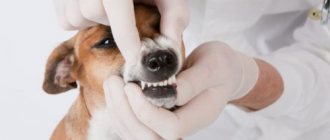
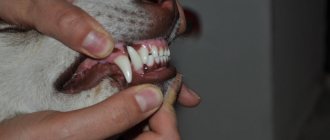
Healthy grin on a dog
The canine dental system is a mechanism made of durable bone tissue. With its help, the animal attacks and defends itself, captures prey and holds it, tears it into pieces and crushes bones.
Dogs show a grin when they feel threatened - they bare their fangs, wrinkle their nose, and look intently into the eyes of the enemy. And, if they are guilty, they stretch their lips very much. At the same time, they look away and whine quietly. In both cases, people see a grin from ear to ear. A healthy individual exhibits strong teeth.
Healthy grin
Already a one-year-old puppy has a full set of 42 permanent yellowish teeth. A deviation in one direction or another indicates a genetic mutation or poor intrauterine development of the fetus.
Note! As a dog ages, the dental crowns wear off and the canines wear down. But with the correct bite (closing of the jaws), this does not cause inconvenience to an older dog.
How many teeth does a dog have, structure
How many teeth does a cat have: diagram of the jaw of an adult cat
The pet's teeth are arranged in a row in a certain order, forming arcades or dental arches. The upper jaw has an arch of 20 teeth (10 on each side), the lower jaw has 22 teeth, 11 on both sides. This is the norm for an adult.
Puppies have 28 baby teeth - equally distributed on each jaw. Veterinarians call understaffing oligodontia, and too much quantity – polyodontia.
Structure
Teeth are wedge-shaped or columnar formations that are fixed in the cells (alveoli) of the jaws.
Structure:
- Crown. Its basis is dentin - a special tissue. Covered with enamel - a strong compound of mineral salts.
- Root – from 1 to 4 in the hole, depending on the type of teeth.
- The neck is the junction of the crown and the root.
Inside the crown is a cavity filled with pulp - loose tissue made up of nerves and blood vessels.
Milk teeth in puppies
Milk teeth in puppies
Babies are born with bare gums. At 6-8 weeks, when breastfeeding ends, they develop temporary milk teeth - 28 pieces, 14 on top and bottom.
The first set of small, sharp teeth begin to change at 3.5 months of age. First, the upper incisors fall out, then the canines and all other elements. The process is completed by 9 months. The shift takes place without the intrusive supervision of the owner. If there are no abnormalities of the masticatory apparatus or inflammation of the gums, there is no need to intervene.
Note! When any problems arise when changing baby teeth, they go to dentistry, where a veterinarian creates a dental record for the dog and treats the pet.
Dental formula of an adult dog
Pets grow up quickly, and by the time they are one year old they receive a second, permanent set of chewing devices. They are designated by numbers and letters. Latin letters are the names of the type of teeth:
- I – incisors (Incisivi).
- C – fangs (Caninus).
- P – premolars (Praemolares).
- M – molars (Molares).
A schematic notation, where the number indicates the number of elements and the letter their type, is called a dental formula. The record is kept in the order in which the teeth are located in the mouth.
The dog's dental formula on the diagram looks like this:
- 2M 4P 1C 3I 3I 1C 4P 2M.
- 3M 4P 1C 3I 3I 1C 4P 3M.
How to read:
- Upper jaw – 6 incisors, 2 canines, 8 premolars, 4 molars.
- Lower jaw – 6 incisors, 2 canines, 8 premolars, 6 molars.
Deviation from the formula is considered a defect, a violation of the breed standard.
Teeth of small breed dogs
Possible complications
As soon as the puppy begins to change teeth, the health of the oral cavity and the general well-being of the pet must be closely monitored. Some breeds have a tendency to delay the replacement of baby teeth and develop oral diseases.
If you do not have experience in keeping dogs, it is better to take your baby to the vet at the age of 8-10 weeks. Delay associated with possible complications may result in irreversible malocclusion.
Note! If you buy a puppy from a kennel, the breeder must provide x-rays proving that the baby will have full teeth. If they are trying to “prove” to you that the puppy’s full teeth are determined by the milk series, it is better to find another breeder.
Gum inflammation
Inflammation of the gums, these are the consequences:
- The eruption of teeth that are too large is a genetic factor.
- The formation of “hoods” of gums, under which food remains and rots.
- Poor nutrition.
It will not be possible to avoid gum inflammation, to a greater or lesser extent. The main thing is to control the process and prevent its rapid development.
In case of severe inflammation, the puppy is prescribed procedures to maintain oral hygiene, or, in extreme cases, anti-inflammatory drugs.
Number of teeth by breed
When do kittens change teeth: symptoms and at what age
In small dogs, the last molars on the lower jaw can be very small and do not affect the chewing of food. Even their complete absence does not prevent miniature breeds from participating in exhibitions. Such dogs include Yorkshire terriers and Chihuahuas.
Sometimes the structure of a dog's jaw is such that 42 elements cannot fit in it - the intercanine space is too narrow. These are, for example, toy terriers, which have 40 units. This situation is considered normal and occurs due to selection.
The number of teeth characteristic of the breed is indicated in the table.
| Breed | Number of teeth |
| Yorkshire Terrier | 40 |
| Chihuahua | 38-40 |
| Toy Terrier | 40 |
| German Shepherd | 42 |
| Retriever and Labrador | 42 |
| Pug | 38-40 |
| French Bulldog | 40 |
| Welsh Corgi | 38-40 |
| Laika | 42 |
| Husky | 42 |
| Cocker Spaniel | 42 |
| Collie | 42 |
| Brussels griffin | 40 |
| Bloodhound | 42 |
| Irish black spaniel | 40-42 |
| Australian heeler | 42 |
| Collie | 42 |
| American Hairless Spaniel | 40 |
| Chinese Crested Dog | 40 |
| Shih Tzu | 38-40 |
| Bull Terrier | 40-42 |
| Doberman | 42 |
| English bulldog | 40-42 |
| Newfoundland | 42 |
| Miniature Pinscher | 38-40 |
| Cane Corso | 42 |
| Tibetan Terrier | 42 |
| Greater Swiss Mountain Dog | 42 |
| Dogue de Bordeaux | 42 |
| Toy poodle | 40 |
| Greyhound | 42 |
| Samoyed dog | 40-42 |
| Siberian Husky | 42 |
| Beagle | 40 |
| Pomeranian Spitz | 38-40 |
Types of teeth
How to determine the age of a dog by teeth and external signs
The anatomy of dogs is such that the elements of the dental arcade are divided into groups. Each performs a specific function.
Incisors
A dog should have 6 incisors on both jaws. But depending on the intercanine space, 7 or 8 elements can be counted. To the left and right of the vertical line that divides the jaw in half, there are hooks. Next come the middle ones, then the edges. The incisors have one root.
Dog fangs
Fangs
These are long, conical teeth that curve outward. Their location is between the incisors and premolars. They are attached to one powerful root. There are 4 of them in the mouth, 2 on top and bottom, 1 on the left and on the right.
Molars, premolars in dogs
Premolars in dogs come directly from the canines. They, like molars, form a group of molars.
There are 4 premolars on each side. They grow on both jaws. Behind them the row continues with molars, which immediately grow permanent. Molars are on both sides. 2 on the top and 3 on the lower jaw. This type of teeth is designed for chewing food.
When do dogs change their milk teeth to permanent ones?
The period of replacement of milk teeth in dogs with permanent ones is the most crucial and important moment in the life of your pet. After all, it is not only associated with the intensive growth and development of the puppy, the formation of its exterior and character, but is also associated with the period of greatest susceptibility to various infectious diseases - which is why it requires special attention and control from the owner!
- The change of teeth in large breed puppies begins at approximately 3–3.5 months of age and ends by 6–7 months. In miniature breed puppies, this process is usually more protracted; the onset of teeth change can be delayed and delayed until nine months of age. At the same time small dogs tolerate it less well and often require the help of a doctor.
- Puppies' incisors are the first to begin to change, and they usually complete their full growth faster than other teeth. This occurs from approximately 3 to 5 months.
- The next to “peck” are the permanent canines, which in puppies grow the longest and reach their final size by 6-7 months.
- first grows from the molars . It does not have a milk variant and appears immediately permanent in the fourth or fifth month of a puppy’s life. At the same time, the largest one, the first molar, grows, then all the other false roots and molars.
Table for changing teeth
The process of changing teeth ideally occurs as follows:
- The root of a baby tooth undergoes resorption (dissolves). The fixation of the tooth in the jaw weakens and it begins to wobble.
- At this time, the permanent tooth is actively growing along its canal, pushing out the milk tooth. If it is still firmly held in the gum, a growing permanent tooth may “hatch” nearby and they will remain together in the jaw for some time. If this lasts no more than a week and is not accompanied by painful processes in the gums, you can wait a little. Until the baby tooth falls out and the permanent one takes its place.
- But if the gums become inflamed or the loss of a baby tooth continues for more than a week, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Teeth in two rows
Changing teeth in puppies - order and timing
Puppies remain toothless for up to 3-4 weeks. Then milk teeth appear, sharp as a needle.
The diagram looks like this:
- Upper jaw: 6 incisors, 2 canines, 6 premolars - 14 teeth in total.
- The lower jaw of a dog: a mirror image of the upper.
This shows that there are only three premolars on each side. P1 grow as permanent at 7-9 months.
The change takes place in this order:
- First, the puppy loses its incisors - the baby is 3-4 months old. It starts with the hooks, then further along the row.
- The canines are replaced at 6-7 months.
- Premolars fall out along with the canines.
By 9 months, the process is completed, and the dog’s molars grow at the same time. In total, by the age of one year the dog receives a full set of teeth.
Important! A physiological feature of small breed dogs is that they lag behind the timing of teeth changes by 1-2 months.
Breed characteristics of tooth change
There are breed specific characteristics of teeth changing. If your pet is applying for a show career, it is better for a veterinarian to monitor the process of changing teeth and bite formation.
Before purchasing a puppy, it should be examined by a veterinarian, since gross malocclusions are immediately visible and they do not “resolve” with age, but only get worse. Upon first request, or preferably in a package with documents, the breeder must provide a photograph of the parents’ bite (sometimes two generations are considered) and an x-ray of the puppy’s jaws.
German Shepherd
German Shepherd – the bite is formed according to a standard pattern. Correct bite - only scissors. The teeth must be complete. Any malocclusion is regarded as defects or gross deficiencies.
Labrador
Labrador – the requirements are similar to those above: correct bite and a complete set of teeth.
Spitz
Spitz - requirements depend on the subspecies. The smaller the Spitz, the higher the risk of problems associated with changing teeth.
Spitz dogs have a common overbite, overbite and underbite, although only scissor bites are allowed by the breed standard.
Jack Russell Terrier
The Jack Russell Terrier is a working dog that must have a full set of teeth and a correct bite.
Laika
Laika is a working dog that must have a full set of teeth and a correct bite. Laikas often have problems developing their bite, since this type of dog is still considered a breed group. Simply put, your pet’s blood may be mixed.
Dachshund
The Dachshund is a working breed, so according to the standard, it must have a full set of teeth and a correct bite.
Yorkshire Terrier
The Yorkshire Terrier is a very problematic breed in terms of health, teeth change, and bite formation. Very often, Yorkies have to have their baby teeth removed because they do not fall out in a timely manner.
Dental problems occur even at a young age. To prevent various diseases of the oral cavity, a veterinarian should examine the dog at least once every six months.
Pug
The pug is a problematic breed in terms of health and teeth change. The standard bite is a pincer bite—the incisors meet in a straight line. A small undershot is allowed, up to 3 mm. Underbite and scissors are deviations. Pugs often experience delays in the loss of baby teeth and crooked incisors.
Features of the dog's condition during the period of teeth change
When chewing devices are changed, the animal's immunity decreases. During this period, the puppy is not vaccinated against parasites and infections - the weakened body cannot cope with the stress.
Dogs tolerate this time well. Itching in the gums happens - puppies put it in their mouths and gnaw on anything. The owners alleviate the condition - they give rubber toys and tendon bones. In rare cases, when lethargy appears, loss of appetite or diarrhea occurs, the puppy is taken to the veterinarian.
Symptoms of the onset of teeth change
At approximately 8 weeks of age, the puppy begins to shed its baby teeth. This period may be slightly delayed if the puppy is a large breed. Loose teeth occur because the molar tooth pushes against the baby tooth.
This is interesting! Most owners do not notice the key point in changing teeth. The baby tooth becomes loose and then simply “disappears.” Most often, the tooth falls out and is swallowed by the puppy while eating.
Symptoms of the onset of tooth loss can vary greatly. In many ways, the clinical picture depends on the dog’s temperament. Signs indicating a change in baby teeth usually appear as follows:
- Restlessness, whining, slight apathy.
- The puppy often rubs its muzzle with its paws.
- Poor appetite.
- Slight increase in temperature.
- Drowsiness.
- Diarrhea that does not lead to dehydration.
- The desire to chew and gnaw any objects.
- Resistance when trying to examine the mouth or feel the teeth.
- Smell from the mouth.
Normally, a puppy’s teeth change without alarming symptoms. The baby is constantly gnawing on something, but remains cheerful and active. During this period, you need to protect valuables from the pet’s attention, since the puppy will be attracted by the smell of shoes, wire braid, wood, etc.
Dental care for puppies
Oral hygiene is a condition for dog health. If dogs don't brush their teeth, tartar will form on them. It injures the gums - periodontal disease develops. A dog with bad teeth suffers from heart, gastrointestinal, and lung diseases.
Milk chewers do not require special care. But this is the most favorable moment to accustom your four-legged friend to daily hygiene procedures.
How to brush your dog's teeth
Caring for permanent teeth of an adult dog
Heredity, lack of calcium and phosphorus in food lead to diseases of the chewing apparatus of dogs. This is predisposed by past illnesses and the owners’ reluctance to care for the pet’s mouth.
The procedure should be daily. If the dog is stubborn, twice a week is enough. Use a special paste and brush from a pet store. They teach you gradually: they let you smell the paste, lift your upper lip, run your finger over your teeth. When the dog understands that there is no danger, they clean the outside (the dog licks the inside with its tongue).
The right time for cleaning is when the dog is tired after active games during a walk. Special chewing sticks also effectively clean the dog’s mouth.
Important! While brushing the teeth, talk to the dog and calm it down. Stubborn animals are not indulged - they gently but persistently bring the matter to an end.
Types of bite in dogs
Bite is the position of the jaws in relation to each other. This is a very important indicator of a dog’s exterior. Animals with malocclusion lose at dog shows - before the competition they are compared with the standard.
Types of bite:
- Scissor-shaped - the upper teeth cover the lower incisors and are tightly adjacent to them. Correct bite.
- Pincer-shaped - the incisors touch perfectly evenly. Direct bite.
- Undershot - the lower jaw is shorter, the upper teeth hang over the lower teeth, there is a gap between the arcades.
- Overshot (bulldog bite) - the lower jaw protrudes forward, a row of teeth covers the upper one.
They trust a specialist to deal with the bite and correct the defect according to the recommendations.
Important! Animals with malocclusion are not allowed to breed the breed.
Baby teeth
Perhaps today, almost every person, even those far from dog breeding, knows how many teeth a dog has. Let us recall that an adult animal (of any breed) normally has 42 of them: 20 on the top and 2 more on the bottom (22). By type they are divided into incisors, canines, molars or molars, as well as false roots or premolars. By the way, for some breeds, for example, for the Mexican hairless, the absence of more than 2 teeth is allowed. However, let's start learning about canine dentistry from baby teeth.
Many dog owners do not pay attention to the condition of their puppies' mouths, thinking that it is not necessary. But it's not right. The puppy's milk teeth must be healthy and that's it. Otherwise, this may indicate some problems with the skeletal system. Many people know how many teeth a dog has, but only a few know how many teeth a puppy should have.
So, the first to cut in puppies are the baby canines, then the incisors and then the premolars (less often vice versa). There should be 2 canines on each jaw, 6 incisors, and 6 primary premolars. In many breeds, the standard allows for the absence of the first premolar. In total, puppies should have 14 baby teeth on each jaw - 28 in total.
The normal bite for most breeds is a scissor bite - the jaws should not touch, but a gap of no more than 1-3 mm is acceptable.
Diagram of the structure of dog jaws
Dental problems in dogs
If a dog shakes its head, whines, or swallows food without chewing, its teeth hurt. This is also indicated by bad breath, drooling, and blood on the gums.
The most common problems that cannot be dealt with on your own:
- Stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa.
- Pulpitis is pus in the root canal.
- Caries is damage to dental tissue.
- Periodontitis – the tissue around the tooth is affected.
- Tartar is hard deposits on the incisors and canines.
The fractures and fractures that dog owners encounter are mechanical or from a lack of minerals in the food.
Malocclusion
Such a deviation is fraught with diseases of internal organs, so owners turn to a veterinarian orthodontist. A professional assesses the condition of the oral cavity and makes recommendations. If necessary, he can install a removable or non-removable brace system.
The time for manipulation is limited – 5-12 months. With age, with a full set of permanent elements, the defect cannot be corrected.
Gum inflammation
Gingivitis - inflammation of the gums causes suffering to animals. Acute and chronic forms lead to loss of dental apparatus and blood poisoning. The dog wants to eat, but cannot because of pain. Whines and squeals - there are purulent ulcers in the mouth, saliva flows profusely.
Reasons: change of teeth, lack of vitamins, decreased immunity, tartar, food allergies. An animal can only be helped in a clinic.
A dog's dental system is an indicator of its health. Normally, dogs have 42 teeth. Nature has provided two sets - milk (28 pieces) and permanent - 38-42 depending on the breed. Dental problems - inflammation of the gums, malocclusion, stomatitis, caries - should be resolved with a specialist. The owner’s task is to accustom the animal to brushing its teeth.
How do they change?
Do dogs lose their baby teeth? Without a doubt!
begins at approximately 3.5 - 4 months, and
this fate befalls around six months (and sometimes 7-8 months). First, the molars grow, then the premolars, then the molars, and the last to grow are the canines. General
(20 at the top and 22 at the bottom).
Many puppy owners are interested in whether it is necessary to pull out their dogs' milk teeth, or maybe they will fall out on their own? In general, nature dictates that the roots of baby teeth dissolve, as a result of which they fall out on their own, and larger permanent teeth grow in their place. In some situations, doggies cut their molars when their baby teeth have not yet fallen out, which for the time being is not a deviation from the norm. However, the long proximity of milk and molar teeth can cause harm to the health of the animal.
At the age of 4 months, the dog's baby teeth begin to fall out and so-called molars - molars - appear. Most often, the following happens: the primary tooth does not fall out, but is replaced by the molar, which means that a molar immediately appears in its place. It is categorically not recommended to pull out a baby tooth that is loose on your own - you can damage the jaw.
In most cases, the owner may not notice that the pet’s incisors are changing. But it is, of course, advisable to monitor this process to make sure that it is happening correctly. After 4 months, you need to visually examine the dog’s oral cavity to make sure that teeth are falling out and new ones are appearing in their place. You also need to ensure that the number of molars corresponds to the age of the animal.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with What to feed your dog: what you should not feed your dog, how to feed it correctly, diet
Already at 7 months, most dog breeds should have a full set of molars:
- at 5 months there should be 12 incisors;
- at 6 months – 16 premolar teeth;
- at 7 months – 4 canines, 10 molar teeth.
The owner of the animal must ensure the correct sequence of appearance of the molars. If growth disturbances are noticed, you should definitely contact a veterinarian, because this may be a clear sign of a disease such as rickets. If the current situation is not sorted out in time and the diagnosis is confirmed, there is a high probability that the dog may become disabled.
Every dog owner should know important information: when baby teeth are replaced by molars, the immune system becomes weakened. During this period, you need to monitor your diet, adhere to a proper and balanced diet, and organize a comfortable living environment for the animal. Be sure to visit a veterinary clinic and check information on vaccinations. There are cases that those that were done to the pet before the period of teeth change need to be done again.