How does inflammation of the paraanal gland in a dog, located under the tail, affect its behavior and is it possible to avoid this scourge? The purpose of this paired organ is to attract other individuals of the opposite sex and frighten potential enemies. But when secretion stagnates, the cavity fills. The dog begins to feel discomfort and pain.
Inflammation of the glands is explained by some dog handlers by the fact that the organ is rudimentary and no longer performs its original function. This can lead to blockage and the formation of a tumor under the dog's tail, which requires prompt response from the owner.
Risk factors
What causes inflammation of the paraanal gland under a dog’s tail? This disease is promoted by:
- sedentary lifestyle of a barking pet, symptoms of obesity;
- negative hereditary preconditions: the paraanal gland most often becomes inflamed in small breeds;
- weakened immune system;
- damage to the posterior part of the body with subsequent bacterial contamination;
- bone-based diet; soft food also leads to the development of inflammation of the secretory organs under the dog’s tail;
- unhygienic living conditions;
- pregnancy period;
- infectious lesions;
- active matings.
Major diseases and damage to the tail in dogs
In the clinical practice of veterinarians, there is a clear distribution of pathological changes in the tail of a dog. There are mechanical damage and processes that arise as a result of complications. Mechanical damage to the tail occurs due to trauma. Various wounds, bruises, and vertebral fractures occur as a result of bites, sudden lifting of the tail, and pinching.
Tail curvatures of a congenital or acquired nature are often diagnosed. In the case of congenital deformities, the cause is anomalies of a genetic nature. Acquired ones arise due to dislocations, fractures and improperly fused tissues.
Main dog tail injuries and pathologies:
- ulcers;
- fractures;
- eczema;
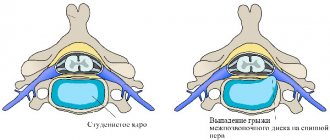
- intervertebral hernia;
- gangrene.
The clinical picture in most cases is clearly expressed. So, as a result of a tail injury, with damage to the tail artery, severe hemorrhage occurs. Damage located near the base of the tail causes phlegmon, spreading to nearby tissues, rectal tissue. As a result, pararectal phlegmon, fistula or paraplegia may develop.
When the tail vertebrae are fractured, the animal practically does not move the appendage, and when palpating the site of the lesion, the animal experiences pain. The skin at the fracture site has a higher temperature than the rest of the stationary part, which remains cold due to poor circulation.
Note! If there is any abnormality in the dog’s tail, you must contact a qualified specialist. This will allow you to quickly identify the pathology and prescribe adequate treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Unusual behavior of the pet and subsequent visual examination will help determine the swelling of the overcrowded gland in the dog under the tail. At first, the dog still looks healthy, but may pull its tail at the base with its teeth. In the future, when the secretion of the paraanal gland thickens, increased anxiety may occur.
The following signs are indicators of pathology:
- The shaggy pet tries to “calm down” the swelling that has formed and begins to roll on its backside on the floor. He diligently licks himself in the tail area, as if looking for non-existent fleas.
- When a dog's secretory glands swell, he feels severe pain during the act of defecation. In some cases, weakness and ignoring food are observed.
- Dogs with this problem are at high risk of blood poisoning. If this happens, the animal's body temperature can jump to 40°C, which leads to a sharp deterioration in its health.
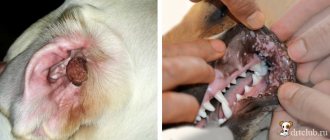
- Upon visual examination, the owner may discover that a lump has formed under the dog’s tail. This impression is created due to the increase in “bags”, which is not observed under normal conditions.
- If the inflammatory process is started, the animal develops an abscess of the paraanal gland.
Allowing this last symptom to develop means exposing your four-legged companion to serious danger. Neglecting the problem can be fatal, so veterinarians unanimously advise owners: if something under the dog’s tail is inflamed, you need to immediately help the pet or seek qualified help.
Tumors in the mammary glands in dogs
According to a number of statistics, this type of tumor makes up more than half of all cancers in dogs.
Mostly female dogs are affected by the disease, but only in one percent of cases is it diagnosed in males. Most often, breast formations appear at the age of ten, sometimes this can happen earlier. The disease is extremely rare in animals under four years of age.
The tumor is described as an uncharacteristic growth of iron tissue that cannot be controlled by the body. It contains atypical cells with an irregular structure. They differ from functional cells, both in their operating principle and in structure.
Cells with a different nature begin to quickly divide and transport their impulses throughout the genetic code. Tumor tissue grows rapidly by cell division. The process of how exactly a tumor arises and develops has been studied for a long time, but it is impossible to obtain more complete information about the process. This is due to difficulties in conducting research.
A malignant formation can develop up to several years without clinically manifesting itself. How quickly a specific tumor will grow and develop is personal in any case, so the prognosis for the animal should always be approximate from the very beginning.
Neoplasms on a dog's chest are divided into benign and malignant. Among all tumors, more than half of them belong to the latter type. The most common is cancer.
A feature of malignant tumors is their metastasis; they can spread throughout the body through the bloodstream or lymph. Harmful cells that have spread throughout the body, in some cases, cause tumors to appear in other organs.
Cancer cells often cause the formation of secondary growth foci in the lymphatic system, and only then do they develop in the circulatory system. Therefore, the first signal of disease progression is the appearance of a secondary tumor in the closest lymph node.
For distant metastasis, the most likely area of spread of lesions will be the respiratory system, but growth in other systems is also likely. The fact that tumors are benign and also malignant is conditional, because any benign manifestation can, as a result of exposure to a carcinogen, develop into cancer.
Rescue measures
The method of curing a shaggy friend from this scourge directly depends on how badly his problem area is inflamed. Sometimes a simple cleaning is enough to alleviate the animal’s condition. In more complex cases, the dog's anal glands must be completely amputated.
The owner can independently help the pet get rid of the disease. How to treat this inflammation at home? To do this you need to follow these simple steps:
- Arm yourself with a sterile glove and Vaseline.
- Transfer the animal to the bathroom for surgery: the secretion in dogs has an unpleasant odor, and it is undesirable for it to come into contact with furniture.
- Insert your finger into the rectum of your barking partner and feel for the glands (dense small balls). Gently press the contents out on both sides.
- After the lump has been treated in this way, it is recommended to wash the dog thoroughly with soap.
- In order to avoid dangerous complications, it is advisable to use anti-inflammatory suppositories.
What should an owner do if a dog’s tail hurts?
If you notice that your dog is tucking its tail, you need to find out what hurts. It is strictly prohibited to independently diagnose and treat your pet. A responsible owner should take his four-legged friend to a professional at the first sign of illness.
After a visual examination and palpation, a veterinarian usually prescribes an X-ray examination of the caudal part of the spine. The diagnostic method allows us to identify fractures, degenerative processes in the vertebrae, and the presence of intervertebral hernia.
In some cases, to establish the cause of the pathology, the animal is prescribed a general blood test and material is taken for microbiological testing.
X-ray of the spinal column in a dog
If the reason that the dog’s tail hurts is mechanical damage to the vertebrae, then depending on the severity, the veterinarian will prescribe treatment. In one case, for the furry patient to recover, applying a splint will be enough, but in another situation, amputation of the organ will be necessary.
In case of inflammatory processes in the area of the paraanal glands, the dog is cleaned in a specialized institution . If necessary, a sick animal is prescribed a course of antibacterial therapy.
If, during a clinical examination, a veterinarian discovers the presence of ulcers and erosions, then the first step is to treat the damage with antiseptic solutions. Depending on the nature of the inflammation, the veterinarian will prescribe an anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antibacterial ointment. If the skin rash is of an allergic nature, the dog is prescribed antihistamines and contact with the source of the allergy is avoided.
We recommend reading about how to x-ray your dog. From the article you will learn about the reasons for performing an x-ray on a dog, preparing a pet for manipulation, and performing x-ray diagnostics at home.
And here is more information about the treatment of dysplasia in dogs.
Tail problems in four-legged friends are most often caused by injuries, diseases of the spinal column, and inflammation of the anal or sebaceous glands. Having discovered an illness, the owner should show the pet to a veterinarian. Treatment depends on the etiology of the disease and can be either conservative or surgical.
Prevention
When a dog develops a tumor under its tail, it looks unpleasant, and a photo of the pathology is proof of this. In addition, even with careful execution of the cleaning procedure, the four-legged friend experiences pain.
It is better to take the following measures in advance to prevent anal gland abnormalities in a dog, since treating this disease is much more problematic:
- active walking at least twice a day;
- proper diet: exclude fatty, spicy, salty, fried foods;
- systematic deworming;
- maintaining a stable weight;
- regular examination of the animal's anal area.
Video of examination and prevention of the dog’s anal area:
Every owner must remember that he is responsible for his four-legged pet. Any disease should be stopped in its infancy so that it does not lead to serious consequences for the health and life of the pet.