Rabies vaccination is given to a person on suspicion or to prevent an incurable disease, which in 100% of cases will lead to death. The causative agent is rhabdovirus, an extremely virulent microorganism that cannot be treated with standard methods of modern medicine. That is why it is extremely important to give a person an anti-rabies injection on time.
When are rabies vaccinations necessary for humans?
After being bitten by an animal with rabies, its saliva entering the wound contributes to the development and further progression of the disease. The probability of infection from a bite is 25-90%. The disease spreads on average from 1 to 8 weeks.
Most often, people become infected from their own pets who have been bitten by infected animals, so a person is vaccinated against rabies almost immediately after being bitten by a potential animal carrier of the disease. Also, from time to time, those who have direct contact with animals: gamekeepers, trainers and veterinarians should be vaccinated against rabies.
Experienced doctor Komarovsky, who specializes in this area, identifies the following symptoms of the disease:
- numbness or pain at the site of the bite;
- aggressiveness, more acute nervous state;
- hydrophobia, i.e. violation of the process of drinking water;
- muscle spasms;
- excessive salivation;
- convulsions or even paralysis;
- and, what is most terrible, coma and death.
Timing of medication administration
You should always try to get your rabies vaccination on time, because it is the most important part of prevention. The disease occurs differently in animals and people, and the timing of drug administration, as well as the development of pathology, depends on the following nuances:
- The time from the moment the virus enters the body until the first signs appear is usually from 10-14 days to a year. That is why rabies vaccination should be performed if there is even minimal suspicion. After all, people, having forgotten about the incident and not seeing any signs in the first weeks, think that it has passed, but the disease can develop a little later. You can reduce the probability to virtually zero with the help of 3 doses of the vaccine and 1 immunoglobulin, and for complete protection it is recommended to complete the entire course;
- The virus is not transmitted from person to another person. However, there have been cases where rabies was transmitted along with a transplanted organ. This is possible while the disease is in the incubation period;
- The rabies vaccine is given mainly to children, because they play with animals more often than others. Sometimes it is not possible to save children because they are afraid to talk about the bite, especially because of the stories that they need to take 40 injections against this virus.
Timely vaccination against rabies helps the body synthesize antibodies. They block the entry of the virus into the nerve fibers, which prevents it from entering the CNS (central nervous system) and causing acute encephalitis. It is from this that patients most often die.
The incubation phase of the disease lasts a certain period of time, which depends on the location of the bite. The fastest developing virus is one that enters the body through the upper part of the body (from the torso and above). Rabies manifests itself much more slowly if the lower half (below the torso) was bitten.
The host of the virus is most often wild animals (wolves, foxes, etc.) and it is they who most often infect people. In second place are stray dogs. If a pet has bitten, then in such a situation they usually do not give rabies injections. After all, such animals undergo annual vaccination and it is enough to observe them for 10 days.
Vaccination rules
For humans, the rabies vaccine is absolutely safe if administered in the correct manner at the right time. To do this, you should consult your doctor before getting vaccinated. The vaccination is considered ineffective after 2 weeks from the moment of the bite of a rabid animal.
The regimen for administering the drug directly depends on the degree of the bite and the elapsed time after infection with the disease. Based on WHO requirements, it may still differ depending on the viral spread in a given region. The rabies vaccination schedule will be discussed in more detail below.
Primary and secondary prevention
In order for the child to develop good immunity, the rabies vaccination is given 3 times. The second injection is usually prescribed a week after the first, and the third after 3-4 weeks. This type of prevention is called primary prevention and is performed to prevent the virus from occurring in the baby.
Vaccinating a child against rabies provides temporary protection against the virus, but if it is not there and the baby has been bitten, then it is advisable to find out whether the animal has this disease. Most often this cannot be done and you will have to undergo a course of injections. It consists of 1 injection of immunoglobulin and 6 injections of the COCAB vaccine, 5 of which must be given within 28 days, and the last within 90 days.
The body temperature most often does not rise after vaccination and it is better to start therapy no later than 1-2 days from the moment of the bite. Immediately after the incident, it is advisable to immediately treat the damaged area. To do this, you should superficially treat the wound with an antiseptic solution and inject immunoglobulin into it. This medicine is recommended to be injected into the surrounding tissues. The dosage is selected individually and is based on the person’s body weight. The remaining permissible amount of medicine should be injected intramuscularly away from the bite.
After vaccination, the injection of immunoglobulin should be made as far as possible from the site where COCAV was administered. This injection is performed only once and this is enough to synthesize antibodies in the blood. Over time, under the influence of the vaccine, the body itself will be able to produce them. Repeated administration of immunoglobulin is prohibited, since the second injection can disrupt the functioning of the produced antibodies and their synthesis.
Often, a standard drug administration scheme is used, namely at 0, 3, 7, 14, 28, 90. They must be carried out strictly on time and it is forbidden to drink alcohol during this period of time, so as not to reduce the effectiveness of the vaccine. It is permissible to interrupt the course of injections only if the animal that bitten turned out to be healthy. Such preventive measures are called secondary, that is, taken after a bite and without prior vaccination.
Where do people get rabies vaccinations?
Immunization against rabies is usually carried out in clinics under the supervision of qualified specialists. The drug is usually administered intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle for adults and children over 16 years of age. For children under 16 years of age, the drug is injected into the femoral region; however, it is strictly prohibited to administer the vaccine into the gluteal muscle. Regardless of age, the dose of the rabies vaccine is administered to everyone the same.
After vaccination, the body begins to form special protective antibodies that help in the fight against rabies infection.
Vaccines used
Vaccination occurs through the administration of rabies vaccine and immunoglobulin, which are differentiated based on their action and are selected taking into account the period of viral incubation, the size and depth of bites, their location and number.
An exclusively rabies vaccine is used only in cases where there are not many bites and they themselves are small, and, therefore, a person has enough time before the onset of viral development.
However, in more severe cases, in which the bites are of moderate or severe severity, and also after ten days after the virus enters the bloodstream, it is simply pointless to wait for the appearance of one’s own immunity. Therefore, a special course of treatment is carried out, i.e. combine the actions of an anti-rabies vaccine and an anti-rabies immunoglobulin, which almost immediately provides passive immunity for a certain period of time. Unlike immunoglobulin, the vaccine provides immunity only after 2-3 weeks for a shorter period of time.
An anti-rabies vaccine is a drug that provides antigenic information about the introduction of infection into the body of an infected person, but it is impossible to eliminate the virus with its help alone. Due to the information it provides, the human immune system promotes the formation of antibodies, which can neutralize the virus. The rabies vaccination helps to acquire optimal immunity for a whole year, and its use is possible even if 2-3 months have passed after being bitten by an infected object.
But the rabies vaccination begins to take effect only after 2 weeks, and until this happens, the body remains without protection from the virus. It is because of this that it is so important to introduce ready-made antibodies to maintain the body’s immunity. Such antibodies are contained in rabies immunoglobulin in concentrated form. They are usually obtained from donated blood from a person or horse that has previously been given a rabies vaccine. This immunity is also called passive immunity, since rabies immunoglobulin antibodies are eliminated from the body after several weeks.
How is a human being vaccinated against rabies?
First of all, when contacting specialized doctors, the wound is washed and disinfected. The doctor then injects rabies immunoglobulin into and around the bitten area, which prevents further spread of the infection when it enters the human bloodstream and nervous system.
On the same day, the infected person is given an anti-rabies vaccine. Subsequent vaccinations are carried out according to the scheme selected by the doctor at the emergency room.
Vaccination is stopped if the animal does not die after 10 days or, after its euthanasia, it has been proven that it does not have this disease.
Why are vaccinations given?
Dogs are vaccinated against rabies for two reasons - to protect the pet and to save your family. You all probably know that an animal infected with rabies becomes uncontrollable, and it is almost impossible to dodge its bites. But even if your dog doesn't get involved in a dangerous fight, he can become infected with the rabies virus from bites from wild animals, such as rats.
Another important point is that the dog becomes contagious even before it shows obvious signs of illness. But the worst thing is not even this! The fact is that rabies is incurable, so an infected person will face a long and painful death. The only solution that guarantees 100% reliability is timely vaccination, after which dogs develop lasting immunity to this deadly virus.
How many injections will be required?
Let's consider several variations of rabies vaccination regimens, which differ in the injection quantity.
The planned vaccination schedule is as follows:
- first injection;
- second injection a week later;
- third injection on the 30th day;
- a year later - revaccination.
The rabies vaccination is effective with regular vaccination for three years, therefore, revaccination in the future is carried out at similar intervals.
For emergency immunization, the scheme is as follows:
- vaccination immediately after infection;
- the second - on the 3rd day;
- third - on the 7th;
- fourth - two weeks after the first rabies vaccination;
- the last one is done on the 30th day.
This is what a standard emergency vaccination plan looks like, but in some cases a sixth vaccination may be needed, which is given three months after the first immunization.
Who should receive rabies prophylaxis?
Preventive vaccination can be of two types: planned and emergency. The planned one is carried out once every three years for the following persons:
- Veterinarians;
- Slaughterhouse workers, workers of services for catching and euthanizing stray animals;
- Infectious disease laboratory workers;
- Employees of animal products processing plants;
- Speleologists (bats can be found in caves, which can also be carriers of rabies);
- People traveling to countries where rabies is endemic.
Remember! Rabies vaccination and alcohol are incompatible things. After you have received the vaccine, rabiologists advise completely eliminating alcohol in all its forms for six months! The ethanol it contains interacts detrimentally with the vaccine, neutralizing its effect and causing negative effects.
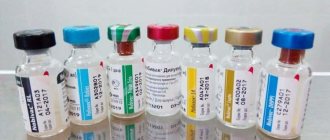
Anti-rabies serum is created from an inactivated pathogen, which was grown in special nutrient media and underwent a cleansing procedure. This makes it impossible to get sick after vaccination. Trade names of some anti-rabies drugs: KOKAV, Rabivac.
Popular Protecting the body from chickenpox by injection vaccination
Animals are also vaccinated against rabies. There is a quarantine after rabies vaccination for a pet, which lasts for a month if the animal has not been vaccinated for a year before, and 14 days, taking into account that the vaccination was constant.
Who is prophylaxis indicated for?
The following people are recommended to be vaccinated against rabies:
- veterinarians;
- people who catch and keep animals without proper supervision;
- laboratory workers who come into contact with infected animals due to their line of work;
- slaughterhouse workers;
- foresters, hunters, taxidermists;
- emergency prevention is carried out for people who have been bitten by an infected object;
- It is also recommended to vaccinate against rabies for people traveling on vacation to places with an increased risk of rabies.
The most popular rabies vaccines
Vaccines for dogs against rabies are represented by drugs of domestic and foreign production. We offer a whole list of the most effective ones.
| Name | Manufacturer country |
| "Defensor 3" | "Zoetis Inc" USA |
| "Nobivak RL" | Intervet, Holland |
| "Rabizin" | Merial, France |
| "Rabikan" | FKP “Shchelkovo Biocombine”, Russia |
| "Biocan R" | Bioveta, Czech Republic |
| "Rabix" | Vetbiohim LLC, Russia |
Main contraindications to immunization
Any vaccination can lead to undesirable consequences if a person has contraindications to it, including rabies. Cases of refusal to immunize include:
- pregnancy (any period);
- allergy to antibiotic drugs;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases or infections;
- When administering the vaccine, there is a history of an allergic reaction;
- immunodeficiency.
Contraindications are valid only when preventive vaccination is carried out. If a person has been bitten by an infected animal, then a rabies vaccination for a person is carried out immediately, even if there are contraindications. Once vaccinated against rabies, the risk of death will be eliminated.
Diagnosis of the disease at the hospital level
A general blood and urine test for rabies in a person without characteristic clinical signs.
Informative diagnostic methods during life:
- Study of saliva, tears or cerebrospinal fluid for virological carriage;
- Polymerase chain reaction (cerebrospinal fluid, saliva);
- Enzyme immunoassay (blood serum, cerebrospinal fluid);
- Immunofluorescence reaction (corneal imprints and a piece of skin);
Additional diagnostic measures:
- Biochemical blood test (glucose level, urea, creatinine, total protein, electrolytes, renal-liver complexes, hemogram);
- ECG;
- X-ray of the chest organs.
Popular Consequences from the side effects of the tetanus shot
Contraindications and features of vaccination in adults, children, pregnant women
Rabies vaccination has side effects: skin rashes, tremors of the limbs, increased body temperature, general weakness, but they appear only in 0.03% of people. Immunoglobulin can result from angioedema, anaphylactic shock, or serum sickness.
The dose of the drug is calculated per 1 kg of body weight - 3-4 ml for children under 16 years of age, for adults - 25-30 ml. For pregnant women, the dose is calculated in the same way as for an ordinary adult.
It is important to remember that for six months it is better to refrain from drinking alcohol, sudden and severe temperature changes and overwork. You also need to consider the compatibility of certain drugs with the rabies vaccine: steroid hormones and immunosuppressants.