What is a disease
This is a painful formation in the thickness of the skin that occurs as a result of the inflammatory process. Inside this formation, pus, microorganisms and fragments of dead tissue accumulate. Intensification of the inflammatory process causes a rapid increase in the size of the abscess or boil.
An inflammatory neoplasm appears on any part of the animal’s body. In this case, both the superficial layers of the epidermis and internal organs are affected. The most dangerous is a perianal abscess (diverticulum), which develops in older individuals. Infection occurs when there is minor damage to the paraanal area.
Abscess concept
An abscess in dogs is an inflammatory process that occurs in the skin, which is accompanied by the formation and accumulation of purulent formations due to necrosis (rotting) of tissue. A bag of pus, pieces of necrotic tissue and pathogenic microflora forms under the skin. Around the sac, the tissue becomes inflamed and the walls of an abscess begin to form, which consists of a surface layer formed by fibrous connective tissue and an internal, pyogenic layer of granulation tissue. If no measures are taken, the bag will grow and bother the animal. In addition to being painful, abscesses negatively affect the overall health of your pet.
The disease can be localized in any part of the body due to mechanical damage: bruises, injuries and injections. And if there are malfunctions in the functioning of the secretory organs, then an abscess of the gland may develop in the dog.
When the paraanal gland becomes inflamed, the excretory canal is blocked and the secretion accumulates inside. Finding no way out, the fluid overflows the gland, and the wall and skin rupture. This is an abscess of the paraanal gland in a dog, which resembles an ulcer.
Reasons why an abscess appears in a dog
The disease develops when the skin becomes damaged and infection enters the wound. It provokes inflammation, which leads to rupture of blood vessels. The appearance of a large amount of pus in this place is provoked by the reaction of the immune system.
Thanks to natural healing processes, the wound heals and a kind of pouch with a crust forms. The pathological process will continue until the connective tissue stretches.
The most common cause of an abscess is trauma after a fight with relatives. The infection is transmitted to the wound from the bite almost instantly. If the dog licks the wound in a timely manner, the likelihood of illness is significantly reduced.
An abscess appears when pathogenic microorganisms enter the wound. Certain breeds are predisposed to its development:
- Chinese Shar Pei;
- English bulldog;
- Labrador.
Dogs of these breeds have short and coarse hair. Street dogs are also prone to infection due to poor living conditions and a high likelihood of contact with sharp objects.
Old male dogs develop abscesses due to pathologies associated with the prostate. Bitches are at risk of developing mammary abscess. And also in puppies playing with sharp objects, inflammation appears at the site of the cut.
Triggering mechanisms for the formation of pathology:
- skin damage;
- surgical operations performed in violation of sanitary and epidemiological standards;
- insufficient animal hygiene;
- decreased immunity;
- elderly age;
- development of parasites.
Treatment of inflamed formation
Treatment of a purulent wound requires professional intervention, since infection increases the risk of developing sepsis in a sick animal.
You should definitely contact a veterinarian if your dog refuses to eat, is lethargic, or has an elevated body temperature.
Therapeutic measures include surgical cleansing of the wound from purulent exudate, the use of antiseptics, antibacterial and restorative drugs, and installation of drainage. Sutures are not used for symptoms of purulent inflammation.
Cleansing the wound
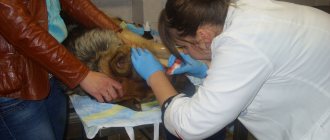
An important condition for successful treatment of a wound with a purulent process is its cleansing. For this purpose, the animal undergoes surgical manipulation in a veterinary clinic. Under local anesthesia, the wound channel is opened, necrotic tissue is excised, and purulent exudate is removed.
During the procedure, the purulent pockets are opened and cleansed. Manipulation, as a rule, is accompanied by infiltration anesthesia with a solution of novocaine with an antibiotic.
After surgical cleaning of the wound, the veterinarian treats the tissue with antiseptic solutions. For this purpose, use a 3% solution of potassium permanganate and a 0.1% solution of Rivanol, similar to hydrogen peroxide. An effective remedy for the antiseptic treatment of purulent wounds is a 2% solution of Chloramine and a 0.5% solution of Chlorhexidine.
Hypertonic antiseptics are often used in veterinary practice to remove purulent contents.
After cleansing and treatment with disinfectants, antimicrobial ointments are used. Levomikol, Vishnevsky ointment, Lincomycin ointment, Tyrosur, Baktroban, Olive liquid have a good therapeutic effect.
To learn how to treat a purulent wound for a dog, watch this video:
Drainage
In veterinary practice, drainage is used to treat deep purulent wounds.
After surgical cleansing of the pathological focus from necrotic tissue and purulent exudate, special tubes are inserted into the wound cavity (passive drainage). The devices are made of rubber or vinyl chloride. Thanks to drainage, pus is removed from the wound. To prevent the tubes from falling out of the wound cavity, they are securely fixed, sewn with rare stitches to the skin of the animal.
Drainage in the wound
The catheter is left in the wound until complete healing. This period can be 5 - 10 days, during which the owner should treat the drained area with antiseptic solutions of Furacilin, potassium permanganate or Chlorhexidine.
Often, in the treatment of a purulent process, veterinary specialists resort to active drainage with the help of turundas. A narrow gauze swab (a bandage rolled into a napkin) is soaked in antimicrobial ointment and inserted into the wound cavity. Due to its hygroscopic properties, such a simple device absorbs purulent exudate. Turundas are placed for 1 - 2 days, after which passive drainage is used using special catheters.
The use of enzyme preparations in the treatment of purulent foci has a good effect. Most often, chymotrypsin, ribonuclease, and bromelain are used for this purpose in veterinary surgery. Gauze pads are impregnated with the drug for the active phase of wound drainage.
The use of proteolytic enzymes reduces inflammation and accelerates tissue regeneration processes. The drugs lyse dead tissue, effectively and quickly cleanse purulent foci.
After the purulent process has been stopped, the veterinarian can stitch the wound. This is done, as a rule, if the damage was torn or, during the development of inflammation, the surgeon had to excise a large amount of tissue. Closure of the damage is carried out strictly after the relief of purulent inflammation, in the presence of signs of granulation of healthy tissue.
Antibiotics
The development of a purulent process in the tissues is accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition of the furry pet. High temperature, loss of appetite, apathetic, lethargic state indicate the development of the body’s general reaction to inflammation. Successful therapy of a surgical disease is unthinkable without the use of modern antibacterial drugs. In veterinary practice, antibiotics of the penicillin, tetracycline and cephalosporin series are used.
Modern penicillins are widely used as antibiotics: Ampicillin, Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, Sinulox, Clamoxil. Doxycycline is effective as a tetracycline drug. Of the cephalosporins, Cephalen, Cephalexin, Cefotaxime, Cefaperazone and others have a high therapeutic effect.
The course of treatment with antibacterial drugs is 10 - 14 days. Preference is given to intramuscular injections.
Antibiotics
Other therapies
In the complex therapy of purulent wounds, general strengthening drugs are also used. Immunomodulators help speed up tissue regeneration: Roncoleukin, Gamavit, Ribotan, Glycopin, etc. Healing is accelerated by therapeutic doses of ascorbic acid, vitamin A, thiamine, and riboflavin.
The use of physiotherapy promotes recovery. Ultraviolet irradiation, vaporization, paraffin treatment, irradiation with a Sollux lamp, used in the second phase of wound healing, significantly shorten the pet’s recovery time. Zinc and ichthyol ointment, the use of tissue therapy according to Filatov and autohemotherapy help to speed up scarring.
We recommend reading about osteomyelitis in dogs. You will learn about the causes of osteomyelitis, symptoms of the disease, diagnosis and treatment. And here is more information about spinal fractures in dogs.
Infection of wounds received by a pet is not uncommon. Purulent inflammation requires the owner to competently provide first aid to the animal. A qualified specialist will perform surgical cleansing of the pathological focus, active and passive drainage.
The use of anti-inflammatory ointments, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, and general restoratives helps to quickly relieve inflammation and regenerate damaged tissues.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease depend on the inflammatory response in the body.
With a hot soft tissue abscess, the following symptoms are observed.
- Sharp pain and increased temperature at the site of inflammation.
- Fever. The dog eats poorly, is lethargic and drinks a lot. It is dangerous for the animal, which can die even after several hours of this condition.
- Refusal to go for a walk.
- Stool disorders and inability to sit (with the development of an abscess in the paraanal area). During defecation, the animal feels severe pain.
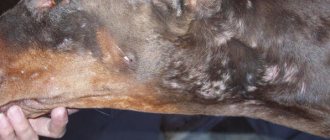
- Lack of hair around the affected area.
- Leakage of blood and lymph.
With cold abscesses there may be no symptoms. The animal may not have a fever. This type of disease is no less dangerous, as it can last a long time (almost the entire life, depleting the animal).
Types and forms of abscesses
In veterinary medicine, there are several criteria by which abscesses are classified.
Morphological composition of purulent formations and bacteria provoking the process:
- hot or spicy;
- cold, or chronic.
- superficial, which develops in the skin and subcutaneous tissues;
- deep, which can be subfascial, intermuscular, intramuscular, subperiosteal, bone, subperitoneal, abscess of organs and glands, depending on the location.
With a benign abscess, thick, creamy, purulent accumulations are formed, with an increased content of leukocytes, without microbes or with little presence of them. A benign abscess can form if low-virulent staphylococci penetrate the tissue or when irritating substances are introduced under the skin. Such an abscess often forms after an injection in a dog.
In a malignant abscess, the purulent formations are watery and thin, with a high concentration of pathogens and low production of white blood cells. The causative agents of the malignant process are purulent-putrefactive and anaerobic microbes. This type of abscess in dogs is more painful and will not go away on its own. It can develop into a more complex form and affect adjacent tissues. Such formations require surgical intervention; in other words, they are removed through surgery.
With a hot abscess, a pronounced inflammatory process is observed, which is characterized by an acute course and the rapid formation of an abscess, which often opens spontaneously, that is, it breaks through and the pus flows out.
With a cold abscess, the main signs of inflammation are weak, and pus accumulates slowly, which makes timely diagnosis difficult. Such abscesses are typical of old and emaciated dogs that move little. An abscess is formed in the presence of low-virulent microorganisms.
Types of abscesses
Veterinarians distinguish between these types of abscesses.
| Criterion | Key Features |
| Depending on tissue morphology | Benign or malignant |
| Depending on the course of the pathological process | Active (hot) or cold (chronic) |
| Depending on the depth of the lesion | Superficial, subcutaneous and internal (located on internal organs) |
There are such differences between a benign abscess and a malignant one:
| Criterion | Benign | Malignant |
| Presence of purulent discharge | Thick, white, opaque | Liquid, yellow, cloudy, sometimes bloody |
| Smell | Absent or weak | Foul odor due to active inflammation or release of toxins |
| General condition of the animal | Satisfactory. Sometimes weakness appears and body temperature rises slightly. | The animal is completely exhausted, there is no appetite |
Diagnostic methods
If you have at least one of the above symptoms, you should contact your veterinarian. The veterinary clinic will prescribe diagnostic measures, depending on the medical history collected by the doctor. Diagnosis is made to exclude diseases with similar symptoms (hematomas, acne, hernias). The following methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- Palpation and history taking;
- Measuring general temperature and temperature at the site of inflammation;
- Biopsy followed by analysis of the contents of the site of inflammation;
- CT, PRT or ultrasound is prescribed for damage to internal organs.
To perform a biopsy, you will need to open the dog's abscess; the procedure is painful, but will help assess the level of complexity of the disease.
How to open a dog's abscess
An autopsy cannot be performed at home. This is what the veterinarian does. Doctors recommend opening an abscess if it progresses quickly or is advanced. Such procedures are performed in the clinic.
- The affected area is treated with an antiseptic. An anesthetic is administered (for example, an injection of lidocaine).
- An incision is made using a scalpel.
- Using a special syringe, the incision is widened.
- The pus is sucked out and the cavity is cleaned.
- The wound is washed with antiseptic drugs.
- The operation is completed by applying a sterile dressing.
In some cases, the veterinarian installs drainage to drain purulent contents.
If the abscess opens on its own, then the wound is treated with an antiseptic solution, bandaged with a bandage and the dog is shown to the veterinarian.
Symptoms of furunculosis in dogs
A furuncle is a cone-shaped, dense swelling, very painful, reaching the size of a hazelnut. As the boil matures, a yellowish-gray spot forms at the top. It means that the purulent-necrotic core of the boil has been formed.
At the center of this shaft is a hair. If the boil opens spontaneously, the rod may come out along with the pus. However, the pus contaminates adjacent areas of the skin and new boils form.
How to help a dog with a boil?
It is better not to treat furunculosis on your own. But it is necessary to provide the pet with the correct first aid and be able to cope with such a problem in situations where professional help is not available. Such treatment should be not only local, but also general.
- If a thickened area of skin on which a boil is formed is detected, the hair on the affected area must be cut off and the skin itself treated with a 75% alcohol solution. At the very initial stage of boil development, alcohol dressings have a good effect. Gamavit for dogs can be administered intramuscularly at the rate of 0.3-0.5 ml per kilogram of animal weight. When the boil suppurates and the top of its cone turns yellow, to speed up the opening, you can apply bandages with Vishnevsky's liniment or 10% ichthyol ointment. At this point, warming compresses are contraindicated. After opening, be sure to treat the wound with brilliant green. Under no circumstances should a boil be squeezed out on its own. It is better to contact a veterinarian for an autopsy.
Homeopathic treatment with the medicine Belladonna-Homaccord gives good results for furunculosis. It is administered subcutaneously twice a day, while simultaneously lubricating the affected area with Traumeel S gel. When boils spread throughout the body, Echinacea compositum is also prescribed.
When to see a doctor
It is necessary to urgently visit a veterinarian in the following cases:
- the affected area of the animal began to rot, the surrounding tissues began to turn black;
- the dog is restless, howls, licks an abscess;
- with active treatment, inflammation does not go away within a week;
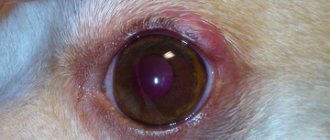
- an abscess appeared on the ear, near the eye, genitals and anus.
Treatment of inflammation
In the initial stage, the disease can be easily treated at home. In 90 percent of cases, the inflammation goes away.
Treatment for a dog abscess will vary depending on the location.
- When the paraanal gland is affected, a blue or red formation is noticeable under the butt. The abscess is opened in the clinic, the wound is treated and a sterile bandage is applied.
- An abscess in a dog on the neck, withers or face can be treated independently at home. Monitor the animal’s condition and strengthen its immunity. For intraorbital abscess, the eyes are washed and instilled.
- In aging male dogs, purulent lesions of the prostate develop. The most effective way to treat ulcers is to remove the genital and prostate glands.
Therapy with pharmaceutical drugs
It is possible to use such pharmaceutical drugs.
- Disinfecting solutions. These include hydrogen peroxide and chlorhexidine.
- Application of dressings with ointments: Levomekol, Liniment according to Vishnevsky, Ichthyol ointment. The duration of application of the bandage is from 2 to 12 hours. Carefully ensure that the dog does not tear off the compress.
- The use of immunomodulatory agents to maintain the immunity of dogs. The best immunomodulators are lemongrass or echinacea. The dog’s body is also supported with vitamin C.
- Antibiotic therapy is also an essential part of the treatment of phlegmon or abscess.
- Extensive inflammation and severe pain are relieved by anti-inflammatory and painkillers - such as Analgin, Diclofenac and others.
You cannot prescribe medications or give injections on your own!
Herbal treatment
Tinctures of calendula, nettle and yarrow are used. Herbal preparations are used in the form of compresses. During treatment, the animal should not be allowed to lick or bite the treated area. It is better to use a muzzle.
Traditional medicine is used to combat infection.
- Compresses on the wound with celandine juice. Soak gauze with this juice and apply to the affected area for no more than 10 minutes. The procedure is repeated several times a day.
- Prepare juice from fresh St. John's wort and calendula, mix them. Add 20 drops of a mixture of natural plant juices and a pinch of table salt to a glass of cool water. Wet gauze with this solution and apply to the affected area.
How to treat the disease
Treatment of the disease is carried out using different methods. The veterinarian should prescribe a course of general and local therapy or recommend surgery.
If a benign abscess is diagnosed in a dog, treatment is carried out with medication, which consists of:
- absorbable ointments used to treat unruptured formations;
- antiseptic solutions for treating wounds in case of spontaneous opening of an abscess;
- antiseptic ointments that are applied to the wound channels.
The affected area should be washed with a syringe so as not to cause unnecessary inconvenience to the pet.
When a malignant abscess is diagnosed, surgery is prescribed to remove the purulent sac. Manipulation should be carried out as quickly as possible, before the disease spreads to adjacent tissues. In the postoperative period, general and local therapy and a course of antibiotics are carried out.
If the paraanal glands are affected, treatment should be carried out in a clinical setting. After examination and determination of the extent of the problem, drug treatment in combination with warm compresses will be prescribed. In more serious cases, the veterinarian will open and treat the abscess himself. Often, additional drainage is required to remove pus. Afterwards, treatment with strong antibiotics is prescribed to suppress pathogenic microflora, using rectal suppositories and local treatments.
Consequences of untreated abscesses
The abscess must be treated and removed. If left untreated, the animal will develop sepsis. So, a superficial abscess on the paw or on another part of the body bursts with pus coming out. A large wound appears in its place. If it is not treated, the infection will spread further throughout the body.
When a dog develops an internal abscess, if it is not removed, the contents can leak into the body's internal cavities. When pus enters the abdominal cavity, the dog develops peritonitis. It is difficult to save the animal.
Prevention
It is very difficult to protect your four-legged pet from developing abscesses. To do this, the owner is recommended to:
- After a walk, check the paws and wipe or wash them.
- The dog must eat well. This is a guarantee of strong immunity.
- Give the animal multivitamin preparations at least 2 times a year.
- Disinfection of cuts and injuries is necessary. They are treated with hydrogen peroxide and chlorhexidine.
- Bath your dog regularly.
- Vaccinate the animal. In this case, immunity is formed and the risk of infection is reduced.
The dog must have a collar while walking. If a dog lives in the yard, it should be in an enclosure. An animal living in an apartment should be regularly walked in a safe place where the risk of infection is minimal.