What is trichophytosis?
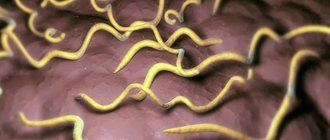
Trichophytosis in dogs is an infectious disease caused by a fungus. It is more popularly known as ringworm.
The fungi that cause the disease are characterized by a high level of resistance to temperature changes and disinfectants, and are also able to survive for a long time in environmental conditions: on wooden objects, litter and in the soil.
The disease is very dangerous, as it can be transmitted not only among animals, but also to humans. It is quite difficult to cure, especially if the disease was discovered too late and is already in an advanced stage.
Vaccination against trichophytosis
We can say that over the past years, scientists have made a lot of progress both in studying the parasitic fungi themselves and in creating methods for their destruction. And the specialists really succeeded a lot. In particular, vaccination against trichophytosis is used not only for prevention, but also for the treatment of this disease.
We would advise using the domestic drug Vakderm. During treatment, it is administered in a dose of 0.5 ml per animal weighing up to five kilograms inclusive. If the pet weighs more, exactly a milliliter is injected. Exactly two weeks later the procedure is repeated, the dosage is the same.
Causes of the disease
Fungal skin diseases can affect absolutely any pet. Infection occurs through food, toys, or after contact with a sick animal.
The likelihood of developing lichen increases in the following cases:
- the dog is not under the supervision of the owners (stray dog);
- the animal's immunity is very low;
- the pet has recently suffered severe stress;
- the dog has been infected with parasites for a long time: lice or worms;
- the animal lacks adequate nutrition.
The body of such dogs cannot resist the development of the fungus, as it is in a greatly weakened state. It is their disease that affects them first.
Ways of transmission of the disease
Infection of a dog with trichophytosis occurs mainly through contact or nutritional means. These are the main routes of transmission of lichen and other fungal infections. The pathogen spores can be in the ground, on the soil surface, plants, manure, feed and even water.
Fungal spores enter the house on shoes, clothes, household items, feed, and other items that have had contact with a sick animal. Therefore, even if your pet does not come into contact with stray dogs, he may well become infected with lichen.
An important role in infection is played by bedding, collars, hygiene products (brushes, combs), muzzles, leashes, and other equipment contaminated with Trichophyton spores.
Ectoparasites (fleas, lice eaters) are also carriers of pathogenic fungi that cause microsporia.
From animal to animal
Pets become infected with lichen upon contact with carriers of pathogenic fungi. The sources of dermatological disease are patients with lichen and animals who have just recovered from illness, which release fungi into the environment with scales and lost hair.
Remember! Trichophytosis affects rabbits, farm animals, rodents, and fur-bearing animals.
From dog to dog
For infection, short contact between a healthy dog and an individual infected with ringworm is sufficient. The risk of infection from dog to dog increases if there are wounds, abrasions, or deep scratches on the animal’s body.
Symptoms of the disease
Trichophytosis in dogs may be accompanied by some specific symptoms. It is worth noting that during the incubation period, owners do not even realize that their pet has a disease, since there are no clear signs at this moment. But after about two weeks, the symptoms appear very clearly.
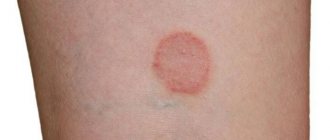
First of all, this is the appearance of a rash. It may be barely noticeable at first, but over time it enlarges and turns red. During the same period, hair loss occurs in the animal, as the fungus grows in the epidermis. The head, ears, lower parts of the paws and base of the tail are most susceptible to the influence of microorganisms. If left untreated, the infection spreads to other parts of the body.
As a rule, the resulting spots on the dog’s skin are very itchy and flaky. After some time, a crust forms on them. At this moment, it is important to pay attention to the health of your pet and begin timely treatment. Otherwise, pus will begin to form under the crust, and it will be much more difficult to cope with the problem. This condition is called “advanced trichophytosis in a dog.” What to do in this case? Immediately contact a veterinarian who will help you select the necessary medications.
Preparing for treatment
What to do if a fungus (trichophytosis) is detected in dogs? Treatment primarily involves following some simple rules:
- Isolate your pet from other animals and children.
- During the treatment period, all family members should pay maximum attention to the rules of personal hygiene.
- The house or apartment where the sick dog is located should be wet cleaned regularly. It is important to use disinfectants.
- All other objects that the dog comes into contact with during the day are also subject to disinfection.
Drug treatment
We remember that trichophytosis in dogs is a fungal infectious disease. Therefore, it is logical that antifungal drugs are used for its treatment, which can be presented in the form of ointments, tablets, and vaccines. In most cases, these products contain iodine, which is not tolerated by fungi. The most common drugs include:
The price of each of the above products is quite low, but they are all very effective in combating fungus.
Before using any of the external products, some preparation is necessary. On the damaged area, you need to carefully cut off the remaining hair, rinse the skin with water and treat with iodine. Next, an antifungal drug is applied directly, for example “Betadine” (solution). Its price, by the way, is about 166 rubles per bottle. You can repeat the procedure up to 2-3 times a day.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that the dog does not lick the product after applying it. Alternatively, you can bandage the affected area.
Along with antifungal medications, your veterinarian may prescribe immunomodulatory medications, nutritional supplements, and vitamins for your pet.
How to treat lichen at home
It’s worth noting right away that it is important to first coordinate the use of any of the folk remedies with a veterinarian. In addition, this type of treatment is still recommended to be combined with drug therapy.
So, how to treat lichen at home? You can get rid of the problem with apple cider vinegar and iodine. In the first case, you need to lubricate the cleaned affected area about 4-5 times a day, and in the second - up to 3-4 times.
Trichophytosis in dogs can also be cured with garlic. To do this, you need to peel one of its cloves and lubricate it with lichen juice. Next, apply a mixture of birch charcoal and plantain juice (1:1) to the affected area. In the absence of the latter, you can limit yourself to only garlic.
Treatment
Dermatophytosis is a complex disease that requires long-term treatment. There can be no question of any self-medication when diagnosed with ringworm. The fungus affects the deep layers of the epidermis, which makes it difficult to effectively use topical medications.
The owner may mistake the visible attenuation of the process for recovery, while the fungus penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin. Relapse in this case is inevitable. In this regard, treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a veterinary specialist with regular mycological examination.
Ointments
The effectiveness of using ointments that have an antifungal effect mainly depends on proper preparation of damaged skin areas. To do this, it is necessary first of all to disinfect the lesions with any antiseptic: a solution of furatsilin, chlorhexidine, salicylic acid.
After this, the hair around the pathological area is cut with blunt-tipped scissors. The wool is burned. If there are crusts, they are softened with a soap solution, after which they are removed and disinfected. The skin is dried with a napkin and a medicinal ointment is applied.
In veterinary practice, the following ointments are used as local antifungal drugs: Zoomikol, Mikoseptin, Yam, Tiabendazole, Griseofulvin, Fungin, Ekalin, Vedinol, etc. The drugs have a pronounced fungicidal and fungistatic effect, have an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, and reduce skin itching. The regularity of applying the ointment is determined by the attending physician.
Antifungal drugs
In cases where the disease takes on a systemic form, veterinary specialists usually use the administration of fungicidal drugs and antibiotics orally in the form of tablets or injections. Nizoral, Intraconazole, Fluconazole, Levorin are used as antifungal agents.
High effectiveness for dermatophytosis is observed with the use of antibiotics that have a fungiostatic effect: Griseofulvin, Amphotericin. The drugs are used for 3 - 5 weeks in the dose and frequency prescribed by a veterinary specialist in each specific case.
In addition to antifungal and antibacterial agents, immunostimulating agents and vitamins, in particular vitamin A, are used in the complex therapy of trichophytosis in dogs. The sick animal is isolated for the duration of treatment. Quarantine is lifted only after two negative results of mycological examination.
Folk remedies
Given the complexity of the disease, folk remedies in the treatment of dermatophytosis in dogs are used as auxiliary ones. Decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, tansy, and sage are effective for soaking crusts and antiseptic treatment of damaged skin. A solution of apple cider vinegar is used for the same purpose.
To learn how to treat ringworm at home with folk remedies, watch this video:
Disease prevention
Such troubles as trichophytosis in dogs can be avoided. To do this, you will need to follow some simple preventive measures:
- carry out daily wet cleaning in the house where the pet lives. In this case, use disinfectants;
- wash the animal’s paws after each walk and bathe it as needed;
- remember that the disease is transmitted by contact and avoid stray dogs;
- promptly rid your pet of parasites;
- the dog must live in appropriate hygienic conditions;
- Provide proper and nutritious nutrition to your pet.
Special attention should be paid to a special anti-infective vaccine. It can be used both to treat the disease and as a prophylactic agent. The most well-known drugs in this area are Microderm and Vakderm. They show the greatest effectiveness in combination with “Baksin”.
Vaccination is carried out in two stages, during which one vaccination is given. The interval between them is within ten days.
It is worth considering that after vaccination the dog’s condition may noticeably worsen. There is no need to be afraid of this process, since it is a completely normal phenomenon and the animal will soon return to its previous life, but with increased immunity.
Source
Diagnostics
To diagnose lichen, an integrated approach is used: clinical signs of infection are analyzed and a number of diagnostic studies are carried out. Diagnostic methods for dermatophytoses include the following: hair microscopy, fluorescent diagnostics, inoculation on special nutrient media. In rare, difficult to diagnose cases, a skin biopsy is used to make a diagnosis. The express PCR diagnostic method is also used to detect lichen pathogens. The latest methods for diagnosing dermatophytoses, such as the ELISA method and the immunohistochemistry method, have high diagnostic value and are beginning to be introduced into practice in modern veterinary medicine.
To conduct microscopy (examination under a microscope), scales of the affected skin and hairs of wool with a changed structure are selected. Detection of hair affected by fungal hyphae allows a positive diagnosis of lichen to be made.
Sowing on special nutrient media (or the fungal culture method) is one of the most accurate ways to detect dermatophytoses. This method allows not only to detect the presence of pathogenic fungi, but also makes it possible to obtain the growth of its culture on a nutrient medium and allows one to determine the type of pathogen. On average, the growth of colonies of dermatophytic fungi lasts from seven to thirty days. Despite its high accuracy, this method can give false negative and false positive results and requires control studies. With a complicated course of the disease, when a fungal infection is combined with a bacterial one, weeping lesions appear on the skin. In this case, in addition to the main diagnostic methods, a cytological method is used, which makes it possible to detect fungal spores in the exudate.
The fluorescent diagnostic method using a Wood's lamp is exclusively an auxiliary test in diagnosing lichen. It is not used as an independent diagnostic method, since it gives both false-positive and false-negative results in a fairly high percentage of cases. The accuracy of fluorescent diagnostics is influenced by many factors: the type of pathogen, the quality of the Wood lamp itself, how warm it was before the study (the lamp must be warmed up for 10-15 minutes before the study), the presence of contaminants on the animal’s skin and fur. To perform the Wood's lamp test, use a completely dark room. Using luminescent diagnostics, it is possible to detect traces of the vital activity only of fungi of the genus Microsporum canis, which contains the pigment pteridine in its hyphae. Under ultraviolet rays, hairs affected by the fungus Microsporum canis glow with emerald-apple light. The characteristic glow of the hairs helps the doctor take more accurate samples for microscopy and submitting the material for inoculation on special nutrient media. If the fluorescent diagnostic result is negative, infection cannot be ruled out.
Subscribe to the newsletter and get a discount at the pet store “Lubimchik”
Thanks for subscribing!
Trichophytosis in dogs
Ringworm, or, scientifically, trichophytosis in dogs is a serious disease that causes a lot of trouble for both the pet and its owner. Unpleasant bald spots on the fur, constant scabies, and an emaciated appearance are clearly not what you expected from your pet when you purchased it. The presence of trichophytosis in a dog will not allow him to give affection to members of your family or perform assigned tasks, especially since a sick animal can infect both its relatives and humans. However, in our time, ringworm in dogs responds well to treatment, and the animal does not need to be euthanized, as was the case before.
Useful video
For information on the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of lichen in dogs, watch this video:
Similar articles
- How to treat ringworm in a cat, what to smear and treat...
How are ringworm and other types diagnosed? ... All Internal diseases in dogs Infections and parasites Care and education Surgical diseases and injuries. Read more - A cat has tubercles on its ears: how to treat it, what to do if it’s...
What are the signs to suspect nephritis in dogs? ... The subcutaneous mite is differentiated from ringworm, dermatoses, and allergies based on clinical signs and laboratory diagnostic methods. Read more
- Ringworm in a domestic cat: where could it come from?
All Internal diseases in dogs Infections and parasites Care and education Surgical diseases and injuries. ... The cat has ringworm on her nose. Infection can be caused by a number of factors Read more
- How to identify lichen in a cat, what it is and how...
All Internal diseases in dogs Infections and parasites Care and education Surgical diseases and injuries. ... Ringworm in a kitten. Read more
- How is lichen transmitted from a cat to a person, to a cat, how...
Infection with the ringworm pathogen most often occurs through direct contact between a person and a sick animal. The risk group includes stray and homeless animals. Street cats and dogs… Read more
Origin of trichophytosis
Trichophytosis is an infectious disease caused by a fungus found on the skin of sick animals and common objects (bed, food bowls, toys, etc.). There are small-spore fungi, which live on the hair of rodents and other small animals, and large-spore fungi, which are also found in dogs. The causative agent of ringworm is able to remain active on the animal’s body for several years. However, directed sunlight turns out to be detrimental to the fungus, destroying it in a few hours.
The most likely way to catch trichophytosis in dogs is direct contact; young animals get sick more often and more severely, with the peak incidence occurring in autumn and winter. The risk group includes stray animals, but due to the high survivability of the fungus, which can persist for several years, pets are also at risk. Factors such as overcrowding, malnutrition, monotonous food, the presence of small cuts, and unsanitary conditions contribute to the occurrence of infection.
Routes of infection
The causative agent of skin infections are fungi of the genus Trychophiton and Microsporum. Pathogenic microorganisms are characterized by high resistance in the external environment. Once on the skin, fungi actively multiply in the upper layers of the epidermis, affecting the hair follicle. Damaged hair breaks off, which is why ringworm is called ringworm.
In veterinary medicine, the routes of infection of four-legged friends have been well studied. Infection of a dog with pathogenic fungi can occur in the following situations:
- Upon contact with a sick animal. Homeless individuals are most often exposed to fungal infections. A pathogenic fungus with pieces of skin enters the healthy tissues of the pet and infection occurs. Not only stray dogs, but also cats pose a danger.
- With indirect contact. In this case, infection occurs through care items contaminated with the fungus: plates, toys, combs, combs, beds, etc. There is a high risk of infection of a healthy dog when using equipment contaminated with fungal spores (collar, harness, muzzle, etc.).
- Through the environment. The high resistance of the pathogenic microorganism in the external environment and to disinfectants makes it dangerous when walking your pet on the street. Fungal spores in soil, sand, construction waste, and dust can land on the skin and cause infection.
- Rodents – mice and rats – are often carriers of fungal spores.
The state of the dog’s immune system plays an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease. Veterinary specialists, based on many years of experience, believe that dermatophytosis affects mainly individuals with a low level of immunity. Malfunctions in the body's defenses are a provoking factor for ringworm. In connection with this disease, puppies and young individuals, as well as weakened and elderly dogs are susceptible to the disease.
The risk group also includes individuals living in nurseries and shelters. The high density of animals contributes to the rapid spread of infection. The situation is aggravated by dampness in the premises, lack of ventilation, and unsanitary condition of the cells.
According to the observation of veterinarians, outbreaks of the disease are most often recorded in the autumn-winter months. This phenomenon is associated not only with the low resistance of a living organism due to vitamin deficiencies, but also with insufficient ultraviolet radiation, which has a detrimental effect on fungal spores.
We recommend reading about caring for your dog's coat. You will learn about the general principles of caring for a dog's coat, brushing tools, and choosing soap accessories. And here is more information about vitamins for dog fur.
Symptoms of trichophytosis
- Increased anxiety
- Decreased appetite, refusal to eat
- Bald spots, baldness
- Skin itching, rash
- Peeling of the skin, appearance of crusts on the skin
- Wrinkled skin, dandruff
- Increased body temperature
- Scabies
- Skin redness
- Claw deformity (onychomycosis)
The incubation period for trichophytosis in dogs lasts several weeks. The fungus gets on the animal's skin and releases toxic elements that lead to inflammation of the skin. Next, the spores penetrate deep into the hair follicles, deforming them and thereby causing baldness. At the same time, small round hairless spots, framed by grayish scales, can be seen on your pet’s skin. Scabs appear that the dog tries to lick and scratch. Sometimes suppuration of the hair roots is possible.
An infected animal begins to constantly scratch the area where the fungus has entered. On bare skin that remains smooth, redness, peeling appear, and a crust forms, from under which pus flows. Constant scabies promotes the spread of microbes, the fur in the area where the fungus accumulates becomes pale, brittle, brittle and soon falls out along with the crust, deformation and thickening of the claws occurs. Next, the infection enters the circulatory and lymphatic systems and causes metabolic disorders, which threatens exhaustion. In a particularly advanced case of ringworm in dogs, an increased number of affected areas is observed, and it is possible that bald spots may combine into one large bald patch. Most often, infection develops in the areas of the forehead, eyes, neck, and paws. A sick animal begins to lose weight, its resistance to external irritants decreases, and the quality of its coat deteriorates.
Course of the disease
Trichophytosis is conventionally divided into 3 forms:
- Superficial
- Infiltrative
- Suppurative
The first case is characterized by the appearance on the surface of the body of clearly defined foci of a pinkish color in the form of a circle or oval, on the borders of which follicular nodules can be seen. In the infiltrative form, swelling and hyperemia of the skin are observed, a purulent crust is formed, and ostiofolliculitis develops. The suppurative form of trichophytosis in dogs is dangerous due to the appearance of numerous folliculitis, combining into a massive infiltrate.
Treatment of trichophytosis
- Ointments containing antifungal substances
- Trimming the skin around the affected areas, in some cases a complete trim
- A course of antibiotics, immunomodulators
- Vaccination
- Applying antiseptics to the skin
- Vitamins
- Sulfur-based medicines
First of all, it is necessary to note the undesirability of any self-medication of trichophytosis, unauthorized prescription of antibacterial ointments, shampoos and other drugs to pets. Such actions will only hinder an accurate diagnosis. There are several ways to treat trichophytosis in dogs, of which the most common is vaccination. The animal is given a special vaccine, and two weeks later the procedure is repeated. Moreover, the vaccine in this case is not only a medicine, but also a means of prevention.
Another popular treatment is the use of antifungal ointments. The wool around the areas susceptible to infection is cut, while the scissors used for the procedure are thoroughly disinfected, and the cut wool is burned to prevent infection. An antifungal drug is applied to the skin, dead scales are wiped with a betadine solution and removed. Infected areas are treated with a solution of salicylic acid, tincture of iodine, scabs and crusts are moistened with warm water and removed with soap and kerosene. It is recommended to use creams with fungistatic and fungicidal properties, antiseptics, wound healing agents, special ointments and shampoos, a 10% alcohol solution of iodine, as well as a suspension of griseofulvin. In addition, treatment of ringworm in dogs includes disinfection of the coat with a 3-5% formaldehyde solution - it is necessary to spray and comb the dog twice against the grain (1 time) and along the coat (2 times).
In the most severe cases, a course of antibiotics or immunomodulators, as well as ultraviolet irradiation, is prescribed. The sick animal is isolated until completely cured, and the room in which it was kept is treated with cleaning agents. It should be noted that trichophytosis in dogs is transmitted to humans, so after contact with an infected animal it is necessary to undergo thorough disinfection. The success of treatment may be indicated by overgrowth of the affected areas.
Treatment methods
A mandatory element of therapy is the daily application of fungiostatic drugs to the affected areas in combination with tablets. It is important to treat all areas in the room where the dog is, with disinfectants that suppress the activity of pathogenic fungi. Only a combination of drug treatment with the destruction of the causative agent of trichophytosis in the home and preventive measures helps to get rid of the dermatological disease.
General rules
Six tips for dog owners:
- Avoid contact with sick and stray animals.
- Give your dog vitamin and mineral supplements to strengthen the immune system.
- Follow all veterinarian prescriptions and do not replace pharmaceutical formulations with folk remedies.
- Combine the use of effective antifungal ointments and creams with tablets or injections for fungal skin infections. If a bacterial infection occurs, additionally give the pet an antibiotic as prescribed by the doctor.
- Thoroughly disinfect hands, bedding, bed, and upholstered furniture. Be sure to treat tables, floors, and all areas where fungus may remain. Towels and rags are washed or boiled and disposed of at the end of the course of treatment.
- Children and adults should not pet a pet, much less allow the dog to sleep on the bed. During treatment, communication with the animal is carried out only with medical gloves, otherwise it is easy for all family members to become infected.
Medicines
All medications are selected by a veterinarian after receiving test results. It is important to have a comprehensive effect on the body, especially with extensive damage to the skin. If there is a significant area where the spots are marked, hair falls out, there is redness and itching, veterinarians recommend cutting off the coat from the animal.
Important details:
- First-line drugs are Griseofulvin and Intraconazole. The active substances act directly on the cell membrane of the fungus, which provokes the development of trichophytosis. Intraconazole causes fewer side effects and has fewer restrictions. Griseofulvin is a more toxic drug that was often prescribed in the past. Gradually, this medicine is becoming a thing of the past, giving way to modern remedies with a milder effect on the body. This potent drug should not be used in dogs with kidney damage or pregnant bitches.
- Sulfur-based ointments are preparations without which it is almost impossible to suppress the activity of pathogenic fungi. The best option is to remove as much hair as possible from the dog’s body for a more comfortable application of the compounds and to reduce the number of spores on the hairs. The clipped part of the cover must be burned so that the pathogenic flora does not enter other areas from where re-infection is possible. Sulfur ointment is quite toxic, it is important to prevent licking of the product. For this purpose, the animal is put on a medical collar.
- External agents with antimycotic action. The appropriate name is prescribed by the veterinarian. Ketoconazole, Nystatin are effective compounds for destroying fungus when ringworm is detected in dogs.
- Vaccines for the treatment and prevention of dermatophytoses are a good option for eliminating pathogenic flora. Specific preparations with a minimum dose of the pathogen are used not only to prevent diseases, like other compounds, but also for the successful treatment of trichophytosis. Veterinarians give vaccinations using Polivak-TM, Microderm, Vakderm. It is forbidden to administer the composition at high temperatures in dogs, infectious diseases, identification of dangerous bacteria in the affected areas with trichophytosis.
Learn about the symptoms and treatment of adenovirus infection in dogs, as well as how to prevent the disease.
What to do if your dog has ear pain and how to help your four-legged friend? The answer is in this article.
Go to the address and read about what you can give your dog for diarrhea using human medications.
Disinfection and hygiene rules
Ringworm is a contagious (infectious) disease. Even a small spot can cause infection to the owner if the rules for caring for a sick animal are not followed.
When trichophytosis is detected, the dog owner must act correctly:
- disinfect all hard objects, floor;
- soft toys, bedding, beds, towels, door mats, and rags will have to be disposed of. Sofas and armchairs need to be treated with an antifungal compound, otherwise the smallest spores can get on the body, clothing of a person or fur of a dog, which will lead to a new round of the disease. Outside the skin, fungal spores remain viable for some time, and thorough disinfection is indispensable;
- when treating spots with lost hair, be sure to wear medical gloves, which are used only once;
- It is forbidden to pick up a dog or stroke it with unprotected crayfish;
- daily wet cleaning with preliminary use of a vacuum cleaner and a disposable dust bag is mandatory;
- It is convenient to clean upholstered furniture and carpets with a steam generator. The combination of high temperature with safe processing allows you to kill the fungus and maintain the good appearance of armchairs, sofas, and floor coverings;
- All family members must follow the rules and precautions: ringworm is very contagious and dangerous.
Prevention of ringworm
Prevention of trichophytosis includes vaccination, a balanced diet, and maintaining cleanliness in areas where animals are kept. Injections with special drugs are practiced both for therapeutic purposes and for preventive purposes. However, many veterinarians are of the opinion that such vaccinations can, on the contrary, provoke infection with lichen fungus. Another risk factor for ringworm infection in dogs is weak immunity, which is often caused by malnutrition or monotonous food. A properly formulated diet with a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements will eliminate the risk of infection with trichophytosis. Finally, if we are talking about a shelter, kennel or other place where dogs are kept together, then it is necessary to ensure an adequate level of living space for the animals and regular sanitization of the enclosures.
Source
What is ringworm in dogs?
Not so long ago, this pathology was considered incurable, so pets were euthanized. Nowadays, many antifungal drugs have been created to help cope with dermatophytosis. At the same time, ringworm is considered one of the most dangerous and intractable types of the disease. Spores penetrate into the environment from the fur of infected animals and remain in it for a long time. When it comes into contact with the skin, the fungus multiplies and is absorbed into the hair follicles, which leads to hair loss.
The infection is considered an anthropozone. This means there is a risk for people and pets. Children are especially susceptible to infection, since their immunity has not yet been formed. The danger is high in illness and in older people. Therefore, it is important for owners to take preventative measures when treating their dog. It is necessary to wear protective gloves and wash your hands with soap and antiseptic. You should limit communication between other residents of the house and your pet.
What does the disease look like on the animal's body?
Let's look at how ringworm in dogs begins. From infection to the appearance of the first signs, it can take from several days to three weeks - that’s how long the incubation period lasts. If the dog has a long and thick coat, then it is not easy to notice lichen at the initial stage.
If the fungus enters the hair follicle, it causes inflammation, which is accompanied by itching and redness of the skin. The animal exhibits restless behavior and often itches. Initially, reddened and slightly swollen tubercles are visible on the skin. At this time, no patches of baldness appear.
Due to the fact that the pet itches a lot and licks the affected areas, a secondary infection occurs. The fungus spreads to healthy areas of the body. The lesions acquire clear edges and become round. The skin dries out, gray crusts and scabs appear.
Foci of inflammation are located in the middle and on the sides of the affected area. Follicular nodes are often observed along the periphery. At this time, the pet notices bald areas. They are localized on the paws, belly, croup, neck, and muzzle. Not only the skin is damaged, but also the claws. They change shape and become thicker.