How inflammation occurs
Inside the dog's eyelid there are a large number of glands that produce mucus to protect the eye. Inflammation of their ducts causes suppuration .
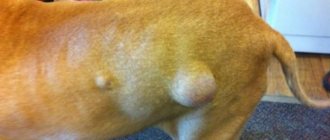
Sebaceous gland blockage
Fluid secreted by the gland may accumulate around it. This occurs due to improper care of the animal or an inflammatory process. The gland becomes filled with purulent masses, becomes inflamed, and breaks out.
Inflammation
Bacteria enter the exudate and cause inflammation. It spreads to the tissues of the eyelid and everything around the eye space. A large inflamed area of mucous membrane appears around the lump.
Types of growths and neoplasms
The growths can affect any layer of eyelid tissue. Statistically, the most common neoplasms on the eyelids in dogs are:
- Adenomas are benign tumors.
- Papillomas are benign growths that can become malignant.
- Adenocarcinomas are rare but are the most common malignant tumor affecting the eyelids.
As you age, the risk of developing:
- Meibomian gland adenocarcinomas.
- Melanomas.
All of the above types of growths are malignant and require timely diagnosis. If cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, the affected cells are removed surgically and healing is monitored.
Less commonly, growths appear on the eyelids of dogs, which are:
- Histiocytomas are benign tumors of the skin.
- Mastocytomas are a benign tumor of the skin and/or subcutaneous tissue.
Meibomian gland adenocarcinoma and adenocarcinoma
They are modified cells of the meibomian glands (lining the upper and lower eyelids). The meibomian glands secrete an oily lubricant that helps and protects the tear glands and the eye itself.
Growths can appear on both the outer and inner sides of the eyelid. In the second case, the neoplasms are visible - they protrude or protrude from the eyelid. These growths have a rich pink color and a lobed structure. If the situation is ignored, the tumors begin to bleed and/or self-opening.
Melanoma
There are two types of eyelid melanoma in dogs. The first type occurs due to degeneration of the skin cells of the eyelids. The growth is a solid, protruding, smooth, pigmented layer of tissue that can be easily removed surgically.
The second type of melanoma occurs when the cells of the pigmented edge of the eyelid degenerate. The growth is noticeable even at an early stage; it is flat, wide, and grows quickly. This type of melanoma is more dangerous because the tumor quickly takes root and may require removal of a large area of the eyelid to completely excise it.
Papilloma
The growth is of viral origin! Papillomas vary in color (from white to pink and red) and have an uneven surface.
Note! Papillomas are more common in young dogs.
Types of barley
Depending on the location, there are 2 types of barley - external and internal. Treatment is prescribed depending on the variety.
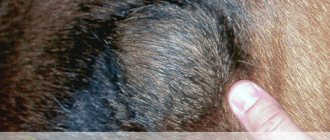
Outer
The inflammatory process occurs as a result of a blockage of the sebaceous gland or an abscess in the hair follicle. At the initial stage, the mucous membrane of the eye becomes red, and later an abscess appears.
Interior
Barley occurs when the fatty gland on the inside of the eyelid becomes inflamed. This process is not visible from the outside. If you pull back the eyelid from above or below, you will find a small bump filled with pus underneath.
Mixed
This pathological phenomenon is rare. Inflammation from one area of the eye spreads to another.
This type of stye occurs in advanced cases, when the dog was not given help at the first signs of illness.
What is an abscess in dogs: causes of the disease
Pathological formations in the form of ulcers arise as a result of inflammatory processes in the body. The cause of inflammation with the development of an abscess is most often mechanical trauma to the dog, followed by the introduction of various infections into the open wound. Due to the struggle of the immune system with external agents, a place with dead tissue and ulcers is formed in the open area of tissue.
There are three types of abscess complexity depending on the location of the inflammation:
- Superficial ulcers are the easiest to treat. It is possible to use products for external application to wounds;
- A subcutaneous abscess in a dog is less treatable, but most often an experienced veterinarian will pull the animal out of its deplorable condition without consequences;
- Abscess of internal organs. Most dogs do not survive the disease on their internal organs; only surgical intervention can save them.
Page abscess in dogs is considered one of the most dangerous. The reason for the development of the disease is the impossibility of hygienic procedures (licking) by old dogs. Infection occurs with the first minor wound on the paraanal glands.
The most common cause of abscess in animals is injury from conflicts with other dogs. The infection is transmitted from the oral cavity to the wound in a few seconds. If the dog does not lick the wound in a timely manner, an abscess will occur with a 90% probability.
Factors that provoke inflammation
Styes occur on the upper or lower eyelid in dogs for several reasons. It is easier to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment if you determine what caused the pathology.
Diseases, fungi
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, its injury, or introduced fungus provoke the development of barley. The damaged mucous membrane does not have a protective barrier; bacteria easily colonize it, causing inflammation and the formation of pus in the wound.
Weak immunity
Viral and infectious diseases, injuries, surgeries, improper care, and unbalanced nutrition weaken the animal’s immunity. During this period, bacteria attack the animal’s body and cause inflammation.
Poisoning
The impact of toxic substances on the dog’s body and in particular on the organ of vision is destructive.
The chemicals corrode the skin of the eyelid, ulcerating it. Germs enter open wounds, spreading infection.
Improper care
An unbalanced diet weakens the pet’s immunity, and the body ceases to resist infections. Diseases occur more often than usual, and the animal has a hard time bearing them.
Violation of hygiene standards leads to eye diseases. They need to be washed regularly, properly care for the skin of the eyes, and remove secretions that accumulate, clogging the glands.
Injuries of the century
Violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane makes it vulnerable to microbes and bacteria. If the damaged area is not treated, pathological processes develop.
Stress
Fright, moving to a new place, change of owner cause stress in the dog.
This condition weakens the animal’s immunity, and the body is not 100% able to resist infections. Being in a stressful state for a long time, the dog begins to get sick.
Forms and types of abscesses in dogs
Symptoms of abscess development depend on the form of the inflammatory reaction. There are two types of disease in dogs:
- The hot form of an abscess is characterized by rapid development and severe manifestations of symptoms (pain, high temperature, abnormal bowel movements, refusal to walk);
- The cold form of the disease occurs with virtually no symptoms. The animal can live with the inflammation for a long time, but the abscess will gradually reduce the dog's health. The absence of symptoms only means that the body cannot resist the agents of infection.
In any case, the owner can feel the presence of an abscess in the dog to the touch, the site of inflammation should “burn”, this is due to increased blood supply to the wound. Pain does not always appear.
Do not allow your dog to develop a fever; the dog may not survive several hours in this state. The veterinarian will prescribe the necessary medications and prescribe the appropriate treatment. A dog's normal temperature should not exceed 39 degrees.
Suppression of the immune system by external microbes, pain at the site of injury, and temperature directly affect the activity of the animal. Dogs with an abscess refuse to walk and eat, but at the same time consume large amounts of water. The owner can verify the presence of an abscess only by thoroughly examining the entire body for the presence of open wounds and tumors, but it is better, of course, to delegate this to a veterinarian.
It is worth noting that abscesses can be benign and malignant. Malignant ones are distinguished by the dark color of the pus, an unpleasant odor, and the general condition of the dog is atypical.
Barley formation process
The disease of the eye mucosa goes through several stages. It is important to respond correctly to pathology at its very beginning.
Initial
The disease begins with slight redness of the eyelid and slight swelling. The ciliary edge becomes inflamed and painful sensations appear.
Maturation period
A few days later, a small ball appears in the inflamed area, on the surface of which a yellow head appears. The inside of the neoplasm is not yet filled with pus.
Purulent
Pathogenic microorganisms located inside the damaged mucosa trigger the inflammatory process further, producing a large amount of pus. Under its influence, the thin mucous membrane of the eyelid can burst, releasing the contents out.
Types of barley in dogs and causes
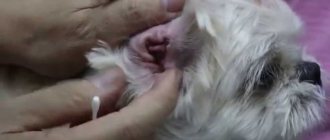
Photo.
Stye on a dog's eye photo Veterinarians distinguish two types of disease:
- Internal - formed on the inner surface of the eyelid, from the outside it looks like a small tubercle.
- External - appears on the outside of the upper or lower eyelid, looks like a small red lump, in which pus forms after some time.
The disease develops when bacteria, fungi or other microorganisms, as well as microscopic mites, enter the hair follicle or sebaceous gland.
Here are the factors that provoke the development of the disease:
- weakened immune system;
- hypothermia;
- diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms (Staphylococcus aureus, etc.);
- eye injuries;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane (conjunctivitis, etc.);
- stressful situations;
- poor nutrition.
Reference. Intensive reproduction of mites, fungi, bacteria and other microorganisms leads to the formation of several styes on the pet’s eyelids, so it is necessary to begin treatment in a timely manner.
Symptoms of stye
The pathology is easy to distinguish from other eye diseases.
Barley has characteristic symptoms:
redness of the lower (upper) eyelid;- swelling, especially well expressed in the interciliary space;
- the appearance of pain (the animal rubs its eyelids with its paw, whines);
- copious discharge in the corner of the eyes;
- the formation of a lump filled with exudate.
The pathological condition causes discomfort and pain to the animal. The pet needs immediate medical attention.
Treatment of the disease
It is important for owners to understand that treatment for barley in a dog depends entirely on its type. Thus, internal barley can only be treated in a veterinary clinic. There it will be cut, washed with saline, and then treated with an antiseptic. Therapy for external barley can be carried out at home. In questions of what to do next and how to treat the sore, the following medical scheme, common to both types of the disease, will help, and it is also suitable for both adults and puppies:
- Both eyes are thoroughly washed with Furacilin solution or decoctions of herbs such as chamomile or calendula. Make sure that the water temperature is barely warm.
- An ointment that fights the inflammatory process must be applied to the lower eyelid of both eyes at least 5-6 times a day. Ointments such as Hydrocortisone and Tetracycline have proven themselves to be effective.
- To enhance the effect, drops with antibiotic components are used, for example, Levomycetin, Desacid, Iris. The full course of treatment is 14 days, 2 drops 2-3 times a day.
People also know an old remedy for treating barley with dry heat using a peeled chicken egg wrapped in a scarf. However, it is permissible to use it only if there is no suppuration in the barley. Otherwise, heat will aggravate the process of suppuration and the dog will only get worse.
Finally, I would like to say that curing stye is not so difficult, but it is even easier to avoid it. To do this, it is enough to ensure that the dog’s menu is enriched with vitamins and minerals. According to statistics, well-nourished dogs suffer from this disease much less often. In addition, do not ignore your pet’s eye hygiene and try not to walk with him in wet and windy weather unless necessary.
Treatment
It is prohibited to treat barley in dogs at home. The eyes of an animal (especially a puppy) should be examined by a veterinarian and therapy prescribed.
Boosting immunity
In order for the body to begin to resist infection, it is strengthened.
The animal is prescribed a course of vitamins, enhanced and balanced nutrition, and walks. During the treatment period, the animal should be protected from heavy physical exertion. Severely weakened dogs are prescribed immunostimulants.
Antibiotic ointments
Antibiotics are prescribed for the eyes in the form of ointments. They act locally, speeding up the treatment process.
For barley the following are used:
- Tetracycline is a drug in the form of a cream. It destroys pathogenic microorganisms: streptococci, staphylococci, mycoplasmas.
- Eye ointment with erythromycin is active against gram-positive bacteria. It is used to treat infectious and inflammatory diseases. The product is applied to the affected area in accordance with the doctor's instructions.
Levomycetin ointment is an antibacterial drug for external use. It is indicated for the treatment of infectious diseases of the skin and mucous membranes, eliminates ophthalmological problems of microbial origin.
The drug destroys microbial infection pathogens and accelerates tissue regeneration.
Drops
Additionally, the veterinarian prescribes topical medications in liquid form – drops. They are easy to use and have a quick effect that appears immediately after application.
Effective for barley:
- Tobrex is an antibacterial, fast-acting drug that kills staphylococcal, enterococcal, and streptococcal infections.
Floxal - drops are indicated for inflammation of the conjunctiva of the upper or lower eyelid, lacrimal bursa, and boils.- Albucid is an effective remedy in the form of drops that fights the causative agent of the disease and quickly relieves inflammation.
Treatment is carried out locally until signs of inflammation completely disappear.
Traditional methods
Once the pus comes to the surface of the boil, dry heat can be used. The egg is hard-boiled, wrapped in a dry cloth, and applied to the inflamed area.
To wash the sore eye, use strong, unsweetened tea or infusion of chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula (1 teaspoon of dried flowers per glass of boiling water).
The ruptured cone is treated with ethyl alcohol (70%). They moisten a cotton pad with it and apply it to the inflamed eyelid.
Physiotherapy
In combination with rinsing and applying ointments, other procedures are prescribed.
For this purpose, UHF or tube quartz is prescribed.
Preparation for procedures
Before examination by a veterinarian, applying ointments or using drops, the dog’s eyelids are washed with warm boiled water or chamomile infusion. It is necessary to remove all discharge accumulated in the eye area.
Duration of treatment
Uncomplicated barley goes away in a week or 10 days. Medicines are used until the symptoms of inflammation completely disappear.
Surgical intervention
The internal stye is opened in a veterinary hospital, without waiting for the contents to come out. After the operation, the wound is treated with antiseptics, and further treatment is prescribed.
Treatment of styes in dogs
Having discovered an ophthalmological problem in a pet, the owner can provide first aid independently before visiting a veterinarian. First of all, it is necessary to treat the inflamed part of the eye with an antiseptic. For this purpose, a solution of furatsilin, a pink solution of potassium permanganate, and chlorhexidine are suitable. It is convenient to use cotton pads during the procedure.
It is not recommended to use cotton wool for processing, so as not to cause microtrauma with its fibers. If there is a purulent phase of barley, in no case should you squeeze the contents out of the cone. Unprofessional actions can lead to the spread of the purulent process to other tissues of the eye and provoke such serious diseases as panophthalmitis, meningitis and even sepsis.
After providing first aid, your four-legged friend must be taken to a specialized clinic. After a visual examination and ophthalmological examination, a veterinarian will confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment for barley in a dog.
In the case of an external lump, the animal is prescribed anti-inflammatory drops and ointments. The most effective for barley in dogs are ointments and gels. Tetracycline and erythromycin ointment perfectly relieves redness and inflammation. These drugs are placed behind the lower or upper eyelid. Treatment is carried out 5-6 times a day.
Hydrocortisone ointment has proven itself well in the fight against barley. The glucocorticosteroid included in its composition not only has an anti-inflammatory effect, but also effectively relieves swelling, reduces itching and has anti-allergic properties. The ointment should be applied to both eyes, and not just to the patient.
Before using the medicinal ointment, it is necessary to wash the inflamed area with a disinfectant solution. A decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage prepared in boiled water is also suitable for this purpose. Medicinal herbs relieve inflammation, reduce swelling and pain, and help soften purulent contents.
In some cases, in addition to the creamy medicine, a veterinarian may prescribe anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drops for a sick pet, for example, chloramphenicol eye drops, Ciprovet, Floxal, Tobrex.
In case of a complicated form of inflammation accompanied by hyperthermia, the furry patient may be prescribed antibiotics or sulfonamide drugs in the form of tablets or injections. To strengthen the body's defenses, vitamins and microelements and immunomodulators are prescribed.
In the event that an animal has internal barley, the veterinarian usually resorts to surgical opening of the lump followed by antiseptic treatment. During the rehabilitation period after surgery and conservative treatment, the dog should wear a protective collar.
The use of physical therapy methods will help improve tissue regeneration processes and thereby speed up your pet’s recovery. In veterinary practice, dry heat - UHF, as well as quartz lamps (tube) - are successfully used to treat inflammation of the eyelid.
Watch this video on how to properly apply eye drops and ointment to a dog:
Disease prevention
A pet's eyelids will always be healthy if the dog has good immunity. Barley is an infectious disease that occurs in weakened animals.
Proper nutrition
The pet's diet must be balanced.
You should not feed your dog high-calorie foods; it is important to provide vitamin supplements.
Strengthening the immune system
Long walks in the fresh air and moderate physical activity help activate the body's defenses. A healthy dog rarely gets sick.
Selection of dry food
It is important to consider the veterinarian's opinion. He will tell you what nutrients your pet is lacking. Based on this, they choose a balanced food rich in vitamins and microelements.
Vaccination
Routine annual vaccinations will protect your dog from many infections. This will strengthen the immune system, and the body will quickly cope with pathogenic microorganisms.
Hygiene
The animal's eyelids are washed regularly, and secretions around the eyes and on the face are removed. This reduces the risk of infection.
The dog has stye on the eye, causes
The cause of this disease can be caused by fungus, microbes, as well as microscopic mites. When one of the pathogens (microorganism) penetrates the hair follicle or sebaceous gland, it begins to multiply intensively, which is why the disease can spread.
Factors influencing the occurrence of barley in a puppy
- Stress.
- Hypothermia.
- Lack of eye care for a puppy (adult dog).
- Weakened immunity.
- Lack of vitamins in the animal’s body (vitaminosis).
- Poor nutrition (not balanced).
- Conjunctivitis.
Types of stye in dogs
- External stye - this type of stye manifests itself in inflammation of the hair follicle or sebaceous gland, redness and increased inflammation appear on the outside of the dog’s eye, and a tumor appears. And after a while, pus may appear in the tumor.
- Internal stye - this type of stye in dogs appears on the inside of the eyelid. Inflammation of the meibomian gland lobule (fatty gland of the cartilaginous plate of the eyelid) occurs.