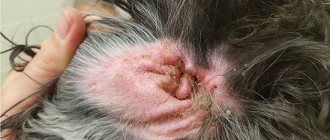
The appearance of itching, peeling of the skin and hair loss often indicate the appearance of atopic dermatitis. The dog becomes restless, often licks and bites the affected areas of the skin; if left untreated, the condition can seriously worsen.
Atopic dermatitis in dogs is a chronic disease that develops against the background of the pathological effects of allergens on the body. Factors in the development of atopy can be:
- taking various medications (if the veterinarian prescribed any course of treatment);
- the presence of such underlying diseases as giardiasis, hypothyroidism, dermatitis of various natures;
- features of the microclimate of the dog’s habitat (houseplants, household dust, allergic reactions to food);
- seasonality (temperature changes, change of home environment, for example, after moving).
Clinical symptoms
Clinical symptoms of dermatitis in dogs manifest themselves as follows:
- severe itching in various parts of the dog’s body;
- thickening of the skin (lichenification);
- hyperpigmentation;
- redness of the affected areas of the skin (erythema);
- baldness, the appearance of areas where hair becomes sparse (alopecia).
One of the clinical signs of atopy is frequent relapses of pododermatitis and otitis media. The dog has serious damage to the spaces between the toes and paws of the animal. In particularly difficult cases, lameness is observed, and with severe itching, the dog begins to behave extremely restlessly. The dog's skin peels, becomes covered with scales, and the hair becomes sparse and greasy. The animal begins to constantly itch and lick the areas of greatest damage - under the tail, between the toes, in the armpit, groin area.
Characteristic symptoms
Signs of pododermatitis most often appear on the front legs.
- severe redness of the skin;
- formation of pustules;
- formation of nodules.
Nodules, blisters, fistulas, bald spots and areas of skin with severe swelling are visually visible. Often the paws become itchy, which causes the dog to constantly lick them and further intensify the symptoms.
With a strong inflammatory process, lameness and enlargement of nearby lymph nodes may appear.
Causes of dermatitis development
The reasons why allergies develop in dogs can be:
- fungal spores;
- pollen, fluff;
- various plants;
- blocks (bites, insect excrement);
- household dust, particles of human epidermis.
Depending on the allergen, the manifestations of the disease may be seasonal, and the frequency of relapses will vary. Periods of relative calm are possible; in particularly severe cases, atopic dermatitis occurs all year round. Conjunctivitis may occur against the background of the disease, and in the absence of timely treatment, quite dangerous complications can develop.
Causes of pododermatitis in dogs
Pododermatitis (or pyoderma) is an inflammatory process on the paws of a pet. The pathology is considered difficult for medical diagnosis. In fact, it is not a separate disease, like a cold, but a sign of a number of diseases, like a high fever or a runny nose. In order to correctly prescribe treatment, the doctor must accurately determine which tissues are affected and by what exactly.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of pathology:
| Localization | Probable Cause |
| The wound is only in one place |
|
| Multiple lesions |
|
To understand how to avoid the disease or choose a treatment method if it appears, you need to get to know the causes in more detail. After all, the underlying disease needs to be eliminated, and only then its manifestations will disappear.
Did you know? If your dog's paws smell like chips, it doesn't mean he ate them. This is the smell of bacteria that settle on the skin of pets whose paws have not been washed for a long time.
Mechanical damage
Foreign bodies penetrate the skin of the paws when the pet runs around the area. The body tries to destroy such an object by attacking it. This is how the inflammatory process begins, followed by suppuration if the thorn is not removed immediately. The damaged finger swells, the pet tries to reduce the discomfort and begins to chew it.
It is quite possible that he will remove the object himself, but he may introduce an infection from the teeth into the wound. Don't wait for this to happen and just help him get rid of the problem. If the surface of the skin is burned, it is washed with water. And then they use anti-inflammatory antibacterial ointments - “Tetracycline” or “Ichthyol”.
Infections
Deep paw infections that are caused by bacteria or fungi are common in dogs. They get inside through the wound surface resulting from a cut with a sharp object.
This causes inflammation and is accompanied by:
- swelling;
- increased temperature;
- suppuration;
- lameness.
To avoid such a development of events, paws after a walk should be washed and inspected for damage. For washing, take a special paw washer. This is a glass with polymer bristles on the inner surface. Fill with water and detergent, put your paw in it and rotate the glass. The result is well-cleaned paws.
Did you know? The microflora of the human body is represented by 40 trillion different bacteria and microorganisms, while the body itself is formed by only 30 trillion cells.
If you notice a wound, it needs to be treated with an antiseptic. Choose Chlorhexidine, Mirastimin, Percutan or hydrogen peroxide - all of them are designed to disinfect the wound surface. Apply the product to a cotton pad and wipe the damaged area. Antibiotics are used to stop the inflammatory infectious process. Lubricate the paw with “Ichthyol ointment” or “Levomekol”. Do this at least 3 times a day until the signs of the problem disappear.
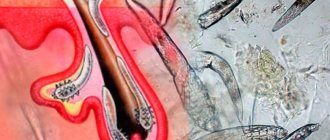
Parasites
The Demodex mite not only parasitizes the skin, but can also cause pododermatitis in dogs. It is believed that mites are constantly present on the skin in small quantities.
But when the immune system is weakened, they begin to actively multiply, which leads to:
- hair loss;
- swelling;
- constant itching;
- bleeding wounds.
Mites live in hair follicles. When one hair follicle is eaten, the parasite gnaws its way through the skin to the next, causing the dog a lot of unpleasant sensations. The tunnels made by mites become colonized with bacteria and inflammation develops. Treatment for Demodex Canis involves several medications and is prescribed by a veterinarian.
The list includes:
- anti-tick drug - “Ivermectin” 1% at a dosage of 0.1 ml per 5 kg of animal weight once, intramuscularly;
- antiseptic for treating the wound surface - “Ichthyol ointment” is applied to the skin every 8 hours;
- immunomodulator - “Immunofan”, “Hemobalance” or “Fosprenil”;
- to reduce the load on the kidneys - “Hepatovet”, “Karsil”.
An antibiotic may also be prescribed if there is a bacterial infection.
Important! Ivermectin is contraindicated in representatives of the Sheltie, Collie, and Bobtail breeds due to breed intolerance. It is also not prescribed to puppies under 6 months and pregnant or lactating bitches.
Allergy
Allergic pathologies very often lead to inflammation of the skin of the legs. The most common causes of allergic pododermatitis in dogs are food and environmental allergens - pollen, dust mites. But such allergies begin between the ages of 6 months and 3 years. Therefore, if your dog is older, then most likely the cause of pododermatitis on its paws is definitely not allergic.
Diagnostic methods
When the first symptoms appear, you should contact your veterinarian for diagnosis. The difficulty in this case lies in the similarity of the clinical picture with other diseases, so it is very important to answer all the doctor’s questions about the dog’s behavior as completely as possible.
During the initial examination, the doctor takes into account the pet’s age, its condition, signs of atopy, seasonality of the lesion and the frequency of relapses. In addition, it is necessary to answer questions regarding the dog’s nutrition, its living conditions, and the presence of pathologies in the animal’s closest relatives.
During the examination, differentiated diagnostics will be carried out in order to identify or exclude the following diseases:
- allergic reactions to factory-made food (irritation rarely occurs with natural products);
- allergic reactions to insect bites, usually fleas;
- scabies;
- drug rash;
- contact dermatitis.
The next step is a clinical examination, ordering a series of laboratory tests that will help identify concomitant infections and diseases. To achieve this, the following measures can be prescribed:
- scraping the surface layer of skin;
- blood, urine, stool tests;
- biochemical analysis of blood serum;
- bacterial sowing;
- endocrinological studies.
The veterinarian immediately prescribes a strict diet with the exclusion of many foods, lasting 6-12 weeks. The dog owner should monitor the diet, as this will reveal whether a food allergy is the cause of the disease.
Treatment
Each type of interdigital dermatitis requires a different approach to treatment.
- With traumatic dermatitis, the main task is to accelerate the healing process of damaged skin. To do this, use zinc ointment, Chemi spray, Kubatol spray or Baldecchi wound-healing zinc powder. Sore paws of the animal should be protected from water.
- If the cause of the disease is stress, the signs of dermatitis, as a rule, disappear on their own after the dog is treated with sedatives Vet Expert Calm Vet, Antistress Bifar, NoviPet, Sanal.
- Pododermatitis caused by subcutaneous mites is treated with antiparasitic agents. In veterinary medicine, Ivermectin or Ivermec is used. These drugs are toxic, so they are not prescribed to pregnant and lactating bitches, and in the case of external use of these drugs, measures must be taken to prevent the dog from licking the medicine from the paw.
- The allergic form of the disease is more difficult to treat than others. Here it is important to completely eliminate the possibility of contact of the animal with the allergen. And if it is a food product, the dog has to be put on a hypoallergenic diet for 2-3 months. Chlorhexidine, Kubatol or tar shampoo are used as symptomatic treatment.
- Bacterial dermatitis (
pyoderma) develops when there is damage as a result of a secondary infection. Its treatment requires long-term use of antibiotics, sometimes several at the same time. Veterinarians usually prescribe drugs with the active ingredient enrofloxacin: Baytril, Enroxil; Enroflon, Enroflox. For better healing and relief of itching, agents are prescribed that have a drying, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect: Baldecchi zinc powder, Canina wound healing balm or alum solution.
Attention! During treatment, conditions should be ensured for unhindered healing of the affected skin. Its surface must always be clean and dry. It is also important to exclude the possibility of the dog licking its sore paws. For this purpose, it is recommended to use a special protective collar.
Treatment, dynamics and prognosis
Atopic allergies take a long time to treat; they require complex therapy measures and lifelong monitoring by a veterinarian. At the very beginning of treatment, it is very important to isolate the allergen and exclude contact with it; sometimes a change of environment is required, including replacing dishes, a muzzle, and a collar. In some cases, you will have to completely replace animal care products, leashes, install an air purifier in the room and carry out a complete anti-parasitic treatment.
Therapy lasts 3-6 months, it includes measures to increase immunity, hyposensitization, which in 60-70% completely eliminates itching and alleviates the general condition. During treatment, the animal is injected subcutaneously or intramuscularly with a suspension of prednisolone. To exclude relapses, antifungal, antibacterial treatment and a course of antibiotics should be carried out simultaneously with the main therapy for 2-6 weeks. Among the main drugs prescribed by a veterinarian are Cefaclor, Amoxiclav, Gentamicin, Cefuroxime and others. The dose is calculated by the veterinarian based on the diagnostic results; usually injections are administered 2-3 times a day.
Antifungal treatment of atopic dermatitis in dogs involves taking systemic medications, including Nizoral, Flucostat, Orungal. They can only be taken as prescribed by a veterinarian, no more than 1-2 times a day. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, as it can cause worsening.
Local treatment includes antifungal and antibacterial agents:
- ear drops (Candibiotic, Aurizon);
- creams and ointments for affected areas (Nistaform, Triderm, Pimafukort);
- moisturizing, cleansing shampoos (for example, Sulfoden).
If the disease occurs against the background of pyoderma, allergies, or parasitic lesions, measures should be taken in a timely manner to completely eliminate them. Additionally, multivitamin supplements are prescribed to restore coat and skin. The course of treatment is at least ten days.
During treatment and after its completion, it is necessary to visit the veterinarian every two weeks . The doctor will evaluate the pet’s condition and the dynamics of therapy, the effectiveness of the measures taken, and the advisability of continuing or stopping treatment. After normalization of the condition, you can visit the doctor less often - once every three to six months, and get tested regularly.
Prevention and treatment of dermatitis.
Preventive and therapeutic measures for dermatitis depend on the type and causes of the disease. Therefore, it is necessary to consider each type separately.
Traumatic dermatitis. In urban living conditions, it is quite difficult to protect a dog’s paws from mechanical damage. During street walks, you constantly come across broken bottle glass, dangerous construction debris and other objects. When you receive injuries, it is important not to “start” the process, to carry out timely and competent treatment of wounds, to control their healing, preventing inflammation from becoming chronic. You need to know that the wound surface must be dry and well ventilated. To do this, when walking the dog, it is necessary to protect the damaged paw from moisture. Special boots will cope with this function perfectly. At home, shoes must be removed, since the wound must be in contact with air. It is also prohibited for the dog to lick the wound.
Contact dermatitis. Dog owners often encounter this type of disease in winter, when the road is generously treated with de-icing chemicals. While walking, the dog may squeal and tuck its paws. Here it is important to completely eliminate contact of the animal’s skin with the chemical irritant. The best way is to use special boots for dogs.
Allergic dermatitis. This is the most difficult type of dermatitis to diagnose and treat. In such a situation, if there is an allergy, the damage is always systemic in nature, that is, not only the paws are affected. Primary foci of the inflammatory process are found on the skin of the ears, the area around the eyes and mouth, and at the base of the tail. They can also be generalized, when almost the entire surface of the skin is affected. If you suspect a food allergy, you should definitely start a hypoallergenic diet. Feeds based on hydrolyzed protein are best suited here. The duration of diet therapy should not be less than 8-10 weeks. With a properly selected diet, during this long period of time, the allergen that causes inflammation stops entering the body, and regenerative processes begin. An improvement in the pet's condition is noted visually - the itching disappears, bald areas on the skin begin to grow back with hair. If this happens, then the diagnosis of food allergy is confirmed. If any positive dynamics are absent, we can talk about atopy - non-food allergies. Here, the allergen for the animal’s body can be any environmental factor, for example, pollen, house dust, poplar fluff, etc. It is not always possible to accurately identify the allergen, so first of all, the veterinarian prescribes treatment that helps eliminate secondary fungal or bacterial complications of allergies. Immunocorrective therapy (Forvet) can provide good help.
Bacterial dermatitis. This is usually a secondary infection, which occurs when there is damage to the paw pads and interdigital folds, as well as if vitamin and mineral metabolism in the body is disrupted or there are hormonal changes.
Staphylococcal dermatitis in dogs (pyoderma) is one of the most common diseases affecting the paws of dogs. The main causative agents of staphyloccal infection are St. aureus, St. albicans, St. Intermedium. These parasites can also be found on the skin of healthy animals. However, if immunity is at a normal level and the protective covering is in good condition, then pathological processes will not develop. If hormonal dysfunction or metabolic disorders are noted among the causes of the disease, then after eliminating this cause and with simultaneous antibacterial treatment of the secondary flora, recovery occurs quickly. Periodically, the infection can be generalized, that is, combined with otitis, scratching, conjunctivitis, hair loss, inflammation of the genital organs and inflammatory processes occurring in the paraanal glands. Here the main reason is immunodeficiency.
Complications of dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis in a dog may not have specific primary lesions; most often, only itching is observed in the ears, paws, axillary area, groin, under the tail. The erythema is usually diffuse, but it can be complicated by self-injury when the dog vigorously scratches the affected area. In addition, other complications of the disease may occur, including the following:
- Hyperpigmentation in areas of skin irritation or inflammation. Most often observed against the background of staphylococcal lesions.
- Lichenification in the form of thickening of the skin with the appearance of folds. Develops against the background of severe skin irritation, worsens with strong licking of the affected area. Most often observed in the armpits, under the tail, on the folds of the body, but it is not uncommon to form near the lips, on the concave part of the auricle.
- Seborrhea can be generalized or localized, affecting the ventral part of the animal's neck, armpits, and spaces between the toes.
- Increased peeling may be a consequence of dyskeratosis or renewal of the epidermal layer after treatment.
- Alopecia is expressed in the form of complete loss of hair or the formation of areas of thinning. Typically focal areas occur due to scratching, licking, or touching the skin.
- Secondary infection manifests itself in the form of erythematous papules, which turn into pustules with the development of the lesion. In some cases, the lesion develops into a ring-shaped lesion, accompanied by the formation of crusts and epidermal collars. Hair falls out in such areas, which is especially noticeable in short-haired breeds.
- Secondary Malassezia infection manifests itself as increased itching in the neck, ears, and between the animal's toes. The lesions have an unpleasant odor, are greasy to the touch, and are accompanied by alopecia, erythema, and lichenification.
- Secondary otitis is observed in 80% of cases when allergies are diagnosed in dogs. In the absence of treatment, the situation worsens, accompanied by excessive secretion of glandular secretions and the further development of an infectious lesion.
In addition, complications such as cysts, furunculosis, and papules between the toes may develop. All this has an extremely negative impact on the condition of tissues, skin, and wool. Animals begin to actively lick and bite the affected areas of the skin, and this leads to bleeding and excoriation.
Atopic dermatitis in animals does not pose a threat to the life of the animal, but the disease should be treated. Otherwise, serious complications may develop, numerous relapses, and the dog will have to be euthanized. In rare cases, spontaneous recovery is observed without the use of medications, but it is better not to hope for this and promptly contact a veterinarian at the first symptoms.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of interdigital dermatitis, it is recommended to provide the dog with high-quality, nutritious feeding, ensure a comfortable mental state and constant moderate physical activity. After each walk, be sure to thoroughly wash and wipe your paws dry, and if even minor damage to the skin is detected, treat the wounds with an antiseptic. The owner must ensure that the animal does not have access to aggressive chemicals used at home.
To prevent infectious and parasitic diseases that can cause dermatitis, the best means are regular vaccination and treatment with insecticidal and anthelmintic drugs.
source