Vocal cords
The ligaments themselves are presented in the form of folds, they belong to the mucous membrane of the larynx, their movement creates sound . If the vocal cords close, the entrance to the trachea may close. This factor influences the fact that dogs are not able to breathe and bark at the same time.
The performance of the vocal cords is regulated by nerve impulses sent by the brain. It is presented in the form of transmission of excitation along the nerve fibers innervating the larynx.
As soon as the owner notices that his dog has no voice, he should immediately take it to a veterinary clinic. This problem may be associated with mechanical damage to the vocal cords, or, in particularly difficult cases, with disruption of normal nervous stimulation of the cords.
Violation of verbal function in a puppy can be caused by a neonatal infection; adults are not susceptible to it.
Causes
So, loss of voice in a dog can be caused by the following disorders:
With a mechanical disorder, the dog's voice is lost due to:
- Abscess of the pharynx . An animal may eat grass while walking, as a result of which seeds and thorns get stuck in the tonsils, pharynx or larynx. The consequence for the pet can be: rapid tissue swelling, infection of the damaged area, or the formation of an abscess.
- Injuries . It is no secret that many owners prefer to feed their pets bones in order to save money, the sharp edges of which can, in turn, cause blunt trauma to the throat or even severe penetrating trauma, the result in which case, as a rule, is pronounced swelling of the glottis.
- Tumors . Pets also get cancer, they may develop malignant neoplasms, polyps that interfere with the movement of the vocal cords, as a result of which the dog loses its voice.
Neurological disorders, in turn, are associated with:
- Congenital paralysis of the larynx . Some dog breeds (German and white shepherds, Rottweilers, Dalmatians) may be born with impaired innervation of the larynx.
- Acquired laryngeal paralysis . A disease of this kind already applies to adult animals (a predisposition exists in Labradors, Irish setters, St. Bernards, and golden retrievers).
- Tumor . In this case, it is worth keeping in mind the primary tumor of the nerves associated with the larynx. Nerve fibers can be compressed tumors of large sizes.
- Hypothyroidism . Impaired functioning of the laryngeal nerves can cause thyroid failure.
- Muscle disorders . As a rule, all autoimmune diseases can lead to disturbances in neuromuscular transmission in the vocal cords.
Many veterinarians note that very often all vocal changes observed in dogs are closely related to respiratory dysfunction. This is because stiff, inflamed or swollen vocal cords prevent air from reaching the trachea.
Reasons for loss of voice
- Mechanical damage and swelling of the vocal cords after a foreign body enters the larynx, inflammation of the pharynx or injury.
- Neurological abnormalities:
- * laryngeal paralysis
– congenital or acquired; - * malignant neoplasms
– tumors; - * hypothyroidism
– disorders of the thyroid gland; - * autoimmune diseases
- allergies.
- Physiological disorders from drying out of the mucous membrane.
- Respiratory viral diseases. A dog has a cold if it has a cough, fever and decreased appetite.
Diagnosis of the disease
The initial examination of the animal consists of a thorough detailed examination. The veterinarian will need to:
- Palpate the neck and submandibular lymph nodes,
- Auscultate lung and heart sounds.
If necessary, a specialist can perform sedation; this modern, gentle anesthesia technique allows the veterinarian to perform laryngoscopy, examination of the pharynx and glottis. Thanks to the use of sedation, the doctor can open the dog's mouth as wide as possible and carefully examine the animal's pharynx to detect:
- Abscesses.
- Foreign bodies
- Paresis of the glottis.
Bronchoscopy can also be used as a method of examining a four-legged patient.
The veterinarian will definitely send the animal for a general blood test, which will help him exclude hypothyroidism from the list of possible pathologies - for this, thyroid hormones are examined.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the doctor examines the dog in detail, auscultates the lungs and heart sounds. Carefully palpates (palps) the neck and submandibular lymph nodes. Most often, sedation is required to perform laryngoscopy, examination of the pharynx, and glottis. In this case, it is possible to open the patient’s mouth wide and carefully examine the pharynx to exclude abscesses, formations, foreign objects and paresis of the glottis. If necessary, bronchoscopy is used.
If an infection is suspected, a virological examination is indicated.
To exclude hypothyroidism, an endocrinological examination (thyroid hormone test) is performed.
Causes of the disease
In veterinary medicine, it is customary to distinguish two classes of reasons due to which a dog loses its voice: mechanical and neurological. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Mechanical reasons
Mechanical dysfunctions of the vocal apparatus occur due to factors such as:
- Throat injuries. Can occur in a puppy if he decides to swallow a toy or too large a piece of solid food. Adults suffer laryngeal injuries from cheap food such as bones. If the bone has sharp edges, this can lead to severe penetrating trauma, which will cause swelling of the glottis, depriving the dog of the ability to make sounds.
- Abscesses localized in the pharynx. Often found in those dogs who like to eat grass while walking. Sometimes, along with harmless stems, thorns and plant seeds end up in the pet’s mouth. They injure the delicate tissues of the larynx, making them vulnerable to infection, which in the future leads to swelling of the affected areas and the formation of harmful abscesses.
Neurological disorders
If a dog has lost its voice, then neurological disorders may well be the pathological cause. The most common among them include:
- Hypothyroidism. Thyroid dysfunction interferes with the full functioning of the laryngeal nerves, which is why the pet cannot bark.
- Congenital laryngeal paralysis. Dog breeds such as German Shepherds, Dalmatians and Rottweilers are especially vulnerable to this type of laryngeal innervation. The animal is not able to make any sounds when it is still a small puppy. Unfortunately, this disease is incurable.
- Acquired paralysis. It most often occurs in breeds such as the Irish Setter, Labrador and St. Bernard.
- Allergic reaction. This leads to the dog’s muscle innervation malfunctioning, which is why he stops barking.
- Oncological diseases. A pet may lose the ability to bark if a malignant tumor appears in its throat, which will interfere with the normal movement of the vocal cords. Treatment of such neoplasms is complex and associated with a lot of difficulties. In most cases, the prognosis for cure is disappointing. It is difficult for the animal to eat, so it quickly weakens and dies.
Veterinarians are convinced that sometimes the loss of voice can be caused by drying out of the oral mucosa, which occurs, for example, because the pet does not have free access to water. Also, the dog is able to stop making sounds if he gets sick with any cold, since at this time mucus accumulates in his larynx, preventing him from barking at full strength.
In addition to all of the above, another reason for sudden muteness is the dog staying for a long time in a room where there is a strong smell. This is especially true for a room that is being renovated or where people smoke heavily. In any case, at the first signs of loss of voice, the pet should be taken to a veterinary hospital, because only a qualified specialist can establish the exact pathogenesis of such a phenomenon.
Loss of voice in dogs: causes and treatment. Why did the dog lose his voice and what to do about it?
These animals are usually much more talkative than cats.
Surely, due to their protective purpose - it is inherent in dogs by nature. However, it also happens that noisy, sociable, restless dogs suddenly fall silent for a long time. Their voice becomes almost inaudible, quiet, and sometimes hoarse.
At the same time, a caring owner sounds the alarm: what is the reason that the dog lost his voice, and how to deal with it?
Why do animals lose their voices?
A dog's silence is not always an alarm signal. Maybe the dog is simply silent because it is offended - and is he depressed? If it lasts one day, then there may be no reason to worry. But if within a few days the owner notices the pet’s unsuccessful barking attempts and wheezing, then this is a real shock for the animal itself.
The most common cause of loss of voice in a dog is damage to the esophagus, larynx, and upper respiratory tract by foreign objects.
Animals, like children, taste everything, so they can harm themselves with a sharp bone, a twig, or a piece of wire.
If a dog eats grass, then seeds and sharp thorns can get stuck in the throat, which leads to tissue swelling, sometimes to secondary infection, and the formation of abscesses.
Laryngeal paralysis in dogs can be congenital, which is typical for Rottweilers, German Shepherds, or acquired. Saint Bernards, Labradors, Setters, and Golden Retrievers are more prone to the latter. Hypothyroidism in animals leads to disruption of the laryngeal nerves. Autoimmune diseases are the cause of failures in the innervation of the ligaments.
Even a common cold or viral illness can make your four-legged friend “mute.”
True, in this case, an attentive owner will always notice other signs of illness, for example, cough, drowsiness, weakness, and increased body temperature.
In dogs, as in people, colds are accompanied by swelling of the larynx. Mucus accumulates there, making barking and any attempts to voice difficult.
Severe penetrating or blunt trauma to the throat leads to swelling of the throat. In this case, the dog remains voiceless for a long time.
In rare cases, the cause of dog muteness is prolonged exposure to a room with strong odors. This could be a smoky home, a house where renovations are being carried out and smells of paints, varnish, and solvent.
It is unlikely that the owner will be able to independently determine the cause of the problem. The absence of voice can be caused by many factors, the determination of which is within the competence of the veterinarian. Therefore, do not delay your visit to him.
How to help a dog with voice loss
So, self-medication on the advice of neighbors and friends is not the best option for solving the problem. After all, you need to start by finding out the cause of the pathology. Watch your dog.
You may notice other signs of trouble that should be reported to your veterinarian. Before visiting the veterinary clinic and prescribing a course of therapy for your pet, you can do something yourself.
For example, ventilate the room more often if the dog is in it, monitor the cleanliness of the water in the animal’s drinking bowl, and change it more often.
Try examining your dog or puppy's larynx yourself. This must be done carefully, in a playful manner, without causing pain to the pet. You may need an assistant for this. But don't overdo it! If you manage to detect any inflammation or mechanical damage, then in order to avoid further injury to the tissues of the pharynx, try to fix the dog in a comfortable position and show it to the doctor.
Sometimes antihistamines, for example, Claritin, Tavegil, Suprastin, help with swelling of the throat. They should be given to the dog depending on its weight.
If the cause of the problem is a cold, then it is necessary to treat it, and the voice will gradually return to normal.
Only a doctor can remove a bone or polypoid formations stuck in the throat.
Some dogs are also “talkers”. They love to bark, whine, and whine, begging for treats from their owner. This constant “chat” can not only amuse or irritate the owner.
If your dog is hoarse, there is a chance that it is due to over-irritation of the tissues in the larynx.
. However, there are other predisposing factors.
Some of them can pose a serious danger to both the health and life of your pet. Let's look at the most common of them.
This is the name for inflammation of the tissues of the larynx. Dogs can get it just like people. The result is either hoarseness or a complete loss of the ability to reproduce at least some sounds.
At the same time, the dog can only “squeak” or wheeze. There are many reasons that contribute to irritation and subsequent inflammation of the laryngeal tissues.
If your dog looks like a frog, silently opening and closing its mouth, but there are no other signs of something wrong, you can relax: most likely, the inflammation arose due to overstrain of the larynx (when the pet likes to bark, there is nothing surprising in this). In mild cases, all problems disappear spontaneously within a couple of days. Unfortunately, this doesn't happen often.
In many cases, it is a disease of inflammatory etiology, resulting from the action of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microflora. The most common cause is hypothermia. A fairly common problem for dogs that constantly live on the street.
Source: https://vvt24.ru/poleznoe/poterya-golosa-u-sobaki-prichiny-i-lechenie-pochemu-u-sobaki-propal-golos-i-chto-pri.html
Diagnosis of the disease
After the animal is taken to the doctor, he will carefully examine it and palpate the submandibular lymph nodes and neck. Then the dog's lungs and heart will be listened to for changes in its tones. If such procedures do not provide an accurate understanding of the cause of muteness, then the use of modern anesthesia techniques such as sedation is acceptable. With its help, you can examine the dog’s pharynx as painlessly as possible in order to exclude the influence of factors such as an abscess, paresis of the glottis or the presence of foreign objects inside the larynx on the lack of voice.
Diagnostics also includes bronchoscopy and collection of blood fluid for general analysis. The latter measure will detect hypothyroidism, which changes the amount of thyroid hormones in the dog's blood.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of suddenly manifested muteness depends entirely on the cause that caused it. Experts offer the following treatment options based on the factors that provoked this phenomenon:
- Oncological neoplasms and paralysis are treated through surgery.
- A foreign body lodged in a dog's throat is removed by a veterinarian during laryngoscopy.
- Colds and viral diseases are highly susceptible to pharmaceutical influence, in particular antibacterial drugs.
- Antibiotics such as Streptomycin and Amoxicillin have proven themselves to be effective against infections.
- Diseases of the immune system and hypothyroidism require the use of symptomatic remedies.
It is important to understand that if your dog loses its voice, you should never treat your dog at home. The only exception is a cold. If the owner is absolutely sure that the dog has caught a virus, then before going to the doctor it is permissible to give the pet milk, honey and a warm chamomile infusion. These remedies successfully relieve inflammation of the animal’s larynx and relieve pain.
Finally, I would like to say that the absence of a voice is a serious symptom that something wrong is happening in the dog’s body. Therefore, if there is unnatural silence in the house at normal times, the owner is obliged to sound the alarm and take the pet to a specialist for an examination. Under no circumstances provoke your pet to bark, do not command him “Voice!”, this can only aggravate the current situation and cause the dog more suffering.
Some dogs are also “talkers”. They love to bark, whine, and whine, begging for treats from their owner. This constant “chat” can not only amuse or irritate the owner. If your dog is hoarse, there is a chance that it is due to over-irritation of the tissues in the larynx . However, there are other predisposing factors. Some of them can pose a serious danger to both the health and life of your pet. Let's look at the most common of them.
Treatment
There is no need to panic if your dog has lost his voice:
- the foreign body is removed during laryngoscopy;
- tumors and paralysis are treated surgically;
- colds and viruses - taking antibacterial drugs;
- hypothyroidism and autoimmune diseases - by symptomatic means.
Before going to the doctor for viruses and colds, it is useful to give your pet a decoction of chamomile and oregano. Warm milk with honey also relieves inflammation.
During allergic edema, you need to give your dog Suprastin - calculate the dose depending on body weight or Claritin.
The physiological cause - lack of water - can be eliminated by drinking plenty of water and walking in the fresh air.
But a course of chemotherapy for malignant neoplasms and hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism requires examination and monitoring by a veterinarian.
Laryngitis
This is the name for inflammation of the tissues of the larynx. Dogs can get it just like people. The result is either hoarseness or a complete loss of the ability to reproduce at least some sounds. At the same time, the dog can only “squeak” or wheeze. There are many reasons that contribute to irritation and subsequent inflammation of the laryngeal tissues.
If your dog looks like a frog, silently opening and closing its mouth, but there are no other signs of something wrong, you can relax: most likely, the inflammation arose due to overstrain of the larynx (when the pet likes to bark, there is nothing surprising in this). In mild cases, all problems disappear spontaneously within a couple of days. Unfortunately, this doesn't happen often.
In many cases, laryngitis is a disease of inflammatory etiology, resulting from the action of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microflora. The most common cause is hypothermia, hypothermia. A fairly common problem for dogs that constantly live on the street.
Psychogenic factors and “talkativeness”
Let us repeat once again - if your dog loves to “chat”, bark and squeal, enjoying everything in the world, his larynx may not be able to bear such loads. Small dogs especially suffer from this. “Fatigue” of the larynx manifests itself quite characteristically - at first the pet becomes more restrained, barks less, and then completely stops making any sounds, with the exception of light wheezing or whistling. But it is not only excessive “loquaciousness” that can lead to such a result.
Severe stress
– the second predisposing factor, and quite a powerful one. Dogs who suddenly become less vocal may be reacting to something new in their lives. Something that makes them anxious. Causes of stress may include a sudden change in daily routine or the arrival of a new family member in the house. Sometimes the shock can be so strong that the dog completely loses his voice, turning into a kind of “mute frog.” As in the case of mild laryngitis, there is no need to worry too much - “vocal” abilities recover on their own after a few days.
Hoarseness of infectious etiology
In addition to laryngitis, hoarseness can be caused by other diseases of an inflammatory nature (infectious and non-infectious etiology). In particular, bronchitis is widespread, and in severe cases there is a high risk of developing pneumonia. It is quite easy to guess the severity of the disease - the animal becomes inactive, its general body temperature rises (intermittent fever is also possible), the pet experiences severe weakness, refuses food, but its thirst does not suffer. The dog cannot bark, a frequent and prolonged cough appears, gurgling and wheezing are clearly audible in his chest.
Note that infectious pneumonia can be a secondary disease, the development of which leads to some forms of helminthiasis. The problem is that the larvae of worms at the first stage of their development must get into the lungs (through the bloodstream). Of course, this does not improve the health of the organ; the likelihood of developing a secondary infection increases sharply. Which, in fact, often happens when a dog’s voice becomes hoarse.
In more rare cases, tracheitis occurs - inflammation of the trachea. With this disease, the most characteristic symptom is not hoarseness, but a cough. It is very strong, paroxysmal. During “attacks” of coughing, the animal may vomit, the irritation of the throat is so great due to the strong cough reflex.
Other predisposing factors
Are there other causes of hoarseness? Yes, quite a lot. If we started talking about problems with the trachea, we need to note two more: its mechanical injuries and airway obstruction . With injuries, everything is clear - if the throat was damaged as a result of some strong impact, this could lead to a violation of the integrity of the trachea. Obstruction is a phenomenon in which the trachea is compressed or pinched by something. Very often this “something” is a tumor. Its etiology does not matter - a benign neoplasm in this case is no less dangerous than cancer.
Sometimes foreign bodies, including parasites and pieces of food, can enter the trachea, causing the animal to develop a severe cough. Because of this, the tissues of the larynx and trachea become severely irritated, resulting in hoarseness.
Why does the dog wheeze?
A common cause of wheezing in French bulldogs, pugs, Pekingese, and boxers is brachiocephalic syndrome. This is a narrowing of the lumen of the nostrils and excessive growth of the velum palatine, leading to a decrease in the volume of inhaled air. The animal almost constantly breathes with its mouth open, whistling and wheezing, and snores at night.
Allergic reactions, tracheal intubation, or foreign objects entering the oral cavity may cause laryngeal edema or laryngospasm. In older animals, paralysis of the vocal and laryngeal cords occurs, which is accompanied by shortness of breath and even fainting. Toy breeds of dogs (Chihuahuas, Toy Terriers, Yorkshire Terriers, Spitz and others) are most prone to tracheal collapse.
At first it begins with a cough, and then becomes aggravated by shortness of breath and loss of consciousness. A dog may wheeze if it suddenly inhales some foreign body, including a piece of dry food. Neoplasms may appear in the respiratory organs, which is accompanied by shortness of breath and coughing, sometimes with blood. One of the most common causes of wheezing, especially in the cold season, is bronchitis or pneumonia. They are usually . Also, wheezing in a dog can occur due to pulmonary edema, which is also accompanied by shortness of breath and pallor of the mucous membranes.
Treatment options
So what should you do if your dog suddenly becomes hoarse? It is necessary to take him to the veterinarian as soon as possible. It is possible that your pet does not have any serious illnesses, but it is still better to be safe. Treatment methods directly depend on the root cause. Thus, foreign bodies from the airways are removed surgically, and tumors that cause obstruction are also removed. If helminths are present, they are destroyed using specialized drugs. Important note - most drugs against larvae are not effective, and therefore the treatment is repeated after about two weeks (at this time small parasites are already in the intestines).
If acute bronchitis or pneumonia develops, it is advisable to take sputum samples to identify the exact type of pathogen. Only after this will the veterinarian be able to prescribe truly effective antibiotics and other antimicrobial drugs. Otherwise, treatment may not be effective.
Why did it happen so?
What to do if your cat or dog loses its voice? Unfortunately, you won’t find a clear answer to this question; first of all, you need to figure out why this happened. There are a number of factors and even serious diseases that can provoke the appearance of such an unpleasant symptom for your pet. After all, for him, the lack of a voice is a real shock, which he needs help to cope with.
- The most common reason for the disappearance of an animal's voice is damage to the larynx, esophagus or upper respiratory tract by some foreign object. It’s not surprising, because animals, like children, taste everything and can easily harm themselves with a sharp bone from a fish or chicken, a knot from a wooden stick, a piece of wire or even a spare part from a toy.
- Sometimes an animal loses its voice from lack of water. Remember that your pet should always have free access to a container of clean and fresh water.
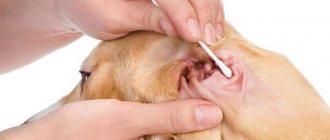
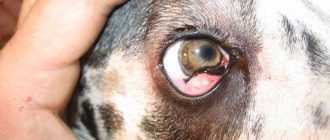
- Sometimes the disappearance of an animal’s voice is one of the symptoms of the disease. For example, otitis media, which is usually accompanied by ear inflammation.
- A common cold or a more serious viral illness can also cause voice loss. Naturally, in this case, the sick animal should also show other symptoms of the disease: for example, drowsiness, weakness, cough, fever, and so on. Typically, colds, just like in humans, are accompanied by swelling of the larynx, where mucus accumulates and makes it difficult for the animal to make sounds.
- Sometimes pets lose their voice if they spend a long time in a room with strong odors, such as solvents, varnishes or paint.
- Sometimes it is difficult for an animal to make any sounds if it is weakened by the effects of anesthesia.
In addition to the above reasons, the absence of a voice can be caused by other, even more serious diseases, for which you cannot treat on your own under any circumstances if you value the health of your pet. An experienced veterinarian will be able to determine the true cause of the problem and prescribe appropriate treatment.