Description of the disease
Atheroma is one of the relatively harmless tumors due to the fact that it does not transform into a malignant neoplasm.
However, there is a risk of significant increase in size, so medical attention is required in all cases. Teenage children are more likely to experience this problem. Boys and girls get sick about the same. The main reason why parents first turn to a surgeon is the presence of a visually noticeable tumor.
The atheroma itself is a small capsule filled with pasty contents. It is sebum, which, due to blockage of one or more glands, did not come out, but remained in the subcutaneous tissue.
Wen on a dog
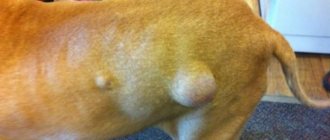
Fats or lipomas are often benign neoplasms of adipose tissue. They mainly appear in dogs of middle and older age groups, after five years. Bitches suffer more often than males. What to do if you find such a tumor in your dog?
Features of lipoma.
Lipomas are round, moderately mobile subcutaneous formations, single or multiple.
Painless. Animals are not particularly troublesome unless they grow to enormous sizes. They are most often localized in the sides, back, and in the sternum area closer to the paws. If the process is prolonged, dogs can interfere with walking, creating mechanical inconvenience. Small lipomas are not subject to ulceration, unlike, for example, tumors of the mammary glands, but they can be easily injured by surrounding objects and the dog itself. Large lesions may have ulcerations. One of the varieties is infiltrating lipoma, which can damage deep-lying tissues; in this situation, treatment is more difficult. Since fat is contained not only in subcutaneous tissue, lipomas can also occur in internal organs, because there is also a fatty layer there. More often they are recorded in the mesentery. Also, benign lipoma can degenerate into malignant fibrosarcoma. This is a dangerous condition. Atypical cells can damage many internal organs, disrupt their functioning and cause the death of the animal. Benign tumors should also not be ignored, since in addition to the fact that, reaching gigantic sizes, they interfere with the movement and mobility of the animal, the risk of their degeneration into malignant and metastasis increases. Also, if the formation has reached a large size, it is more difficult to carry out an operation to remove it, both from a technical point of view and from the point of view of restoring the animal’s body. Minor surgical procedures are naturally easier for dogs to tolerate.
If you detect any neoplasm on your pet’s body, it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Reasons for the appearance of wen
As with other neoplasms, the exact cause of lipomas in dogs is unknown. Predisposing factors for the appearance of these types of formations are considered to be genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders, inactive lifestyle, diet rich in carbohydrates, and excess weight.
Diagnostics
An experienced oncologist can most likely suspect a lipoma, based only on examination, palpation and personal experience. However, you should not be arrogant, just as there is no point in owners guessing whether it is a wen just by appearance or not, and trying to make predictions. Valuable time may be lost if you are faced, for example, with a mastocytoma. But this is a very dangerous type of tumor.
- First, a fine-needle biopsy of the tumor is performed. The resulting material is transferred to a glass slide, stained and viewed under a microscope. The method does not give a 100% result, but there is still a high probability of determining the type of tumor.
- Ultrasound. It is possible to conduct a study of the formation itself in order to examine the structure: the presence of cysts, vessels. An ultrasound may also be required to rule out abdominal lipomas and metastases.
- X-ray. Alternative to ultrasound. You can visualize the shadows of large neoplasms in the abdominal and chest cavities.
- CT and MRI are used for a thorough cancer search, especially when there is a suspicion that the process is malignant.
- Blood tests and heart screening are required if surgery is planned.
- To accurately confirm the diagnosis, the removed tumor or part of it is sent for histological examination. With this diagnostic procedure, they look in more detail not at isolated cells, but at the structure of the altered tissue as a whole. The histology result has to wait about 3-4 weeks.
Treatment
Surgical excision of the tumor is predominantly used. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Anesthesiologists recommend undergoing a number of tests before surgery: heart screening and blood tests. Many owners ask, what will change? The fact is that, depending on whether there are concomitant diseases of any of the organ systems, the anesthesiologist selects an individual scheme according to which anesthesia will be given, what drugs are needed, whether preparation is required before the operation or treatment after. The owner has the right to refuse additional diagnostics, but in this case the surgical team cannot be fully responsible for the outcome of the operation. If the tumor is small, then the operation is quick, as is the recovery period. With the infiltrating type of lipoma, it may be necessary to remove part of the muscle tissue. After surgery, a short course of antibiotic therapy, suture treatment, and wearing a protective collar or blanket will be required, depending on the location of the lipoma.
The age of the animal is not a contraindication for surgery. However, there are a number of reasons why surgeons may refuse, such as severe concomitant diseases. In this case, a decision is made on alternative treatment methods, for example, radiation therapy. In general, the prognosis for lipoma is favorable; relapses do not occur often. In each case, the dog should be examined again by a doctor, as another, malignant tumor may appear that looks similar to a lipoma.
Symptoms of atheroma in children
In 80-85% of cases, apart from the visual defect, children do not present any other complaints. Uncomplicated atheroma is characterized by:
- painlessness;
- mobility;
- elasticity upon palpation.
The skin over the surface of the tumor is smooth and does not fold. The clinical picture may change when the contents of the atheroma become inflamed against the background of the addition of bacterial flora. In this case, patients may note:
- pain when pressed;
- redness and increase in size of the tumor itself;
- local increase in body temperature.
If the above symptoms occur, you should immediately seek help.
This situation threatens the penetration of infection into nearby tissues and blood with the spread of microorganisms to distant areas of the body and can cause a deterioration in the general condition of the child. Atheromas occur in areas of the skin that are rich in sebaceous glands. Therefore, they especially often have the following localization:
- scalp;
- face and neck area;
- shoulder girdle, armpit area;
- back.
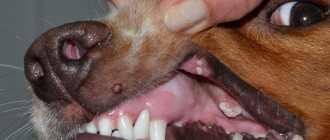
Neoplasms occur less frequently in the groin area and scrotum (in boys). In these areas they have the appearance of a skin growth and require differential diagnosis with other skin tumors.
Symptoms
Symptoms of atheroma include:
- formation (dense, spherical), filled with a light mass. It is usually white or light yellow;
- clear boundaries of the tumor. And if you click on it, the boundaries may shift;
- a noticeable duct of the sebaceous gland (but it may not exist);
- absence of pain as such. Exceptions are cases when the formations are constantly damaged, rubbed by clothing, etc.;
- location either in groups or one tumor at a time - both options are possible;
- sizes from 5 mm to 4 cm. Individual tumors of this type progress over the years, very slowly changing in size.
In connection with the last point, let us clarify that atheroma on the face or other part of the body usually develops in three variants. The first is breaking open and becoming an ulcer. The second is overgrowth with thick connective tissue. In such a situation, the tumor remains in its original form throughout the patient’s life and does not change. The third option is the most unfavorable - the tumor degenerates into malignant, that is, skin cancer develops.
Do you have symptoms of atheroma?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Causes of atheroma in children
Atheromas in children occur due to a violation of the secretion of sebum by the corresponding glands.
When the excretory duct is blocked, the secretion of the gland has nowhere to go. It is secreted into the subcutaneous space, where a dense capsule is formed around it. Common causes of atheroma development in children are as follows:
- Using children's cosmetics (creams, ointments, moisturizing masks) in excessive quantities. Sometimes parents, in an effort to protect their child’s skin from harmful external factors, use cosmetic products uncontrollably. This leads to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands with blockage of their excretory ducts.
- Hormonal changes in the child's body. Infants and teenage children are traditionally at risk. It is during these periods that changes in the concentration of sex hormones occur. Against this background, acne appears, the function of the sebaceous glands is disrupted, and conditions are created for their blockage.
- Seborrhea. This is a dermatological disease that leads to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands in a certain area of the skin.
- Genetic predisposition or congenital structural features of the skin. Atheromas most often occur in children after 3 years of age. If neoplasms are detected in children immediately after birth, the doctor may assume the presence of problems with the sebaceous glands that developed in utero.
In addition, factors that increase the risk of developing atheromas are poor personal hygiene, metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes) and frequent mechanical damage to the skin.
Causes
The causes of such tumors are called disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous glands. This happens due to various factors. For example, the skin does not exfoliate well enough and dead skin cells do not come off, or the patient has hyperhidrosis. Doctors say that in many cases, heredity plays a key role - that is, a tendency to such a disease.
To the mentioned causes of atheroma we add the following:
- hormonal imbalance;
- high viscosity of sebum;
- problems with excretory function;
- work in which the skin is constantly covered with dirt and irritating substances;
- bad environmental influences;
- hygiene problems;
- cosmetics, antiperspirants and deodorants that narrow the ducts of the sebaceous glands.
These same factors can contribute to the development of other skin diseases.
Diagnosis of atheroma in children
It is relatively easy to identify atheroma.
Even at the stage of the initial conversation with the patient or his parents, the surgeon assesses the general well-being of the child, collects anamnesis and analyzes complaints. When examining a neoplasm, the doctor pays attention to its size, location, pain, and the presence of redness. Before surgery, the surgeon prescribes a number of tests to comprehensively assess the child’s condition:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for infections (HIV, syphilis, viral hepatitis B, C);
- ECG, fluorography.
The child is also examined by an anesthesiologist and pediatrician before the operation. A mandatory diagnostic method is histological examination of tumor tissue after its removal. At this stage, it is possible to determine whether it was an atheroma or a lipoma (a tumor similar in appearance).
Treatment of atheroma in children
The optimal method of treating atheroma in children is its surgical removal.
However, the age of the patient decides a lot here. Thus, most pediatric surgeons, in the absence of severe clinical symptoms, recommend a wait-and-see approach. Sometimes the swelling may resolve on its own. This is especially true for newborns and infants. In such cases, the development of the neoplasm is observed until the age of three, and if it persists, only then is it removed. . Surgical intervention can be carried out traditionally using a scalpel or minimally invasively using a laser. In the first case, the surgeon excises the tumor with a capsule, which eliminates the risk of relapse. After this, cosmetic stitches are applied to the tissue to achieve the best aesthetic result. Laser removal in children is used for small tumors. Using this technique, it is possible to avoid incisions and the formation of postoperative scars. In both cases, a comprehensive examination of the child is first carried out with the selection of the optimal treatment option.
In the postoperative period, the child may be prescribed the following groups of medications:
- painkillers;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antibacterial.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating discomfort and preventing infection of the postoperative wound.
Treatment
The only treatment for atheroma that produces results is removal of the formation by surgery, laser or radio wave. The operation, as a rule, does not take much time (up to half an hour), is performed under local anesthesia and does not require too complex and lengthy rehabilitation.
If the situation is advanced and severe inflammation, infection, or an abscess has formed, emergency surgery is required. But in this case, the tumor is not removed, but only cleaned. Complete removal occurs after healing, after about three months.
Depending on the patient's initial condition after surgery, he may be prescribed antibiotics or other medications.
Questions
- Which doctor treats atheroma in children?
A pediatric surgeon is involved in identifying and treating atheroma in children. - Is it possible to cure atheroma without surgery?
Sometimes in the early stages of the disease the surgeon chooses a wait-and-see approach. In 20-35% of cases, atheroma can resolve on its own. However, if the capsule is formed and the tumor is large, it will not be possible to do without surgical intervention. - How dangerous is atheroma in childhood?
Atheroma is a relatively safe tumor. It does not become malignant, rarely becomes complicated and is not accompanied by the development of permanent defects. However, this does not eliminate the need to consult a pediatric surgeon. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis and select treatment. In addition, atheroma can sometimes become inflamed due to the addition of bacterial flora and cause a deterioration in the child’s well-being. - Is it possible to play sports after surgery?
After surgical removal of atheroma, it is recommended to refrain from active activities for 2-3 weeks. This will allow the tissues to fully heal and recover.
Disease prevention
Since the causes of most types of cysts are unknown, veterinarians give general recommendations for preventing this disease. First of all, the owner must provide the dog with proper and balanced nutrition. Doctors recommend specially formulated foods that contain the required amount of vitamins and minerals for every day.
It is important to maintain dog hygiene, brush your pet regularly, cleaning the fur from possible accumulations of dirt, and also trim the fur. The dog should be washed with special products that will wash the coat and skin. Long-haired breeds are washed 2 times a month; dogs whose coat has medium pile need only be bathed once every 2 months. Washing too frequently dries out your pet's skin and disrupts its water balance.
It is necessary to regularly examine the dog’s skin; if neoplasms appear, a visit to the veterinarian cannot be postponed.
Atheroma is a cyst that occurs as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland duct.
Normally, the sebaceous glands in dogs and cats, located throughout most of the body, produce an oily secretion that lubricates and moisturizes the surface of the skin. The ducts of the sebaceous glands are located in the hair follicle, so it is believed that the development of sebaceous cysts is associated with obstruction of the follicle, which leads to the accumulation of secretions and the formation of atheroma. Follicle blockage can occur due to various reasons, such as improper hair growth, poor hygiene, or skin infections.