rest. Having secured it, you need to put something cold on your stomach and area of the cross. You should not give the animal food, give an enema, or try to influence its condition in any other way. The animal must be taken to the hospital immediately.
Bloody vomiting.
- There are many types of hematemesis. Hungry vomiting once before eating is normal for dogs and should not cause much concern. But if it recurs at least 2 times, you need to urgently consult a doctor - most likely, such a disorder is caused by a violation of the bacterial background of the gastrointestinal tract, serious liver diseases, pancreas, or parasitic infestation (worms entering the dog’s body). The following features should also be taken into account: scarlet vomiting occurs in diseases of the esophagus, and if the problem is in the stomach, the blood will be dark red. In any case, if your dog is vomiting blood, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Blood in stool.
- The danger of this bleeding lies in the fact that the owner cannot always notice it. Typically, the degree to which blood stains the stool (the stool becomes tarry and dark red in color) depends on how much internal bleeding there is in the stomach or small intestine. It is usually caused by severe damage to the rectal lining, disease or prolapse of the rectum, hemorrhoids or tumors. The owner's behavior after detecting this symptom should depend on the cause of its occurrence. If the bleeding is slight, there is a high chance that it is caused by constipation. Try giving the animal a little castor oil and feeding it oatmeal with milk, completely eliminating meat and fish products. If the bleeding is severe enough and does not stop for several days, you should take your pet to see a doctor. Only a specialist can correctly diagnose the disease that caused the symptom.
Blood in urine.
- The appearance of blood in the urine most often means that the dog has kidney problems, urinary tract disease or bladder disease. Depending on the underlying medical condition causing the symptom, your dog may have an increased urge to urinate, or it may be painful. If you notice any of the above signs, you should definitely take your dog to a clinic where he can get help. But if the situation is critical, and there is no opportunity to visit a doctor, you need to put something cold on the dog’s lower back and give him approximately 100 milliliters of nettle to drink. No-spa, calcium chloride or Vikasol can also help (must be administered intramuscularly).
Uterine bleeding.
- Most often, this type of bleeding is caused by injuries, tumors, inflammation of the uterus, or is a consequence of childbirth and various types of hormonal imbalances. If the blood loss is not too profuse, the dog usually manages to lick off drops of blood before the owner notices. If it is strong enough, the blood may flow in a small stream and blood stains will remain where the dog was lying. Uterine bleeding is not always accompanied by any other symptoms. If the bleeding is severe, the animal may become lethargic and apathetic; often in such cases, dogs refuse water. In any case, after uterine bleeding is detected, the dog should be taken to a doctor as soon as possible. If this is not possible, you need to give your pet warm milk or low-fat chicken broth, put something cold on the belly and, if necessary, inject 2 milliliters of Vikasol.
What should the owner do?
If the animal has bloody discharge, you should not hesitate. The pet needs urgent specialized care and treatment.
Urgent contact with a specialist
It is important to get your dog to a veterinarian quickly. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Finding the exact cause of bleeding from the anus is not easy. To do this, a specialist examines the animal, collects anamnesis, prescribes tests, and ultrasound of internal organs.
What to do is strictly prohibited
You cannot prescribe medications at home, especially those intended for people: if an animal has damage to the stomach or intestinal mucosa, this is detrimental to it.
You should not give an enema if there is bleeding - this worsens the pet’s condition, especially if there is mechanical damage to the intestinal walls.
Causes of bloody diarrhea
It is important to remember that bloody diarrhea in a dog is not a separate pathology, but a reaction of the body, signaling problems in the functioning of the stomach and intestines.
The most common causes of loose, bloody stool in dogs include:
Diarrhea
- Chemical poisoning. Chemical substances entering the animal's body cause poisoning. In addition, they interfere with blood clotting, which leads to increased vascular permeability. As a result of this process, the dog begins to poop blood.
- Traumatic enterocolitis. Mechanical injury to the intestine caused by ingestion of a foreign body with sharp edges.
- Helminthiasis and dysbacteriosis. Certain types of helminths that parasitize the intestines damage its mucous membrane. And since the mucous membrane is permeated with vessels, it also experiences a load of parasites,
Animal treatment: therapy methods and remedies
Nursing a sick pet should be entrusted to specialists at a veterinary clinic.
Self-medication: why you shouldn’t do it
At home it is impossible to determine the cause of the pathology. To do this, it is necessary to conduct an endoscopic or x-ray examination, ultrasound, and take clinical tests.
In any case, the use of medications without making an accurate diagnosis is dangerous for the dog’s life.
For helminthiasis
Treatment depends on the cause of the pathological condition. If worm eggs are found in the dog’s feces, the following drugs are prescribed to destroy them: Drontal Plus, Prazicide, Inspector Total S.
If there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract
For severe bleeding, Vikasol, Calcium Gluconate, Dicinone are prescribed.
To relieve pain, you need to take antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Papaverine). To normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract in the post-traumatic period, Catozal, Veracol, Clamoxil are prescribed.
To restore the intestinal microflora and stop diarrhea, probiotics are needed (Lactobacterin, Symbiolact, Enterol).
Neoplasms in the intestines
The tumor can only be removed surgically. Treatment of intestinal cancer is supplemented with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The owner needs to mentally prepare for this difficult stage in the dog’s life.
Infections
If the infectious origin of the disease is confirmed, antibacterial therapy is indicated. The following broad-spectrum drugs are effective: Ceftriaxone, Amoxicillin, Levomycetin.
Prevention
To avoid intestinal pathologies, the following recommendations should be followed:
- it is necessary to reconsider the pet’s diet, the food should be balanced;
- do not give the dog food from the owner’s table (tubular bones, smoked meats, sweets);
- deworm the animal 3 times a year;
- If infectious diseases develop, immediately contact a veterinarian to avoid extensive damage to internal organs.
Household chemicals, small and sharp objects should be kept out of the reach of animals.
Causes
There are a number of causes for bloody diarrhea in dogs. These can be either diseases or exposure to unfavorable factors, for example:
- various poisonings;
- viral infections;
- bacterial infections;
- diseases of internal organs;
- helminths;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- the presence of a foreign body in the digestive tract;
- injuries;
- allergy;
- intestinal tumor;
In case of poisoning with low-quality, expired food for dogs or various poisons, bleeding in the digestive tract may occur in dogs. This is due to changes in blood composition due to the action of toxins.
During viral infections, the intestinal mucosa is disrupted, it becomes thinner and easily injured, thereby causing intestinal bleeding. Infections caused by bacteria also damage the intestines, such as salmonella, forming ulcers in the intestines that bleed.
Worm infestations, irritating the dog's anus with severe itching, force it to fidget on the floor and scratch it, thereby injuring it. Helminths cause diarrhea in dogs and, together with blood from the damaged hole, can give a similar symptom. Leptospirosis, multiplying in the animal’s liver, has a negative effect on blood vessels and blood composition.
Dysbacteriosis, a disruption of the normal microflora in the dog's intestines, together with poorly digested food, irritates the intestines, thereby causing diarrhea with blood in it.
A severe bruise or compression of a dog’s internal organs can severely damage them and cause not only diarrhea, but also severe intestinal bleeding. Also, a foreign body, such as a swallowed bone, can scratch the intestines, and even the anus.
Medications and vitamins that are not suitable for a dog also sometimes cause this symptom; replacing them with others stops this disorder.
Various intestinal cancer tumors in dogs can cause a similar symptom through their growth and development.