Brucellosis in dogs is one of the most dangerous pathologies. Fortunately, it is not observed so often in pets. The risk group includes individuals who have had contact with wild foxes, rodents, as well as farm animals or products obtained from them (meat, milk). More often, brucellosis develops in sexually active adult dogs.
Causes and mechanism of infection
The causative agent of the infectious disease is the very small, non-spore-forming aerobic bacterium Brucella (Brucella canis). The strain is unusually resistant to external adverse factors and has an increased ability to penetrate the body. Harmful bacteria can be destroyed by boiling, treating with a disinfectant (a few minutes is enough), or pasteurization (at least half an hour).
The danger of brucellosis is that its consequences are extremely destructive for the animal’s body. Males develop infertility and orchitis. Bitches who are very susceptible to infection during pregnancy are at risk of spontaneous abortion from brucellosis.
Infection occurs during mating, but can also occur through contact of healthy pets with secretions from the mouth, nose, and genitals of infected individuals. Sometimes cases of infection by airborne droplets are reported.
Brucellosis is transmitted to offspring from a sick mother. Moreover, even if infection does not occur in utero, puppies will become infected during birth.
Risk and danger of infection for humans
Since there is no guarantee of complete recovery when treated with antibiotics, and the dog becomes a carrier of this infection, owners should be aware that they are putting themselves and their loved ones in danger. Brucellosis easily enters the body through healthy, intact human skin, developing and destroying the central nervous system, genitourinary organs, heart, blood vessels, and musculoskeletal system.
The pathology is so dangerous that, destroying the internal functioning of the body, it will inevitably lead to disability. Brucella actively develops meningitis, sciatica, arthritis and encephalitis and leads to infertility in young people. At risk are veterinary professionals, breeders, people who interact with blood, secretions and infected dogs, as well as people with weakened immune systems. You can read about standard scenarios for the development of brucellosis below.
Symptoms of burcellosis in humans
What do you need to know? Brucellosis is incurable, so you should take care of your safety and the safety of your loved ones. If your pet has been infected with brucellosis, then you have a choice: the healthy life of your children or your dog.
Clinical picture of brucellosis
The infectious period lasts several weeks. Then signs of the disease appear, and they are quite blurry, and therefore they are often confused with other pathologies.
Brucellosis, symptoms in dogs:
- weakness, depression, general exhaustion;
- severe enlargement of subcutaneous lymph nodes;
- slight hyperthermia;
- loss of libido;
- greenish-brown discharge (in bitches);
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- weight deficiency;
- joint damage - arthritis, bursitis (rare).
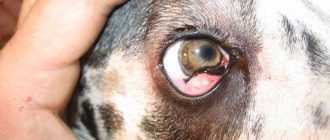
In some cases, infections affect the eyes, kidneys, brain, and intervertebral discs. Signs of brucellosis will indicate infection of these body systems.
Symptoms that directly indicate brucellosis in bitches are damage to the reproductive system: delayed estrus, infertility, infection of the uterus, which leads to the death of the offspring - the birth of still puppies or spontaneous abortion. Severe inflammation develops in the uterus, which leads to retention of the placenta after childbirth.
In male dogs, infections of the epididymis, epididymitis develop, and sperm quality decreases. When it is produced in the testicles, it continues to remain immature. In an infected male dog, you can observe an enlarged testicle, scrotum, scrotal dermatitis, and prostatitis. If brucellosis becomes chronic, the testicles become wrinkled and atrophy.
Infected dogs pose a danger to other animals for an average of 12 months. Males, even after treatment and recovery, can often remain carriers of the strain. After a spontaneous abortion, the female continues to spread bactericidal secretions for six months.
Measures for diagnosing the disease
Diagnosis of the disease consists of conducting specific serological studies. The biomaterial used to determine the pathogen must be fresh, not exposed to disinfectants or direct sunlight.
If brucellosis is suspected in a dog, a veterinary specialist in the laboratory must carry out differential diagnostics necessary to exclude yersiniosis (intestinal bacterial infection). In veterinary medicine, specific definitive tests for brucellosis in dogs are used, which make it possible to differentiate the pathogen.
Diagnosis of brucellosis is also carried out using other serological tests. To make an accurate diagnosis , performed by the polymerase chain reaction method is used. The study is based on identifying a specific DNA fragment of the brucellosis bacterium. The results of the study are received within 24 hours.
Diagnosis and treatment of brucellosis
In order for a doctor to diagnose brucellosis, he needs to conduct a number of diagnostic tests:
- bacterial culture on a bactericidal medium;
- biological samples;
- serological tests;
- PCR studies;
- agglutination - detection of antibodies to the pathogen.
If the examination results are not informative enough, the diagnosis is repeated after a month. Until this time, the animal is considered to respond positively.
During the examination, the doctor must exclude diseases in the dog that can also contribute to spontaneous abortion. These include: salmonellosis, chlamydia, canine plague and a number of other infectious and non-infectious diseases.
Treatment of brucellosis in sick dogs does not imply any specific regimen. But if recently infected animals were euthanized, today they are treated with antibiotics (if the disease was detected in the early stages). However, antibiotics, although they help control the infection, are not able to completely destroy it - from time to time the animal will spread the infection.
To prevent this phenomenon, dogs who have had brucellosis are recommended to be sterilized and removed from breeding to prevent transmission of the virus to their offspring.
There is no exact information regarding immunity after brucellosis. There are cases where the dog got sick again.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of brucellosis are very similar to other infections in dogs, making diagnosis difficult. The diagnosed dog examination includes:
- examination of vaginal secretions;
- semen fluid examination;
- examination of the aborted fetus;
- identification of existing antibodies to Brucella (agglutination);
- serological analysis;
- immunofluorescence analysis;
- immunochromatographic analysis (ICA);
- immunoelectrophoretic analysis (IEF).
Diagnosis can be repeated after a certain period of time if the results do not provide certain information. Before this, the dog is considered a carrier with a positive reaction to the infection.
A series of tests are carried out in the laboratory to detect bacteria
Also, in parallel, diagnostics are carried out to exclude infection with salmonella, leptospirosis, Carré disease (distemper), toxoplasmosis, and dysthyroidism.
Is there a danger to humans?
Yes, and a very serious one, since brucellosis is a zoonotic infection and is transmitted from animals to people. Brucella canis can easily penetrate the human body even through intact skin. Even if there are no scratches or wounds on your hands, infection is quite possible. The bacterium affects the reproductive, cardiovascular, nervous and musculoskeletal systems.
A person may remain disabled for life and will not be able to have children in the future. Infection leads to the development of dangerous diseases such as meningitis, encephalitis, and arthritis.
At-risk groups include veterinarians, breeders and others who interact with the blood and secretions of pets. For an ordinary owner, the chance of contracting brucellosis from a dog is not so great.
However, for the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to follow safety rules, for example, if there is a suspicion that newborn puppies are infected with brucellosis, it is better to examine them using disposable gloves, and then wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
There is a danger of infection in people with reduced immunity, for example, after a long illness, so during this period, communication with your four-legged pet should be kept to a minimum.
Brucellosis is not curable and is very dangerous for people, and no method of protection can protect a person 100%. Therefore, you need to weigh the pros and cons as to whether it is worth the risk, especially if there are small children in the house. Sometimes euthanasia becomes the only right decision.
Prevention
Veterinary practice has experience in using vaccines for preventive purposes. Farm animals are vaccinated, but an effective drug has not yet been invented for dogs.
Mandatory preventive testing for brucellosis is carried out:
- in nurseries when keeping two or more dogs;
- if there are questionable test results;
- with existing diseases of the reproductive system;
- in case of arbitrary abortion in females;
- when mating pets.
Animals kept in nurseries have a high risk of contracting burcellosis
Disinfection
If you are the owner of a four-legged friend, then for preventive purposes it is worth regularly treating the premises with carbolic acid (phenol), formaldehyde solution (formalin) and other disinfectants. It is worth paying attention to the nutrition of pets and removing raw meat products and milk from the diet if they were acquired from infected farm animals.
Cleaning the room where your pet lives with special disinfectants will protect your loved ones and prevent infection.
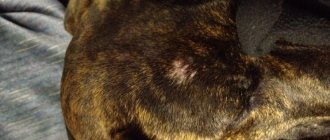
Manifestations of infection
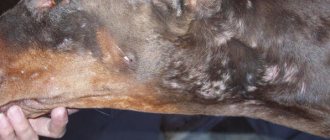
Brucellosis in animals often becomes chronic, with cyclical relapses. It is noted:
- hyperemia of subcutaneous lymph nodes;
- lethargy;
- weight loss;
- disturbances in the functioning of the spleen and liver;
- joint diseases.
Pain may occur, due to which the dog may refuse to move and will lie motionless for a long time.
But the main symptoms of brucellosis in dogs are observed in the reproductive organs:
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- vaginitis;
- orchitis;
- prostate diseases;
- endometritis;
- inability to mate.
A characteristic symptom of the disease in bitches is spontaneous abortion. Subsequently, the animal exhibits:
- temperature increase;
- greenish-brown vaginal discharge.
In male dogs, the pathogen can remain asymptomatic in the prostate and testes for a long time, which often causes the spread of infection if it is actively used for mating.
Pathological signs of infection
After autopsy of a sick dog, the following signs of brucellosis are noted:
- enlarged swollen lymph nodes, which have a gray-yellow color in cross-section;
- small papules in parenchymal organs;
- an increase in capillary tissue, the presence of lymphoid infiltrate in the kidneys;
- the presence of an inflammatory process of the uterine mucosa due to abortion of fetuses;
- necrosis of the chorionic papillae of a focal nature in the placenta;
- atrophy of the seminal canals.
Vascular necrotic changes (phlebitis, arteritis) are also noted in the prostate gland, scrotum, and vagina.
How is brucellosis diagnosed in dogs?
Brucellosis can be one of the causes of infertility in dogs of both sexes, and occur without manifestations. Therefore, this fact, as well as other disorders of the reproductive system, must be taken into account when examining the animal.
Standard diagnostics are carried out using the following methods:
- bacterial sowing on a nutrient medium;
- serological tests;
- agglutination (antibodies to the pathogen are detected);
- PCR studies;
- biological samples.
Data! A study was conducted in Russia, for which 45 dogs were selected, five of which were clinically healthy, the rest had various diseases of the reproductive organs. Among healthy dogs, the causative agent of brucellosis was found in one, as well as in 28 animals with problems with the reproductive system.
If the test results are unclear and there are doubts about the diagnosis, the dog is isolated and re-examined a month later. If the result is questionable again, the animal is considered to react positively. With a bacterioscopy with a positive reaction, but with a negative bioassay, the result of the analysis for Brucella is determined to be suspicious.
Brucellosis
Allergy
Arthritis
Encephalitis
7522 20 January
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Brucellosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus
Brucella
.
These bacteria are highly resistant in the environment and can remain viable for a long time.
In Russia, the disease occurs in the southern regions where livestock farming is developed. Professions associated with an increased risk of contracting brucellosis are shepherds, milkmaids, veterinary and zootechnicians, employees of bacteriological laboratories, workers in meat processing plants, slaughterhouses and factories processing animal wool.
Causes of brucellosis
Brucella is transmitted to humans from sick animals, mainly goats and sheep.
Transmission of Brucella occurs through food (thermally untreated milk and dairy products, meat), direct contact with sick animals, as well as through inhalation of Brucella contained in dust in the habitats of sick animals and during cutting of their carcasses.
Brucella can penetrate the placenta, leading to intrauterine infection of the fetus, and can also be excreted in breast milk.
Transmission of Brucella from person to person is impossible by other means.
After entering the human body, Brucella intensively multiplies in lymphoid tissue.
Brucella can persist in the body for a long time and unnoticed by humans, causing a chronic course of infection.
Classification of the disease
Brucellosis can develop as a result of infection with various types of Brucella, for example,
Brucella melitensis, Brucella abortus
. There are certain features of the course of brucellosis caused by different types of pathogens, but these differences relate mainly to epidemiological aspects.
Depending on the duration of the disease, brucellosis can be acute, subacute and chronic. Separately, residual (residual) changes are distinguished that persist after recovery from infection and liberation of the body from the pathogen.
Symptoms of brucellosis
The first symptoms of the disease usually appear 1–6 weeks after infection.
More often, brucellosis begins subacutely - nonspecific symptoms occur, such as weakness, malaise, headache, joint and muscle pain.
The increase in temperature in the subacute period is insignificant, followed by a rise to higher values. Fever often has a wave-like course. In rare cases, enlargement of the lymph nodes is observed, and painful subcutaneous nodules are found.
Brucellosis is characterized by allergic manifestations on the skin (diffuse redness, rashes, etc.).
From the cardiovascular system, there is a decrease in blood pressure, an increase in heart rate, and the possible development of inflammatory processes in the heart. Damage to the respiratory system (bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.) may also occur.
Chronic brucellosis is characterized by damage to the musculoskeletal system, expressed by joint and muscle pain and limited joint mobility.
Damages to the nervous system are manifested by burning and tingling along the nerve fibers.
Diagnosis of brucellosis
Diagnosis of brucellosis consists of a thorough history taking and objective examination of the patient.
Laboratory methods used in the diagnosis of brucellosis include a clinical blood test with the determination of the leukocyte formula, in which signs of an inflammatory process in the body can be detected. However, this method does not provide identification of the pathogen. For this purpose, bacteriological, serological and molecular genetic methods are used.
What is the treatment for brucellosis in dogs?
Although antibiotics can successfully control the infection, they cannot completely eradicate it, so any dog infected with brucellosis should be treated as infected for the rest of its life. Even if an acute infection is treated with antibiotics, the dog may still be able to spread the bacteria periodically for the rest of its life.
Surgical neutering of an infected dog reduces the spread of the disease in the environment, thereby reducing the risk of infection to other dogs.