Why does the disease develop?
Many factors lead to the development of dermatitis in dogs. Among the main reasons are:
- damage to the skin of varying degrees (insect bite, scratching, wound);
- medicines (most often, these are external preparations used for a long time, for other purposes or in high concentrations);
- thermal effects;
- infection of various origins;
- parasites (fleas, lice and others);
- internal disorders (often endocrine in nature);
- allergies to internal and external influences (food, medications, hair care products, etc.).
Dermatitis in dogs is often a consequence of the simultaneous influence of several factors. For example, when a flea bites, bacteria enter the wound and an inflammatory process develops. The owner, without contacting a veterinarian, uses a medicine that “always helps everyone.” As a result, the dog gets an allergy, the process drags on and becomes chronic.
Local treatment of the disease
Unfortunately, today there is no medicine that can cure primary seborrhea. This means that the only thing dog owners can do is control the disease. To do this, they need to understand that measures to dull the symptoms of seborrhea will have to be taken continuously throughout the pet’s life.
If an animal suffers from primary seborrhea, the main remedy for their treatment will be special shampoos. Among the huge range of such medical products, you should choose based on the individual characteristics of your pet.
If your dog is suffering from the dry form of the disease, moisturizers may help. If the problem, on the contrary, is increased oiliness of the skin, it is necessary to use shampoos that control the sebaceous balance of the dermis and remove crusts from its surface.
Unfortunately, in some cases it is impossible to control the disease with shampoos and conditioners. Therefore, sometimes veterinarians prescribe additional drug treatment to their patients.
As already mentioned, in such cases, dogs often suffer from secondary infections. If the infection has already appeared, the dog is usually prescribed antifungal agents as well as antibiotics.
Improvement can also come from using special nutritional supplements that include omega 6 and omega 3.
Also, drugs that slow down the process of cell division can help with seborrhea. This is usually cortisone, which can change the rate of epidermal renewal.
In addition to this main function, this medication provokes atrophy of the sebaceous glands. The only, but no less serious, disadvantage of drugs of this type is the presence of an extensive list of side effects.
This is why cortisone is used only in particularly severe cases.
Vitamin A and retinoids (its derivatives) are also required to keep the skin in normal condition. Therefore, veterinarians often recommend using it for primary seborrhea.
If the desired effect is not achieved, pet owners can try using etritinade, a retinoid famous for its high effectiveness. However, this drug also has serious side effects, including keratoconctivitis, which immediately disappears after taking etritinade.
Treatment of ear dermatitis begins with wiping the affected areas with antiseptic solutions. Hydrogen peroxide and soda solution are good for this purpose.
If the skin becomes very wet, you can use zinc ointment to dry the skin. With an allergic nature, treatment of ear dermatitis in humans includes oral administration of antihistamines (Zyrtec, Erius, Cetrin, Suprastin).
These remedies are aimed at reducing itching and reducing the severity of the allergic reaction. Drops with antibiotics or glucocorticoids (Sofradex, Polydexa) are also used to treat ear dermatitis.
For atopic dermatitis in children, the doctor prescribes complex treatment. To quickly eliminate itching, antihistamines are prescribed. And in order to eliminate signs of inflammation in the ear canal, doctors prescribe drops.
This disease can be treated with tampons that are placed in the ear canal. They help eliminate signs of inflammation and relieve itching. A tampon can be prepared at home. Dampen a small piece of gauze, roll it up and soak it in hydrogen peroxide.
You can also soak a tampon with Pyoctanin or Boric acid.
At home, you can prepare a folk recipe that has proven itself well. However, before using the prescription, you must consult your doctor.
To prepare you will need elecampane root and pork fat. These components must be mixed. But the doctor should tell you the proportion, which will be calculated depending on the severity of the disease.
In any case, if you notice the first signs of the disease, you should consult a doctor. After all, only a doctor can determine the type and severity of ear dermatitis, as well as prescribe the necessary treatment.
It is important to find out the cause of the allergic reaction and only then eliminate it. Only after this event will the treatment be effective.
Treatment of the disease is carried out on an individual basis, taking into account the characteristics of the course and type of dermatitis. There are some rules that are suitable for treating any type of rash.
- Foci of inflammation can be wiped with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, soda or laundry soap.
- If there is weeping, you can apply solutions of picric and boric acids to the skin. Drying ointments (Zinc) are also used.
- Antihistamines are prescribed to eliminate itching. Children can take Zyrtec, Cetirizine, Parlazine drops. Adults are advised to take Zodak, Loratadine.
If atopic dermatitis is diagnosed, treatment is carried out using:
- a drop of Sofradex (steroid and antibiotic);
- a drop of Polydex (an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drug);
- Geocorton ointment (antibiotic).
Seborrheic dermatitis can be treated using the above antibacterial drugs if infection is present. In addition, treatment includes the use of agents aimed at eliminating crusts.
- Hair washing should be done using Skin-cap shampoo. Due to the pyrithione in its composition, it fights fungus, inflammation, and also soothes the surface of the skin.
- An ointment with an antifungal component can be applied to the skin. These include Bifisam, Lamisil, Mycospor.
Crusts and purulent contents must be carefully removed without damaging the skin surface.
Treatment of contact dermatitis involves completely avoiding contact with the allergen. For any type of disease, vitamin therapy has a positive effect.
The patient is prescribed vitamins A, B, E to restore the surface of the skin and strengthen the immune defense. Antibacterial drops can be used to treat dermatitis in the ears.
If there is a lack of calcium, then injections of calcium gluconate are given. Oral medications may also be prescribed.
Restoration of the affected areas is carried out using UHF and UV procedures. Lotions and compresses made using medicinal herbs also have a beneficial effect on the surface of the skin.
Therapy for ear diseases is prescribed strictly by a doctor. But the most important thing should be getting rid of the allergen or irritant.
Next, the complex is something like this: Ointment or cream. Broad-spectrum external medications that should relieve inflammatory processes on the skin and at the same time heal wounds.
Diet. The doctor will prescribe the optimal diet and will definitely focus on what needs to be excluded from the menu.
Physiotherapy. A course of sessions for UHF therapy or phototherapy.
Antibiotic drugs. Often, treatment of problems in the ear area comes down to compresses, but not every dermatitis responds to such therapy.
Therefore, in order to reduce the risk of relapse, the doctor prescribes the above set of procedures. At home, you can prepare an ointment based on butter with the addition of elecampane, walnut leaf and horse sorrel root, previously crushed into powder.
Lubricate the affected area twice a day. Therapy is exclusively symptomatic and consists of several main areas.
Treatment of dermatitis with such localization should begin by treating the lesion with disinfectant solutions. Typically, 3% hydrogen peroxide, concentrated solutions of baking soda or laundry soap are used.
Using picric or boric acid in a solution, bubbles and wet areas are treated, and inexpensive zinc ointment will help dry them. Itching is relieved by ingesting antihistamines - Zodak, Suprastin, Loratadine; in pediatric practice, Parlazin and Cetirizine drops are used in children.
Treatment of ear dermatitis should begin by treating the lesion with disinfectant solutions. Therapy of allergic dermatitis includes instillation of a combination drug containing elements of steroids and antibiotics - sofradex or its analogue polydex.
The affected fragments are treated with corticosteroid ointment in children, this is Geocorton; the allergen should be categorically excluded. Treatment of fungal dermatitis is different in that in addition to exclusively medications, attention should be paid to therapeutic hygiene.
You should wash your hair with shampoos with a pronounced antifungal effect - nizoral, Skin-cap with a high content of zinc pyrithione. The success of treatment is also ensured by applying ointments with similar properties - Mycospor, Bifisama, Lamisil.
The ear canals, auditory conchas and behind-the-ear areas are freed from pus, crusts and scales, which makes it possible to stop the path to deep infection. A special part of the therapy is a special diet, from which coffee, all types of citrus fruits, chocolate, and foods containing gluten are excluded.
It is useful not to eat sweets, baked goods and cookies during the treatment period, and to saturate the body with vitamins A, E, minerals, and calcium. UHF and UV procedures and folk remedies can improve the effect.
Treatment of ear dermatitis should be carried out only after consulting a doctor. Only an experienced specialist is able to recognize the disease.
The above symptoms may be symptoms of other pathologies that require different therapy. The diagnosis is established by examining the lesion.
In some cases, the doctor may take a scraping to determine the pathological flora (fungal or infectious). The first-priority treatment measure for the disease is the elimination of the provoking factor.
Particular attention should be paid to new objects that have been in contact with the skin at the site of pathology. Because even the highest quality treatment will have little effect if the irritant continues to act.
To eliminate ear dermatitis, the following are used: Local antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs. Various ointments are prescribed that relieve swelling, eliminate skin itching and restore the condition of the skin.
Antihistamine tablets orally. They are used if the patient complains of severe, unbearable itching of the skin in the affected area.
Hormonal ointments are prescribed if anti-inflammatory and antihistamines do not give the desired effect. Affected areas should be regularly treated with hydrogen peroxide, warm water and soap, or a weak solution of soda.
If bacterial flora is present, antibacterial ointments are prescribed, and if a fungus is detected, antimycotic agents are prescribed. When the process is mild, they are used in the form of ointments.
However, if there is severe purulent inflammation, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics in the form of tablets for at least 5 days. Traditional medicine methods Traditional medicine for ear dermatitis should be used in combination with medications prescribed by a doctor.
In addition, traditional recipes should not be used without consulting a doctor, as they contain herbs that can also cause an allergic reaction. Among the methods of traditional medicine, herbal medicine is used to eliminate ear dermatitis.
Patients are recommended to take teas and infusions of herbs and infusions that have anti-inflammatory and antihistamine effects. Among these, the most popular are: No matter whether it is contact, atopic or seborrheic dermatitis in the ears, treatment is selected for each patient separately.
It is prescribed based on the results of diagnosing the disease. It must be said that the choice of drugs is not always successful, since the individual characteristics of the body play a large role.
If, when using any remedy against ear dermatitis in a person, the treatment does not bring a positive result, then the drug is replaced by another. Diagnostics and traditional therapy The principles of the treatment program are reduced to the following areas: Identification and elimination of the factor that caused the disease using a strict diet.
Relieving symptoms with external and internal medications. Correction of the body's protective properties with the help of medications and psychological therapy.
As part of the ear dermatitis treatment program, the doctor selects medications and procedures. First of all, the patient must exclude all allergic foods from the diet.
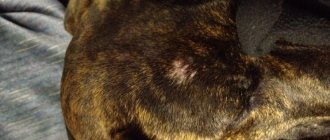
Common symptoms of dermatitis in dogs
There are general signs of pathology that you need to pay close attention to:
- redness of the affected area;
- increased skin temperature in the area of inflammation;
- hair loss (thinning or breaking off hair, thinning, complete loss);
- thinning of the walls of the capillaries (leading to their damage and bleeding);
- itching;
- swelling of the damaged area;
- painful sensations.
Subsequently, the focus of inflammation increases in size, spreading to other parts of the body. Ulcers, crusts, and suppurations appear. The dog's behavior changes, sleep and appetite are disturbed, and immunity is greatly reduced.
Photos of dermatitis in dogs
Diagnostics
During the appointment, the specialist will not limit himself to just examining the dog. The owner will need to tell about the conditions of detention, feeding habits, duration and frequency of occurrence of the pathology. Laboratory diagnosis of dermatitis in dogs includes taking blood and urine, scrapings from the sites of injury for microscopic and bacteriological analysis. If a microbe is detected, it will be necessary to test for its sensitivity to antibacterial agents, which in the future will serve as the key to successful treatment.
Local treatment and special therapy
Treatment for dermatitis in dogs includes local treatment and systemic therapy. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease, since without this any local treatments will have no effect. For this purpose, the type of feeding is changed, antiparasitic agents, antibiotics and other drugs are prescribed.
If atopic dermatitis is observed in dogs, treatment requires identification of the allergen. Most often it is a certain type of food. The easiest way to install it is if the diet is prepared independently, and ready-made commercial feed is not used. Pets are given beef, chicken, cottage cheese, as these products are less likely to cause allergies. Porridges, vegetables and other products containing large amounts of carbohydrates and practically devoid of proteins can be used without restrictions.
Local treatment is of primary importance for any parasitic, fungal skin diseases. Thus, dermatomycosis in dogs must begin to be treated by removing the fur. In case of small lesions, the hair is removed around the outbreak; in case of generalized infection, the entire dog is subjected to haircuts - this way it is possible to deprive the fungi of food and improve the contact of the pathogen with the active substance. The following are used as treatment:
- chlorhexidine solution;
- sulfur ointment;
- griseofulvin.
Reduce the inflammatory response with steroid ointments (prednisolone, hydrocortisone). They are applied to the affected areas. They are especially good at reducing the inflammatory response in allergic and contact inflammation of the skin. Preparations containing corticosteroids can relieve itching, so they are also used for fleas, ticks, and if acral dermatitis is detected in dogs.
Before applying the medicine to the skin, it must be cleaned. Cleaning criteria depend on the extent of the lesion. Thus, minor inflammation requires only removal of hair around the perimeter, and in case of severe purulent inflammation, accompanied by the formation of ulcers and crusts, it is necessary to wash the wound with an antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate solution).
To eliminate fleas and ticks, special means are used:
- cypermethrin and other pyrethroids - available in the form of drops on the withers, injections, tablets;
- ivermectin, aversectin – injectable drugs with high efficiency and prolonged action;
- butox – liquid for external use.
The most common types of dermatitis in dogs
Since there are many causes of dermatitis and their combinations, the disease can be of different types. Each of them is characterized by its own distinctive symptoms and treatment approaches. The most common types of dermatitis in dogs are briefly described below.
Pyotraumatic dermatitis in a dog
Pyotraumatic
With pyotraumatic dermatitis in dogs, the infection penetrates from the surface into the deeper layers of the skin, leaving behind plaques and a thickened stratum corneum. The deeper it penetrates, the more papules (pimples) and pustules (pustules) will appear on your pet’s skin.
Treatment consists of using antibacterial drugs.
Allergic
Allergic dermatitis in a dog
Allergic dermatitis is considered the most common in dogs, since any object can be an allergen. Experts note that in most cases, skin allergies are provoked by external parasites, food and cosmetic care products. Symptoms include: severe itching, redness of the skin, scratching, rashes, swelling.
The basis of treatment is elimination of the allergen and symptomatic therapy.
Atopic
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is one of the varieties of the previous form. The clinical picture is the same: dry epidermis, rashes, very severe itching. Additional characteristic signs include the development of otitis media and pododermatitis. The pathology develops mainly in dogs under 5 years of age who have similar heredity. It is noted that atopic dermatitis “loves” such dog breeds as: dachshunds, sharpeis, bulldogs, setters, Dalmatians and a number of others. At the same time, anything can become an allergen.
Treatment consists of identifying and eliminating the allergen, carrying out symptomatic therapy, and preventive measures to prevent otitis media.
Flea
Flea dermatitis in a dog
The salivary secretion of fleas contains more than a dozen allergenic components that lead to flea dermatitis in dogs. The severity of symptoms depends on the individual susceptibility of the animal. Signs of pathology can be: alternating wet areas and areas covered with crusts. In the chronic course of the disease, the pet exhibits excessive skin pigmentation on the abdomen and hair loss. It is characteristic that the dog’s ears, muzzle and paws are almost not affected.
Treatment consists of getting rid of fleas and symptomatic therapy. Prevention is of great importance for recovery - the use of a parasite collar, disinsection of the environment in which the dog lives.
Interdigital dermatitis in a dog
Pododermatitis
Interdigital dermatitis in dogs, or pododermatitis, develops between the animal's toes, mainly on the front legs. If the lesions are single, it can be assumed that the disease is provoked by injury. With extensive damage to the limbs, the cause may be insects, allergies, or infections. Symptoms: bleeding nodules, boils, pain leading to lameness.
Treatment is symptomatic.
Seborrheic
Seborrheic dermatitis in a dog
Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by genetics. With this disease, the process of keratinization of the skin accelerates, which is visually manifested in numerous scales, oily epidermis, but dry hair. Your pet may have brittle nails; The inflammatory process on the skin is clearly visible, accompanied by severe itching. In the future, the disease is complicated by secondary infection with all the ensuing consequences.
Treatment is carried out in two directions: local therapy and a systemic approach.
Acral
Acral dermatitis in a dog
Symptoms of acral dermatitis include thick, ulcerated patches of skin caused by your dog licking the area excessively. Pathological behavior of an animal can be caused by allergies, parasites, infection and other factors that must be detected and eliminated before treating the skin.
Treatment consists of the initial elimination of the provoking factor and a therapeutic effect on the damaged epidermis. Limiting your pet's access to the itchy area is of great importance. In addition, antidepressant and psychotropic drugs are used in therapy.
Diagnosis of dermatitis of the external auditory canal in dogs and cats
Diagnosis requires physical and dermatological examination, knowledge of dermatological history and development of clinical signs. Otoscopic examination is the first diagnostic method of choice for assessing the external auditory canal and should be performed in every patient with signs of otitis externa. It is important to note that a healthy ear canal may have small amounts of yellowish or brown wax. Through otoscopy, the clinician can evaluate the presence of inflammation, exudate, hyperplasia, stenosis, foreign body, neoplasm and evaluate the tympanic membrane. Depending on the degree of pain, inflammation, and stenosis, it may be necessary to use modern systemic corticoids for two to three weeks before performing an adequate otoscopic examination.
Cytological analysis of the contents of the ear canal is necessary for diagnosis, and samples should be obtained from both the pinna and the external vertical and horizontal canal. Cytology can provide early information about the inflammatory response and the microorganisms or parasites involved in the pathological process.
Prevention of dermatitis
In many cases, the development of dermatitis in dogs can be avoided. The main preventive measure is proper care of your pet’s fur and skin:
- regular hygiene measures as contamination occurs;
- combing without letting the hair roll;
- selection of combs in accordance with the characteristics of the animal;
- Regular inspection for the presence of parasites and their removal if detected.
Proper nutrition will also help prevent dermatitis, as well as deworming the dog every three months. In addition, a preventive measure would be a timely visit to a veterinarian when any pathology is detected, and not an independent choice of medications.
Treatment
It should be noted that independent attempts to diagnose dermatitis and begin to treat your pet for it can lead to the most dire consequences. If your dog is constantly itching, there is no need to guess what is happening to him, because there can be a lot of options. They are installed during tests in a veterinary hospital.
At home
At home, the owner can only provide first aid. Self-medication in case of dermatitis is excluded, since the course of the disease can be aggravated by a chronic condition, the appearance of purulent-putrefactive formations on the skin and general intoxication of the dog’s body.
First aid:
- Prepare the affected skin area for further treatment: trim the hair, treat with an antiseptic (hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, miramistine), clean the skin of dead cells and formed blood crusts. Apply ointment or powder - antiseptic.
- If there are no open wounds, lubricate the affected area of skin with a solution of iodine or brilliant green.
- For dermatitis caused by injury, cooling dressings can be applied.
- Check the animal's fur for the presence of parasites (fleas, ticks). If found, carry out sanitary treatment against insects with a special shampoo.
- Treatment with novocaine blockade will help relieve pain and calm the animal; for this, a 0.25% or 0.5% solution of novocaine is administered.
- Eliminate cereals, canned food, bread, potatoes in any form and red meat from the dog’s diet.
Important! After taking all pre-medical measures, contact your veterinarian!
Vet
The main task of the veterinarian is to determine the cause of the skin lesion. To do this, an anamnesis must be collected, a clinical examination of the animal must be performed, and laboratory tests must be taken ( stool samples, blood samples, skin scrapings and bacterial cultures ). Then the doctor relieves the itching, numbs the pain and treats the affected area. If necessary, prescribes antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids, antihistamines, antiparasitic drugs, local anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial ointments, restorative and detoxification therapy .
Important! Strictly follow the dosage of medications prescribed by your veterinarian! Do not confuse units of mass and units of volume - this is very, very important!