Reasons for the development of nephritis
Veterinary practice shows that the most common causes of kidney inflammation in dogs are the following:
- Past infectious diseases . Pathogenic microorganisms that cause infections such as leptospirosis, canine distemper, viral hepatitis and enteritis, as a rule, lead to the development of nephritis. Pathogenic bacteria and viruses enter the kidneys through the bloodstream or lymphogenous route. In this case, the disease is considered as a complication after an infection.
- Hypothermia. A long walk in bad weather, walking decorative dog breeds in unfavorable weather conditions without protective clothing, bathing a pet in open bodies of cold water, keeping a pet in damp, unheated rooms are the main causes of the development of inflammatory processes in the kidneys. A weakened immune system makes the situation worse.
- Helminthiases. Helminthic infestations lead to intoxication of the body with waste products of parasites, which is accompanied by dysfunction of the excretory system and the development of inflammation in the kidneys.
- Intoxication . Poisoning of four-legged friends with poisonous plants, toxic fumes, household pesticides, pesticides, and solvents is a common cause of the development of renal pathology. Toxic substances are mainly excreted through the kidneys, damaging their cellular structure and disrupting the normal processes of formation and excretion of urine.
- Insect bites . Biological poisons and toxins from bites of midges, bees, and ticks have a pronounced nephrotoxic effect. By affecting the kidneys at the cellular level, toxins lead to the development of diffuse inflammation.
- Injuries . As a result of mechanical damage or compression of organs, an inflammatory reaction occurs in the renal tissues.
- Use of medications. Arsenic-containing medications, creolin and other medications can harm the body's excretory function.
Veterinarians also note cases of nephritis in dogs that have been eating spoiled food for a long time. The risk group includes stray animals and dogs of decorative breeds with poorly developed undercoat.
We recommend reading about how to boost your dog’s immunity. You will learn about the causes of low immunity in dogs, signs of this condition, recommendations, vitamins and folk remedies to improve the condition of your pet. Find out more about treating colds in dogs here.
Effective Ways to Treat Kidney Disease in Dogs
To understand a dangerous urinary tract disease, you need to know that a dog's kidneys are in continuous operation, cleaning and filtering the blood of toxins.
If kidney function is impaired, the amount of toxins in the blood increases and the risk of poisoning the dog’s body increases.
Kidney and urinary tract diseases in dogs are quite common, regardless of age and breed, so it is important to understand the causes and symptoms of this dangerous disease. Knowledge will help you not to start a problem, but to promptly contact a veterinary clinic to help your pet.
Causes of the disease
Nephritis is an inflammation of the kidney tissue, pyelitis is a purulent inflammation of the kidney structures. Often these processes occur together, which is why the infectious disease is called pyelonephritis.
It is caused by bacteria entering directly into the dog's kidney. In addition, any viral or fungal infections suffered by animals negatively affect the condition of the renal system.
If the dog's immunity is good and the number of bacteria is small, the animal's body has enough strength to prevent the growth of bacteria.
The situation changes radically when there are risk factors that create a favorable environment for the rapid proliferation of bacteria. These include:
- hypothermia;
- poisoning;
- oncology;
- diabetes;
- inflammation of the bladder, prostate gland, uterus;
- injuries in close proximity to the kidneys;
- kidney pathologies;
- low level of immunity;
- overwork, stress.
Which breeds are most susceptible to the disease?
Today, a large number of dog breeds are known, differing from each other in individual characteristics. But, nevertheless, among this diversity, it is possible to systematize the commitment of certain breeds to kidney pathologies:
- Miniature Schnauzer, Bichon Frize, Shih Tzu, Miniature Poodle, Lhasa Apso - more than 80% of females are between the ages of one and 8 years.
- Miniature Schnauzer, Lhasa Apso, Cairn Terrier, Yorkshire Terrier, Cocker Spaniel, Bichon Frize, Shih Tzu, Miniature Poodle - more than 70% of males are between the ages of six and 12 years.
- Dalmatian, English bulldog - on average, 85% of males are under the age of one year and upon reaching the age of three to four years.
- German Shepherd, Bobtail - more than 90% of males are between the ages of four and nine years.
Main symptoms
Careful observation of a dog’s behavior is the key to timely recognition of an insidious disease. This will eliminate wastage of time and allow the veterinarian to start treatment on time.
The main symptoms of pyelonephritis are:
- the animal becomes lethargic, arches its back;
- refuses food, thirst increases;
- frequent urination and pain during it;
- there is blood in your pet's urine;
- The dog's gait changes and becomes swaying.
At an advanced stage of the disease, the animal constantly lies on its side, vomiting practically does not stop, and the dog becomes painfully lethargic.
Diagnostics in a veterinary clinic
As soon as the first suspicion of kidney pathology is detected, you must contact a veterinary clinic. Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease caused by various infections, so only tests will help the doctor prescribe medications targeted at the identified infectious group.
Treatment is prescribed based on the results of diagnostic measures:
- Analysis of urine;
- detailed blood test;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Treatment method and prognosis
The treatment regimen usually contains antibacterial and diuretic medications. If the animal is suffering from pain, the veterinarian will prescribe painkillers.
In addition to taking medications these days, it is necessary to switch your pet to a dietary diet. The food menu should be discussed with your veterinarian.
We should not forget about immunostimulants - they will help increase the body's resistance to infectious pathogens.
During treatment of pyelonephritis, the dog should be under medical supervision. Until your pet fully recovers, you must undergo a urine test weekly.
You cannot use medications without a veterinarian’s prescription - this can cause harm to your pet’s weakened body.
Recovery occurs within two to three months, provided that treatment is started in a timely manner and the animal has no pathologies.
What to do at home
It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate due to the high risk of death of the animal.
The therapy is prescribed by a doctor, and the owner must organize care for the pet.
If there are difficulties in eating food in the first days of illness, then you need to rub it through a sieve and feed it to the dog.
For the diet, you can use lean meats (chicken), supplemented with vegetables.
Carbohydrates should be excluded for a while (potatoes, pasta and baked goods).
Provide the dog with a comfortable bedding, avoid hypothermia and drafts.
It is recommended to show your recovered pet to a doctor at least once a month. This is necessary to ensure that infectious agents have disappeared from the dog’s body.
Further, a preventive examination of an animal that has suffered a severe inflammatory disease should be performed at least once every six months.
Possible complications
Pyelonephritis in dogs is a disease whose symptoms will progress until they lead to disability or death of the animal. To save a dog, treatment is carried out only in a specialized clinic.
Timely treatment will help stop the disease.
In an advanced state, the disease progresses, initiating serious irreversible destruction of the renal system and the occurrence of abscesses, the removal of which is only possible through surgery. In other words, a pet’s direct path to disability.
Prevention measures (diet)
The main preventive measures include:
- avoiding hypothermia of the animal;
- placing the dog in a warm and dry place;
- if signs of a disease of the genitourinary system are identified, treat them promptly;
- annual medical examination of the pet, especially when it reaches the age of eight years;
- free access to clean water;
- absence of stressful situations.
Veterinarians attribute 70% of success to the selection of proper balanced nutrition: the dog’s menu should include food that is balanced in terms of nutrients, vitamins and minerals.
Feed manufacturers produce medicinal brands. To choose a suitable line of food for your pet, it is better to consult a competent doctor.
If for any reason the use of ready-made food is not suitable, then you can take into account the following recommendations for the use of products in the diet of dogs:
- Small quantities of meat such as rabbit, chicken, beef.
- You can use high-quality offal in your diet (good liver, heart and kidneys).
- Cereals should be limited due to their high carbohydrate content.
- It is important to obtain fats: directly pressed vegetable oil (vitamin E), chicken or rabbit fat.
- Vegetables put through a blender with the addition of chicken or rabbit broth.
Your veterinarian will tell you more about organizing proper nutrition and adding vitamins to your dog’s diet.
Authors of the articles: Belanta Clinic team
Source: https://www.belanta.vet/vet-blog/pielonefrit-u-sobak/
The renal pelvis is dilated in the fetus: possible causes and health consequences
An ultrasound examination, which every pregnant woman should undergo, is not only a way to “get to know” her baby, but also a method for diagnosing most intrauterine pathologies and congenital anomalies. According to statistics, one of the common problems at this stage of development is pyeloectasia - expansion of the renal pelvis. It is detected in approximately 2% of all pregnancies. What may be associated with renal pyeloectasia in the fetus, is this condition dangerous, and does it require treatment: let’s try to figure it out.
Symptoms of pathology in dogs
The action of one or another negative factor leads to spasm of blood vessels in the kidneys and the development of ischemia. Increased production of the hormone renin leads to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, impairing their permeability.
The pathological process as a whole leads to general hypertension, azotemic uremia, chronic renal failure. Products of protein metabolism - urea, creatinine - accumulate in the body, which is accompanied by intoxication. All this is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Increase in body temperature by 1 - 1.5 degrees. The dog has a hot and dry nose and increased thirst.
- The general condition is depressed. A sick animal is lethargic, apathetic, avoids active physical activity, and is reluctant to go for a walk.
- Appetite is reduced or completely absent.
- Change in posture - the dog arches its back unnaturally and takes a forced position.
- Pain syndrome. When palpated in the lumbar region, the dog shows anxiety and even aggression. Often a sick animal tries to bite the owner when stroking the back.
- Violation of the act of urination. The chronic form of the disease is often accompanied by polyuria. In acute nephritis, on the contrary, urine production decreases, anuria or oliguria is observed. When urinating due to pain, the dog takes unnatural positions, whines, and worries. The inflammatory process is accompanied by frequent urination. The urine is cloudy.
In severe cases, brown urine is observed due to the presence of blood in it due to damage to blood vessels and the release of red blood cells. The content of pus in the urine is due to the action of pathogenic microflora in the kidney tissues.
- The color of visible mucous membranes changes from a healthy pink to pale or bluish.
- Swelling in the abdomen, thighs, submandibular and groin areas is caused by the retention of salt and water in the tissues due to increased production of antidiuretic hormone.
- General intoxication of the body is accompanied by vomiting, an unpleasant uremic odor from the pet, constriction of the pupils, convulsions, and in severe cases, paralysis. Dyspepsia is one of the manifestations of intoxication of the body with protein breakdown products.
High levels of nitrogenous substances negatively affect the body's respiratory system, causing inflammation. In this regard, dogs with nephritis often show symptoms of bronchitis and bronchopneumonia.
Types of kidney diseases in dogs - features of diagnosis and treatment
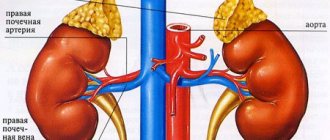
The kidneys perform an important function as filters, freeing the body from dangerous and unnecessary substances. 20% of the blood passes through the kidneys, so many toxins and infections begin to immediately affect this organ.
As a result, kidney disease in dogs is widespread. They are caused by infections, poisoning, improper feeding, mechanical and physical factors. The diseases are manifested by changes in urine, pain during urination.
The choice of treatment is based on the diagnostic results.
Diffuse inflammation of the kidneys in dogs is called glomerulonephritis. The development of the disease is associated with the appearance of immune complexes circulating in the vascular part of the kidneys and gradually deposited in the glomerular apparatus.
This provokes an inflammatory reaction, causing the tissues to become saturated with neutrophils, macrophages and other blood cells.
Various factors, acting individually or together, lead to the development of pathology:
- infectious agents;
- parasites;
- neoplasms;
- metabolic disorders (hyperadrenocorticism, diabetes mellitus);
- use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Primary damage to the renal glomeruli leads to tissue proliferation and sclerosis of the kidney. Glomerulonephritis is a common cause of kidney failure. Dogs also develop heart failure and high blood pressure. The disease can occur in dogs of any age, breed and gender.
Inflammatory kidney disease in dogs does not manifest itself clinically early on, and the disease is usually discovered incidentally through laboratory urine tests. The symptoms of the pathology are influenced by the intensity of protein excretion in the urine. In dogs, weakness and exhaustion are noted at the onset of inflammation. As the kidneys become damaged, signs of failure begin to appear:
- polyuria;
- thirst;
- subcutaneous swelling;
- abdominal dropsy;
- vomit;
- exhaustion;
- dyspnea;
- retinal hemorrhages and blindness.
When analyzing urine, an increased protein content is detected, which is also characteristic of urinary tract diseases, tumors and foreign bodies. But these diseases are also characterized by the presence of red blood cells in the urine sediment.
A characteristic sign of glomerulonephritis is proteinuria without urinary sediment.
But at a late stage, when most of the glomeruli are involved in the pathological process, the protein concentration may decrease.
The cause of proteinuria can be identified using urine or blood electrophoresis. Using X-rays and ultrasound, it is almost impossible to detect characteristic changes. Under ultrasound guidance, a kidney biopsy is performed, which is necessary to exclude amyloidosis.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis requires changes in the maintenance and feeding of the dog. It is necessary to limit physical activity and provide the pet with a warm, dry room. Feeds with a large amount of protein are used in the diet. On the first and second days it is recommended to prescribe a suitable diet. And then gradually include easily digestible food without table salt into the diet.
An important point in treatment is suppression of the immune response:
- prednisolone;
- cyclosporine;
- azathioprine.
The use of glucocorticoid drugs is contraindicated if nitrogen is detected in the urine. Treatment is carried out until the level of protein in the blood is restored and it disappears from the urine.
Antibiotics and cephalosporins are prescribed for focal infectious processes. Dogs are given ampicillin, oxacillin, azithromycin, kefzol, cefamezin. At the same time, sulfonamide drugs are used. If signs of blood appear in the urine, animals are given hemostatic drugs. Dogs are prescribed aminocaproic acid, vikasol, dicinone, calcium chloride, calcium gluconate.
Pyelonephritis
The disease is of infectious origin - most often the bacteria spread through the blood vessels, less often the spread occurs through the lymphogenous route.
Less commonly, pyelonephritis in dogs develops as a result of pathologies of other genitourinary organs.
Animals with increased pressure in the renal pelvis (difficulty in the outflow of urine), other impaired renal function, and also after hypothermia are predisposed to pathology.
Clinical picture of the acute form:
- fever;
- rapid pulse;
- breathing is shallow, frequent;
- no appetite;
- exhaustion.
The chronic form of pyelonephritis is characterized by periods of exacerbation, when signs appear, but they are not so pronounced. Changes in the functioning of the genitourinary system are typical. When palpating the lumbar region, a painful reaction is noted; dogs also experience pain during urination, urine is released in small portions, the pet often changes position, and may whine.
Urine contains various impurities - blood, pus, flakes. When studying urinary sediment, a large number of red blood cells, renal tubular epithelium, leukocytes, and bacteria are found in it. The density of urine is increased, the protein content is increased. To clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound and MRI diagnostics are performed.
For treatment, antibiotics should be used that are excreted by the kidneys without changes in the liver.
The sick animal is given rest, placed in a warm room, avoiding hypothermia. For the first 1-2 days of treatment, the dog is prescribed a starvation diet. Then the diet includes easily digestible foods, rich in protein and low in sugars and salt.
To suppress microflora, it is necessary to conduct a course of antimicrobial therapy. Drugs of choice:
- ampicillin;
- amoxicillin;
- tetracycline;
- trimethoprim;
- gentamicin.
Treatment with antibiotics and sulfonamides is continued for 1-2 weeks. Before starting the course, it is recommended to do a bacterial culture to test for sensitivity to antibacterial agents. If there is no positive effect, it is necessary to change therapy.
The complex of therapeutic measures must include diuretics. The dogs are given an infusion of saline and plasma replacers. Dicarb, Lasix, and Urolesan are used as diuretic drugs.
Non-inflammatory kidney pathologies
These diseases are characterized by dystrophic changes in tissues with predominant involvement of the tubules of the medulla. In severe and chronic cases, the pathology develops into sclerosis when the kidney parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue. Causes of pathology:
- primary kidney diseases in dogs;
- poisoning with arsenic, lead, zinc;
- use of ivermectin, sulfonamides, hormonal drugs;
- systemic pathologies;
- kidney stones in dogs;
- metabolic disease.
Sick dogs show exhaustion, decreased interest in food, and lethargy. Digestive system disorders are often observed.
As the pathology progresses, symptoms of renal failure begin to appear - swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, especially in the eyelids and dewlap, superficial pulse, weak filling.
Often there is an increase in nervous excitability, accompanied by convulsions.
The initial stage is characterized by a decrease in urination, the urine becomes dense. But as the pathology progresses, the density of urine decreases (to 1.001 g/l), diuresis increases, and the properties of urine change.
Signs of nephrosclerosis:
- vomit;
- eczema on the skin, itching;
- mucous membranes become anemic with an earthy tint;
- swelling of the limbs;
- dyspnea;
- weakening of cardiac activity.
A characteristic symptom is a strong decrease in the density of urine with frequent urination. When examining urine, protein, epithelium, small amounts of blood cells, and casts are found in it. Ultrasound and kidney biopsy are used for diagnosis.
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the underlying pathology and compensating kidney functions. Therapy depends on the etiological factor. So, in case of poisoning, antitoxic therapy is carried out - specific antidotes, adsorbents, diuretics are used, and physiological solutions are infused.
To suppress the infection it is necessary:
- antibiotics (tetracycline, amoxicillin);
- sulfonamides (sulfatrimethoprim, sulfadimezine);
- immunostimulants (interferon, mixoferon).
Perinephric blockade has good effectiveness. Novocaine is injected into the fatty tissue surrounding the kidneys in the lumbar region. It is recommended to use antibiotics together with novocaine.
Nephrosclerosis is often accompanied by disorders of the digestive system. Therefore, it is recommended to use laxatives and adsorbents to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract. A gentle diet is prescribed, and on the first day of treatment it is recommended not to feed the dog at all. Then enzymatic preparations and antiseptics are used.
Aplasia
Kidney aplasia is a congenital anomaly in which the organ is an underdeveloped rudiment lacking normal renal structure.
With unilateral aplasia, the function of the atrophied organ is taken over by the second kidney. Due to long-term compensatory work, it hypertrophies (increases in size). The disease does not manifest itself symptomatically. It can be discovered randomly during an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Bilateral aplasia is an anomaly that is not compatible with life. The kitten dies in utero or in the first two to three days after birth due to renal failure.
Classification
In veterinary medicine, it is customary to divide nephritis in animals according to the nature of the process into acute, subacute, chronic and subchronic. The chronic form of the disease is a complication of acute nephritis. In the chronic course of the disease, hyperthermia is galloping in nature, and the symptoms of intoxication are weakly expressed. The acute form of the disease is accompanied by a feverish state, pronounced intoxication, and the rapid development of uremia.
Based on the form of the pathological process, veterinary specialists distinguish between diffuse and focal nephritis. In the first case, the inflammatory process affects all kidney tissues - the pelvis, parenchymal tissues and the vascular network of the glomeruli.
In the case of focal pathology, inflammation is localized in individual glomeruli. This form of the disease passes without hypertensive phenomena and edema. The blood flow in focal nephritis is not disturbed, and the symptoms of intoxication in the animal are not observed in this regard.
Special cases of the disease
The consequences of kidney disease during pregnancy should be considered, since this topic is especially exciting for expectant mothers. Moreover, they cause discomfort, which creates an additional reason for stress for a woman. There are two types of occurrence of this disease:
| Before pregnancy | During pregnancy |
| In this case, doctors order a full examination and leave the woman under constant medical supervision, since the stage of the disease could have moved forward long ago, and the consequences could be irreversible for both the pregnant woman and the unborn baby. In extreme cases, a decision may be made to terminate the pregnancy. | Here, special importance is attached to the presence of infections in the body, which can be treated. The pregnant woman is prescribed complete rest and the necessary medications are prescribed, which indicates the possibility of conservative treatment. The main thing is to prevent the disease from becoming acute, otherwise the outcome will not be happy at all. |
During such a period, the expectant mother simply needs the care of loved ones. Especially considering the fact that physiological and mental health are closely interconnected. Timely visit to the hospital can prevent the worst consequences, so never delay going to the doctor. Firstly, his consultation will help you monitor your health, and secondly, you will protect not only yourself, but also your loved ones, in particular, children.
Treatment
After a complete examination and diagnosis, the animal is prescribed a course of therapy. Its duration and methods will depend on the form of the disease and the degree of complexity. The animal must be provided with the correct and comfortable living conditions; the room must be clean and well ventilated.
If nephrosis was caused by poisoning, it is necessary to completely neutralize them. To do this, the stomach is washed and enemas are given to the animal. The diet uses milk and egg whites. If the cat's owner knows what could have poisoned her, an antidote is used. A course of broad-spectrum antibiotics is prescribed if pathology occurs due to infection.
To resume and normalize the body's metabolic processes, hormonal medications are used for nephrosis in cats. To relieve swelling, agents with a diuretic effect are used.
Diagnostic methods
Having discovered symptoms of nephritis in a four-legged friend, the owner should immediately contact a specialized institution. A veterinarian, in addition to a general examination of the animal, palpation of the kidney area, tonometry, will prescribe a clinical blood and urine test.
Red and white blood cells, renal epithelium and salts are found in urine. Proteinuria and hematuria are characteristic conditions for kidney inflammation. A clinical blood test usually shows an increased level of protein, leukocytes and creatinine.
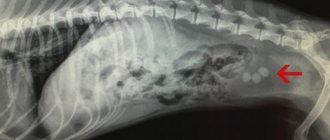
An effective tool in making a diagnosis is ultrasound examination. The method allows you to identify the localization of inflammation, estimate the size of the diseased organ, and detect destructive changes in the parenchyma.
Ultrasound
Contrast x-rays and a kidney biopsy can help make the diagnosis. The disease should be differentiated from nephrosis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, and inflammation of the bladder.
Symptoms of the disease
Impaired kidney function leads to a high degree of swelling, as well as general intoxication of the body. This means that the work of this organ is extremely important for the normal functioning of the entire body. That is why, if you discover such symptoms as a special, sourish, sharp unpleasant odor of urine, excessive or insufficient urination, a change in the frequency of urination, an abnormal color of the excreted fluid (sometimes mixed with blood), you should immediately contact a specialist.
The presence of kidney stones is characterized by an abundance of blood in the urine. In this case, urine may come out in drops, after which blood is noticeable on the dog’s genitals. Also a sign of urolithiasis are increased thirst, a sharp drop in appetite, fever, fever, weight loss, unpleasant odor from the animal’s mouth, vomiting and diarrhea. At the same time, the pet’s gait also changes – it becomes a little stiff, the dog lowers its croup. In addition, when suffering from kidney stones, the dog behaves extremely restlessly, often whining during bowel movements.
If you put the symptoms of kidney disease together, the most common signs are:
- severe pain in the lumbar area;
- uncontrolled urination;
- inability of a male dog to assume a normal posture when urinating.
Norms for ultrasound of fetal kidneys
Normally, a longitudinal ultrasound scan reveals the fetal kidneys as a bean-shaped or oval formation located in the lumbar region. On a transverse scan they have a round shape and are identified as paired formations on both sides of the spine.
One of the structural units of the kidney is the calyces, which, merging with each other, form one common cavity - the renal pelvis. Gradually narrowing, the pelvis continues into the ureter. The ureter drains into the bladder.
Using an ultrasound machine, the doctor can visualize the pyelocaliceal system starting from the 14th week of intrauterine development. Normally, the diameter of the renal pelvis should not exceed:
- in the second trimester – 4-5 mm;
- in the third trimester – 7 mm.
Examination of the internal structure of the organ becomes possible after 20–24 weeks of pregnancy. During this period, it is already possible to diagnose some developmental anomalies:
- agenesis (absence of one or both kidneys);
- atypical location of the organ (dystopia);
- increase in size;
- expansion of the calyces and (or) renal pelvis;
- cystic changes in the kidneys.
The fetal ureters are not normally visualized.
Treatment of acute and chronic forms
Therapy for infectious kidney inflammation necessarily includes the use of antibacterial drugs. The best option would be to prescribe antibiotics after a microflora sensitivity test. In veterinary practice, in the treatment of acute forms of nephritis, penicillin antibiotics, cephalosporins, and tetracyclines are used.
Among penicillins, Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Ampiox have a good effect against renal infection. Of the cephalosporins, veterinarians use Cephalosporin, Cephalexin, Cobactam, Cefazolin for acute nephritis.
The drugs are active against streptococci and staphylococci, the most common causes of nephritis in dogs. Tetracycline drugs, such as Doxycycline, have a bactericidal effect on most pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation in the kidneys.
Antibiotics for the treatment of nephritis in dogs
Sulfonamides and nitrofurans have a good therapeutic effect for nephritis in dogs: Sulfalene, Sulfadimethoxine, Norsulfazole, Furadonin. If the level of urea in the blood is more than 25 mmol/l, treatment is carried out only with nitrofurans that have a small molecular weight: Furazolidone, Furagin. The course of treatment with antibacterial drugs is at least 10 - 14 days.
In the acute form, it is important to immediately detoxify the body. For this purpose, the animal is prescribed intravenous infusions of glucose solution, calcium chloride, saline solution, and rheopolyglucin.
Treatment of acute and chronic forms of the disease involves the use of diuretics: Potassium acetate, Furasemide, Clopamide, Ammonium chloride. As diuretic drugs, on the recommendation of a doctor, a sick dog can be prescribed herbal preparations in the form of bearberry decoction. The animal is also prescribed sedatives and, if necessary, painkillers, for example, Baralgin, Spazgan, No-shpa.
For high blood pressure, dogs are given reserpine. In case of symptoms of heart failure, drugs such as digitalis, Cardiamin, and Caffeine are used.
The success of treating kidney inflammation depends not only on the use of medications. It is of no small importance to follow a 24-hour fasting diet followed by transferring the animal to a low-protein diet. Until complete recovery, the dog is fed cereals and vegetables, low-fat fermented milk products. It is recommended to give meat in the diet in the form of broths. Salt is strictly prohibited.
For information on the causes, symptoms and treatment of nephritis in dogs, watch this video:
How to treat kidney disease?
Treatment depends on the severity of the disease and symptoms, its causes, and whether the disease is acute or chronic.
Chronic kidney disease is usually irreversible, but it can be managed to reduce symptoms and slow progression to kidney failure or kidney failure. If the root cause of the disease is known, then the prognosis of treatment depends on it. For example, in the case of a bacterial infection, antibiotic therapy should be administered. Limiting foods and feeds containing phosphorus and omega-3 fatty acid supplements (such as fish oil) are beneficial for dogs suffering from chronic kidney disease. Specially formulated foods are also available for these dogs. ACE-inhibiting drugs help improve blood flow to the kidneys and prevent high blood pressure.
Dogs with acute renal failure can sometimes be managed with symptomatic treatment. In some cases, recovery of kidney function is possible, but both short- and long-term outcomes depend on the cause and severity of the kidney damage. Treatment usually consists of intravenous fluid therapy over several days or weeks. Dogs with acute renal failure require careful monitoring of acid-base balance, changes in which can be life-threatening. Vomiting and loss of appetite should be controlled. Your veterinarian may need to do regular blood tests to determine how your dog is responding to treatment, but your pet's behavior and appetite are also good indicators. With the appearance of appetite and good health, the intensity of treatment may decrease, but, in any case, long-term and regular monitoring of the dog is required.