Causes of hypersalivation
Saliva is the secretion of the salivary glands (sublingual, parotid, submandibular) that enters the mouth. It is a colorless transparent liquid. The role of saliva is its antibacterial effect, protecting the oral cavity from the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria due to the content of antiviral elements in it.
In addition, it helps dogs digest food by moistening hard pieces before swallowing.
The norm for saliva production is 1 liter per day (for a medium-sized dog), but when feeding dry food, more is produced. Exceeding the volume indicates dysfunction of the glands responsible for secretion production. A number of factors contribute to this:
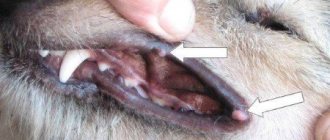
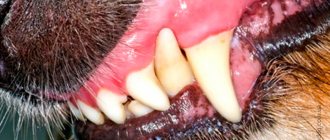
- Dental diseases. Caries, stomatitis, tartar, and periodontal disease cause painful sensations that the body tries to neutralize through copious secretion of saliva.
- Dislocation of the jaw. The dog is unable to close its mouth, causing it to constantly drool.
- Ear diseases. Near the ears are the large parotid glands, which help produce saliva. In the presence of injuries, inflammations, tumors, fungal infections in the ears, the glands begin to intensively produce secretions.
- Viral infections - rabies, parvovirus enteritis, leptospirosis, canine distemper. These are very dangerous diseases that threaten not only the dog, but also its owner.
- Chronic pathologies - diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidneys, spleen, gall bladder, ulcers, tumors, gastritis
- Gynecological disorders, for example, diseases of the uterus.
- Poisoning, botulism. A dog can be poisoned by low-quality or heavy foods (fatty meat, sweets), toxic substances (poison, household chemicals), garbage, etc. Penetrating into the stomach, toxic substances irritate the organ and cause an outflow of bile and gastric juice.
- Licking and eating certain types of lizards and toads.
- Stress. A change of residence, separation from the owner, the appearance of another pet in the house, and even a regular trip to the veterinary clinic by car can cause strong psycho-emotional stress and, as a result, hypersalivation.
- Heatstroke. Overheating causes evaporation of saliva, which activates the processes of thermoregulation, increased blood supply to the tongue and hypersalivation.
- Helminthiasis. With helminthic infestation, salivation is accompanied by vomiting.
- Portosystemic shunt.
- Epilepsy. Drooling is usually a warning sign of an epileptic seizure.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Insect bites if the dog tries to eat them.
- Tumors, cysts of the salivary glands or oral cavity.
- Diseases of the immune system.
Veterinarians also note a number of causes of hypersalivation that are not associated with pathological processes. For example, salivation can be caused by the entry of a foreign body into the oral cavity - fragments of bones, branches, etc. In females, copious saliva is secreted during pregnancy due to hormonal imbalance. In puppies, hypersalivation is observed during the period of teeth change.
Many owners notice increased salivation in their dog when trying to give it medication. And finally, the activity of the salivary glands is activated before eating, after excessive physical activity - these are normal phenomena that do not require medical intervention.
Causes of increased drooling
It is important for owners of four-legged pets to know what reasons can cause excessive salivation in a dog. Such knowledge will help determine the need for emergency hospitalization or the admissibility of providing first aid at home. There are physiological and pathological options for increasing the amount of discharge. The features of the first category were discussed above, now it’s time to consider the reasons why drooling increases in dogs with liver disease and other diseases. In the voiced variations, age does not play a role, therefore pathology can manifest itself in puppies and adults.
Intestinal disorders
If the gastrointestinal tract does not function properly, four-legged pets face not only ptyalism. Owners may also notice a change in stool: more often than not, it becomes looser. This may indicate acute and chronic gastrointestinal diseases. Excessive drooling due to gastritis and other diseases in dogs is accompanied by refusal to eat, weight loss, pain, and weakness.
Infectious diseases
When walking outside, dogs often encounter various negative factors, such as infections, viruses and bacteria. Once in the body, they begin to multiply and cause a different clinical picture. For example, hypersalivation can be considered one of the symptoms of rabies, enteritis, botulism, piroplasmosis, leptospirosis. These are very dangerous diseases that can be fatal.
Non-communicable diseases
There are also less contagious diseases that may periodically be accompanied by sialorrhea. These may include a cough, runny nose and, as a result, an increase in body temperature. The main thing is to pay close attention to the well-being of your four-legged pet and, at the slightest suspicion of complications, consult a specialist.
Diseases and injuries of the ears
Fun fact! The largest gland that is responsible for drooling in dogs is located in the ear area.
Diseases and traumatic lesions of the ears can cause excessive discharge from the animal's mouth. Otitis, tumors and injuries in this organ are extremely difficult to identify without qualifications, so you should not put off visiting a dog doctor for a long time.
Oral diseases
Oral diseases are the most common cause of increased discharge. Inflammation of the mucous surface, pathology of the dentition and gums, a stuck foreign object - all this can lead to ptyalism. Periodically, diseases are accompanied by the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the animal’s mouth.
Psychological reasons
This category includes overexcitation, nervous tension, a surge of joy and pleasure. All situations are associated with changes in the dog’s usual state of mind, which is why the body reacts with excessive salivation.
Another factor may be hyper-relaxation. Some owners of four-legged pets may notice that when the dog sleeps, a small puddle of saliva collects under the cheek.
Stressful situations
An injection, a sudden change of environment, a long separation from a loved one cause a feeling of stress in a four-legged pet. Such a complex condition can cause hypersalivation, as the influence of the central nervous system on reflexes.
Complications after vaccination in dogs
In some cases, vaccination can lead to an allergic reaction, anaphylactic shock. Such a clinical picture as ptyalism, shortness of breath, cyanosis of the mucous membrane, weakness, is a reason for urgent consultation with a doctor.
Which breeds are more susceptible
In representatives of some breeds, hypersalivation is due to peculiarities of the anatomical structure. These are dogs with massive muzzles, loose, fleshy jowls and shortened jaws:
- Shar-Pei;
- Maltese;
- bulldogs;
- boxers;
- Saint Bernards;
- Newfoundlands;
- mastiffs,
- Great Danes;
- Caucasian Shepherd Dogs;
- bloodhounds.
These dogs drool for any reason: in cold or hot weather, before eating, out of joy or excitement. You can often notice saliva on them during sleep. The phenomenon, which is called false ptyalism, is not considered a serious fault of the breed, but many breeders try to prevent dogs that are too “loose” from being bred.
When choosing a puppy, it is advisable to pay attention to its parents. If they are constantly slobbering and getting everything dirty, then their babies will be the same. In this case, all that remains is to accept it and constantly wipe the dog’s face.
What to do if your dog is drooling?
Consider a case where a family friend's breed does not include excessive drooling. In this case, the owner’s actions are simple:
- It is necessary to observe the animal, see if there are any other features of behavior or food intake that have not been observed before;
- Conduct an examination of the ears and auricles, in case there are ear mites in dogs
or any other disease. As a rule, with sore ears, the dog will squeal when touched or regularly try to scratch them with his paw; - If the dog is a girl, remember the last time she was in heat;
- Pay attention to the chair. In case of poisoning, there may be diarrhea;
- Check the integrity of the teeth and the presence of wounds in the mouth;
- For easily stressed individuals, expand your social circle, identify hidden complexes and try to eliminate them either independently or with the assistance of an experienced training instructor;
- Visit a veterinarian.
It is worth noting that increased salivation in dogs can occur not only in case of illness, so it is necessary to carefully monitor this process. In veterinary medicine it is called hypersalivation.
In certain dog breeds, strong salivation is associated with their anatomical features. These breeds include boxers, mastiffs, basset dogs, and bloodhounds.
A lot of saliva is also released from the mouth before eating food and dog treats, during physical activity or during times of severe stress.
When should you worry?
If the secreted saliva has become viscous, opaque, an unpleasant odor has appeared from the mouth, and the color has changed to yellow-brown, then it is better to immediately consult a veterinarian for advice. These signs can be a consequence of the appearance of various diseases: inflammation of the glands, periodontal disease, stomatitis and others.
It is especially alarming if changes appeared unexpectedly and there was no reason for this. The animal may have a serious infection, such as rabies. In addition, the cause of the abundant appearance of saliva can be disorders in the animal’s body: inflammatory processes in the stomach and intestines, ulcers of the stomach, mouth, throat, the appearance of tumors, decreased immunity, foreign bodies, diseases of internal organs, epilepsy, distemper, etc.
Hypersalivation can also occur due to toxic substances entering the animal’s body, as well as drugs, animal and plant poisons.
Main symptoms
The signs leading to hypersalivation are varied, therefore, the clinical picture will vary. Thus, dental problems are indicated by decreased appetite, careful and slow absorption of food, itching in the jaw area, and drooping head. The dog constantly whines, growls, including at the owner, and reacts inadequately to touches on the face.
When poisoned, the dog experiences severe thirst, vomiting and diarrhea. He often experiences fever and pale mucous membranes. Saliva is thick.
Viral infections are characterized by a sharp decrease in appetite, lethargy, apathy, fever, and increased thirst.
In any case, if hypersalivation occurs in combination with other signs, you should immediately contact a veterinary clinic.
Diagnostics in a veterinary clinic
When contacting a specialist, the owner must tell in detail about the dog’s lifestyle, peculiarities of keeping and feeding, contacts with other animals, medications used recently, and other symptoms. The veterinarian’s task is to differentiate normal drooling from salivation, accompanied by gagging and smacking.
To diagnose the disease, the veterinarian will conduct a complete neurological and physical examination of the animal (special attention to the oral cavity and neck area) and diagnostic tests, including a complete blood count (general, biochemical), urine tests, stool tests, ultrasound, x-rays, biopsy ( if a disorder of the immune system is suspected), washings from the mucous membranes.
Treatment method and prognosis
There is no single treatment regimen for hypersalivation. After identifying the cause that caused the excessive secretion of saliva, the doctor develops it on an individual basis, based on the diagnosis, the animal’s health condition, age, etc.
For dental diseases and tumors, teeth cleaning and surgery are used. Removal of a foreign body, if the owner could not get it at home, may require the use of anesthesia and sedation. Antibiotics and antiviral drugs are used to treat oral infections and inflammatory diseases.
If a dog's drooling is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, it is prescribed maintenance therapy with adjustments to nutrition and fluid administration.
As for the prognosis, it all depends on the root cause. If hypersalivation was caused by a dangerous disease such as rabies, which cannot be treated, then the prognosis is unfavorable.
The main reasons why a dog drools
There are a number of reasons why drooling or, scientifically, salivation occurs.
- Breed trait.
Indeed, some breeds have a breed predisposition to drooling. These animals include: the Caucasian Shepherd breed
, Mastiff, German Boxer, Basset, Shar Pei, etc.
- Ear diseases.
Of all the salivary glands: sublingual, zygomatic, submandibular and parotid, the latter produce the most salivary fluid. Therefore, any injuries and diseases of the ears lead to increased production of saliva. Diseases include various types of fungi, otitis media, inflammation, and ulcers.
- Infections.
It is not difficult to detect an infection; as a rule, in addition to excessive salivation, the pet becomes lethargic, refusal to eat, and involuntary urination may occur. Body temperature may be elevated as the immune system begins to fight the virus. It is worth noting that it is not possible for an animal to defeat the virus on its own, so the only correct decision is to immediately show your pet to a veterinarian, who, based on symptoms and possibly clinical tests, will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
- Mouth cavity problems.
Such problems include diseases of the teeth, gums and their injuries. In most cases, they are the answer to the question of why a dog is drooling. Caries, stomatitis and even ordinary tartar in dogs
can lead to the appearance of saliva, which will act like an antiseptic on a sore spot. However, a trip to the veterinarian is mandatory, because by identifying the cause, it will be possible to eliminate it, and therefore reduce salivation to a minimum. For example, if an animal eats and spits out food, rubs its mouth with its paw, bites carefully, or delays the eating process, then something is wrong. Examination of the mouth may reveal either a foreign object stuck between the teeth, damaged gums, or dark yellow teeth (tartar). The smell will also help you understand that something is wrong with the oral cavity.
The presence of blood in saliva indicates some kind of trauma to the tissues of the mouth.
- Poisoning.
The animal may become poisoned. The object of poisoning can be: food not intended for four-legged animals (chocolate and other sweets), stale food, household chemicals, fruits, plants, etc. Poisoning can occur both at home and while out and about. It is not difficult to identify it; the pet produces copious thick saliva.
- Hormonal disorders.
The reason why a dog drools
girls, it may also be hidden in a hormonal disorder. Some owners, not engaged in breeding, do not carry out the operation of castration of the animal. Accordingly, there is a risk of hormonal imbalance and cancer.
- Problems of internal organs and chronic diseases.
When a pet’s disease begins to affect its internal organs: kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract, etc., increased salivation may be a side effect. This is especially noticeable in adult animals.
- Animal hyperactivity.
If an animal does not fully expend its energy over the past day, it becomes easily excitable. First of all, such breeds include decorative breeds, however, among large dogs there can also be individuals. A number of individuals bark from the abundance of emotions, others make a puddle, and still others run around at breakneck speed. And there are animals that simply drool.
- Animals that are easily stressed.
Some pets easily panic and become stressed. The body's protective reaction to this is simple - copious amounts of saliva are released. For example, if you fail to accustom your pet to a confined space—a carrier—in puppyhood, you may eventually end up with a dog that is afraid of closed doors, elevators, and the same carrier. Some are afraid of loud sounds, new terrain, and other four-legged relatives.
What to do at home
The first thing an owner should do if they notice unusual drooling in their pet is to carefully examine the oral cavity. There may be a foreign body stuck there that needs to be removed. If a wound has formed in your mouth, it should be disinfected. A veterinarian's help may only be required if the wound becomes suppurated.
If a dog drools profusely before eating or after excessive exercise, the owner does not need to do anything. As soon as the pet eats or calms down, the process of copious salivation will stop.
If you experience stress caused by traveling in a car, you need to train your dog to travel. It is better to start with small distances, gradually increasing them. This trains the animal's vestibular apparatus. Over time, your four-legged pet will understand that traveling in a car does not threaten him with anything terrible.
It happens that a dog gets very nervous at shows. In such cases, it is advisable to walk him more often, introduce him to other people and animals, and change the environment. It is advisable to seek the help of a dog handler. If the situation is severe, the veterinarian may prescribe sedatives, homeopathic remedies, and herbal decoctions.
If the owner is sure that the dog has been poisoned, he can provide first aid to it using products intended for humans. Activated carbon and Enterosgel are suitable. However, if the symptoms of poisoning do not go away, it is necessary to show the animal to a veterinarian.
Small puppies are always gnawing on something during the period of changing teeth, as a result of which saliva constantly flows from their mouths. No worries. This is a normal physiological phenomenon. When baby teeth are replaced by molars and the gums stop bothering the baby, excessive salivation will stop. The only thing the owner can do to help the puppy is to provide him with as many toys as possible that he can chew.
What to do?
Before taking any active steps, you should carefully observe under what circumstances hypersalivation occurs and whether it is accompanied by any associated symptoms. If your dog drools heavily before eating, exercising, or during a trip, there is no need to worry - this is only a periodic phenomenon that does not require any intervention.
But if drooling is accompanied by thirst, fever, diarrhea, vomiting, convulsions or other alarming signs, you should immediately contact your veterinarian.
*Based on the results of my own work and colleagues from nld.ru, dogipedia.ru, jvet.ru
If your dog greets you with a mouthful of drool, this may in principle be normal, but it may also be a sign of health problems.
Excessive salivation is called hypersalivation. If you are the owner of a dog with a sagging lip, such as a mastiff, then excessive saliva production is normal. This excessive discharge is related to the structure of the face, but not to any medical problems. However, in other cases, such excessive salivation in a dog
may be a reason to contact a veterinarian.
If your dog suffers from a fear of thunderstorms, or is having a hard time with separation, then salivation in large quantities is normal because... at these moments the animal experiences stress and a feeling of fear, which is accompanied by salivation. There are other cases when saliva may be released profusely - a desire to enjoy delicious food. Remember, you’ve probably also ever salivated when you thought about food. The same is with a dog, if, for example, it hears the smell of meat or just hot dogs, the process of salivation may begin.
Common causes of excessive salivation
are hidden in the animal's mouth.
The culprits of this process can be inflammation of the gums, mouth ulcers, tumors, cuts and abscesses. Carefully examine the animal's mouth and try to determine whether the above-mentioned symptoms are present in the oral cavity. If you find anything like this, be sure to consult your veterinarian. Note that salivation in dogs
can also be caused by dental problems.