Localization of papillomas in dogs
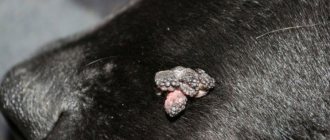
Papillomas are round formations of a pinkish tint with a smooth surface. Their growth is accompanied by darkening and a change from the original appearance to a rough one, reminiscent of a miniature cauliflower.
The location of papillomas determines their type:
- paw pads - pad;
- oral cavity, nose and lips – oral;
- thighs or lower body – multiple;
- abdomen and armpits – transitional cell;
- genital organs – genital;
- head or eyelids - cutaneous.
Young animals are more likely to suffer from the oral type of neoplasm, while older animals are more likely to suffer from multiple neoplasms.
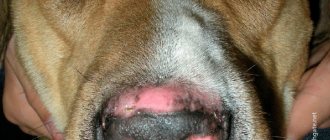
Papillomas in a dog's mouth
What types of papillomas are there (description with photo)?
The virus is capable of infecting cells of the skin or mucous membranes. It is rarely malignant in nature, but sometimes degenerates. The owner should be especially concerned about warts that have begun to grow rapidly or bleed. Depending on external characteristics and location, warts are divided into the following types:
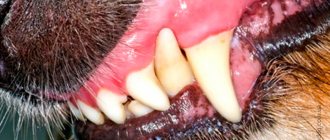
Oral papillomas
- Papillomas of the oral cavity. As a rule, they occur in young animals. The virus affects the mouth, nose, lips, tongue. As you can see in the photo, warts can have a diameter of up to 1 cm, white or gray in color. The disease is very contagious, but it is transmitted exclusively to dogs and does not threaten the owner.
Transitional cell neoplasm
- Transitional cell neoplasms. The disease usually affects young animals. It looks like a round tumor covered with small pimples, which are found in sponges. The growth is easy to recognize by comparing it with the image in the photo. Such papillomas often appear under the arms or on the stomach, but sometimes they are also found on the pet’s ear or eye.
Skin warts
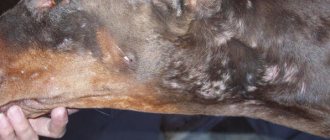
- Skin warts. This virus is usually localized on the animal's paws and back. It leads to the appearance of benign lumps, the size of which almost never exceeds 1 cm. Outwardly, these papillomas resemble a tick. They do not cause any particular discomfort to the dog. The exception is skin lumps that form on the paws. The disease most often affects older dogs.
- Pigmented papillomas. These growths are located mainly on the abdomen of small breed dogs. Outwardly, they look like a sulfur match head with a thin base. If the disease gets worse, there will be a lot of papillomas and they will become covered with scales.
- Genital warts. The disease is extremely rare in dogs. These are single tumors of small size.
Risk group and routes of transmission
The risk of infection is increased in:
- older dogs and puppies;
- animals with weak immunity, reduced due to a chronic disease or recent illness;
- pets belonging to pugs, cocker spaniels, spitz, miniature schnauzers and terriers.
The appearance of papillomas is due to:
- using a contaminated syringe during vaccination;
- interaction with personal belongings of an infected animal;
- direct contact with a sick dog;
- non-sterile instruments used for grooming.
Infection occurs from warts located on the cheeks and mucous membranes (lips, mouth).
If papillomas affect the ears, paws or neck of a pet, then it does not pose a danger to other animals.
As an animal ages, it becomes more susceptible to the virus.
Treatment of viral papillomatosis
Therapy for the disease can have several directions. Warts in dogs usually appear due to a loss of strength in the animal, so treatment is aimed at restoring the dog’s immunity. The second therapeutic direction is the fight against the growth itself. It can be cut out with a scalpel or destroyed with substances that can decompose cells. The choice of a specific remedy to combat papilloma will depend on its location, size and structure.
Conservative therapy
There are special medications that veterinarians have been using to treat dogs for many years. For papillomatosis, the following medications are used in veterinary medicine:
- Novocaine. The drug at a concentration of 0.5% is administered to the dog intramuscularly. The dosage is calculated according to the following formula: half a milliliter of the product is taken per 1 kg of animal weight. Veterinarians recommend administering the medicine very slowly and carefully, while constantly monitoring the dog. If the dog begins to get nervous, his pulse quickens, the administration must be stopped. The course of treatment should consist of 3-5 procedures, between which you need to take breaks of 4 days.
- Local use of Novocaine. The drug can also be administered directly under the seal in a dosage of 0.5 ml. Injections are recommended every 2-3 days until the formation disappears.
- Gamavit. This drug is an immunomodulator that helps increase the animal’s body’s defenses. The dosage and schedule of administration of the drug should be prescribed by a doctor. You can use the instructions for the drug and calculate the dose yourself. Analogues of Gamavit are Maxidin, Fosprenil.
- Iodine. Papillomas can be cauterized with a regular alcohol solution of iodine. However, a sore that appears on the oral mucosa or on the lower eyelid cannot be removed using this method.
Papillomas in dogs were once effectively treated with herbs. In this regard, dandelion, celandine and garlic juice have proven themselves well. The product should be lubricated daily on the sore spot. To remove sores on the oral mucosa, you can use a mixture of castor oil and baking soda. Lubricating warts with a mixture of linseed oil and honey has a good effect. At home, traditional methods are the most acceptable because they do not pose a danger to the dog.
Surgical intervention
If conservative treatment does not give any results, in cases where therapy requires serious measures due to damage to the lump, it should be removed surgically. You can operate on a dog using a scalpel, but today innovative technologies are increasingly used for this.
Laser treatment of warts provides a much better effect. This method is considered minimally invasive, and at the same time it allows you to remove the entire tumor without any traces. It is believed that the operation is painless, but veterinarians administer local anesthesia before it to remove as much discomfort as possible from the treatment.
Another option for fighting is cryodestruction. The essence of the method is to use liquid nitrogen to freeze the wart. Under the influence of very low temperatures, pathological cells are destroyed, after some time only a small scar remains at the site of the lump. True, this procedure is also not pleasant.
Causes of papillomatosis
The main cause of the disease lies in the viral papillomavirus, which affects the skin and mucous bodies. Taking advantage of any microcracks, it penetrates into the body. The growth actively multiplies, capturing surrounding tissues and transforming them into tumors, and leads to chromosomal instability.
The virus is not always active after penetration. Sometimes it assumes a dormant state ranging from 7 to 60 days. Some animals do not notice the changes at all. In such cases, the incubation period lasts the entire dog's life.
Activation of the virus is provoked by:
- operations performed using general anesthesia;
- stressful situations;
- corticosteroids taken on a long-term basis.
Papilloma virus
Despite the low risk of malignancy of the neoplasm, it is better to show an animal with papillomas to a doctor. Although the chances are small, degeneration into a cancerous tumor is quite possible.
Only dogs get sick with papillomavirus.
Humans and other pets cannot become infected from an infected animal.
Symptoms of the disease
You can suspect something is wrong by:
- Lameness. When the paws are infected, it is difficult for a dog to make normal movements.
- Bleeding. The appearance of blood is a dangerous symptom inherent in a malignant formation. This sign also occurs when a sore is picked off while scratching, but only a veterinarian can find out the true cause.
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth. Injured papillomas attract harmful bacteria, leading to the appearance of suppuration.
- Excessive drooling. Sores accumulated in the oral cavity make swallowing difficult.
- Decreased appetite or a transition to exclusively soft foods, accompanied by a decrease in weight.
- Frequent attempts to bite into the paws. Interdigital papillomas cause a strong feeling of discomfort, forcing the dog to look for any way to eliminate the source of the problem.
Don't ignore warts.
If overgrowth occurs, your pet may develop papillomatosis or squamous cell carcinoma.
Diagnosis of warts on the body
It is impossible to do without a medical diagnosis, since the appearance of papillomas can lead to cancer.
Symptoms that are simple at first glance raise questions upon direct examination. For example, the detection of tumors in the female genital area is a real problem for the average person.
The following diagnostic procedures are used:
With insufficient immunity, a benign formation develops into a malignant one
Treatment of the disease and removal of papillomas
If the neoplasms are benign and do not bother the animal, then it is not necessary to remove or treat them. Treatment is carried out for dogs at risk and from an aesthetic point of view.
The therapy used is divided into:
Promptly
It is used in the presence of pain and severe discomfort. With this treatment:
Medication
Classic variation based on:
If the pet is in good health, the disease goes away on its own.
In this case, a repeated relapse is excluded, since the animal is equipped with immunity from papillomavirus.
It should also be noted that vaccination uses a sample of neoplasm tissue. The resulting vaccine is injected under the skin 2 times with a break of 7 days. Effectiveness becomes noticeable at the end of 1 month from the start of treatment.
Thus, for a complete recovery, the pet will need a month with vaccination, 2-3 months with drug therapy, and 1 month with surgery. Moreover, in the case of surgical intervention, the visible effect is noticeable immediately after the operation.
Basically, the disease occurs in a mild form and viral papillomatosis eliminates itself
Complications of the disease
Papillomas can degenerate into malignant tumors, but the risk of such an outcome is low. It is also important not to trigger the disease in dogs at risk. Due to low immunity, it is more difficult for them to survive the disease.
Against the background of papillomavirus, secondary fungal and bacterial infections develop. Abrasive sores in the oral cavity can lead to stomatitis.
Despite the acquired immunity, the recovered dog becomes a carrier of the virus and poses a danger to animals at risk.
What is papilloma?
Papillomatosis is a viral disease that is quite common in dogs. Papillomas in dogs, the treatment of which should not be delayed, are benign growths. Outwardly, they look like cauliflower inflorescences. Tumors are caused by infection of epithelial cells with DNA by papillomaviruses. The virus promotes the growth and division of epithelial cells, resulting in chromosomal instability and mutations.
Having penetrated the body, the virus may not manifest itself immediately: it may take several weeks, or even a month, before the first signs appear. The pathogen is quite tenacious in the external environment.
Viral papillomatosis can be transmitted from one animal to another through contact, medical instruments and care items. However, the disease does not pose any danger to humans.
Caring for a sick dog
Adherents of traditional medicine advise using:
- garlic;
- spurge;
- dandelion;
- celandine;
- dry ice;
- rowan;
- linen threads and other options.
Wart in a dog
The use of such methods increases the risk of developing fibrosarcoma, and the use of folk remedies on the mucous membrane of the eye can permanently deprive the pet of vision.
After removing the tumor, wait for complete healing. Treat the area with medications recommended by your doctor until the crust falls off on its own. As a rule, dietary adjustments are not required, but in case of damage to the oral cavity, it is better to temporarily switch to soft and liquid foods.
During treatment and care, purchase a special collar.
In it, the dog will not be able to lick off the ointments used.
Adviсe
The following tips will help you monitor your pet's health:
- Regularly inspect the animal for tumors.
- If you notice papilloma in another dog, do not let your pet near it.
- The immune system can be strengthened by long walks and vitamins.
- Papillomas in dogs that were treated in a specialized institution will heal much faster than those removed at home.
- If there is a tumor, do not allow your pet to comb or tear it.
- You can lubricate the wound with celandine only if the dog cannot reach it with his tongue.
A 24-hour veterinary clinic is a faithful assistant for any pet illness!