The medical term “hypoglycemia” in dogs refers to a condition of the body in which a pathological decrease in glucose levels is observed in the blood of living creatures. It is considered normal when the mentioned indicator is approximately 3.5-7.5 mmol/liter. It turns out that if it drops below 3 mmol/liter, then you should start to worry about the health of your pet.
Hypoglycemia in dogs: symptoms and treatment
What is the danger of hypoglycemia?
Citizens who are not knowledgeable in medicine or veterinary medicine may not understand the dangers of such a condition as hypoglycemia, since it would seem that a drop in the level of glucose in its blood can harm an animal. However, hypoglycemia is extremely dangerous for animals, since glucose is responsible for performing many functions in the dog's brain and body. Provided that there is not enough sugar in the blood at all times for the normal functioning of the body, dogs may experience the following negative consequences:
- convulsions;
- hypoglycemic coma;
- death.
An examination by a veterinarian will either confirm or refute your suspicions.
Of course, no owner wants this for his pet. To prevent the development of this pathological condition, read this material carefully.
First aid
An attack of glycemia always looks scary, and besides, few dog owners, especially inexperienced ones, know what to do in such cases. Meanwhile, providing first aid at home is very simple; even a novice breeder can cope with simple and simple steps. You can give your four-legged pet a subcutaneous injection of glucose, give it a solution, or simply rub it into the gums.
In the absence of glucose, you can simply give your dog water with added sugar or honey.
The pet, naturally, will not want to drink sweet water and will resist manipulation. In this case, it is necessary to open his mouth and forcefully pour in the liquid. In this case, you need to act very carefully so that the dog does not choke.
For the procedure to be successful, it is advisable to find an assistant to hold the dog. To relieve an attack, you need to give a drink every 5 hours. If the animal is unconscious, the procedure is prohibited, as this may lead to aspiration into the respiratory system.
Vitamin B and carboxylase are used to normalize cardiac activity.
Further treatment is aimed primarily at stabilizing glucose levels and eliminating the factors that caused the pathology.
Reasons for low blood glucose levels in dogs
To understand how to get rid of hypoglycemia, you need to find out its cause. Thus, the basis for the development of the condition we are interested in in dogs can be completely different reasons. Let's look at them in more detail.
Juvenile hypoglycemia
The first and, perhaps, on the list of the most common causes of low blood sugar is juvenile (literally translated “characteristic of youth”) hypoglycemia. This variety, as you might have guessed, occurs most often in puppies whose age does not exceed three or four months.
The juvenile form of the disease is characteristic only of small puppies
The juvenile variety of the disease is characteristic only of puppies, since their small, not yet fully formed organisms are very often simply not able to effectively regulate the content of glucose in the blood, while having an increased need for it.
Any problem in the body can provoke juvenile hypoglycemia:
- nervous tension;
- cooling;
- hunger;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- helminths, etc.
Nervous tension can trigger juvenile hypoglycemia
Puppies of Toy breeds and slightly larger dogs are most often affected by this disease.
Malnutrition or hunger
However, hypoglycemia can also develop in adults, and it is often caused by malnutrition or outright starvation. This often happens when a dog lives on the street or the owners feed it incorrectly, giving:
- cheap industrial feed;
- vegetable soup or other non-nutritious natural food that is completely unsuitable for dogs.
However, not only the level of glucose contained in the animal’s blood, but also its general health depends on feeding, so forget about saving and give your pet what it needs.
For dogs, food, as for humans, is primarily a building material for the body. Its low quality or insufficient quantity leads to the development of a lot of pathologies
Excess physical activity
Excessive exercise and high-intensity training, which are often present in the lives of both hunting, sporting and most ordinary dogs, can also cause the development of serious hypoglycemia. To cope with the occurrence of such conditions, you just need to change the intensity of the load.
Addison's disease
Another cause of the disease in dogs may be the so-called Addison's disease, in which chronic insufficiency of the adrenal cortex occurs, causing a decrease in blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of Addison's disease
Incorrect insulin dose
Another reason for the development of hypoglycemia in adult animals may be an excessive amount of insulin administered to dogs suffering from diabetes mellitus. This situation often occurs when:
- the veterinarian has no experience in selecting drug dosages and did not cope with the task;
- The owner accidentally injects the wrong amount of medication into the dog over a period of time.
Remember: a disease such as diabetes is not a toy, so you need to be more attentive to the health of your pet.
Self-selection of insulin dosage for dogs with diabetes can lead to the death of the animal
Intestinal absorption disorders
Disturbances in the absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract can also cause a dog to develop a lack of glucose in the blood. You need to understand that this condition is also caused by some disease, and in this case you will have to fight not with a decrease in glucose, but with the factor that causes the pathological condition.
Insulinomas and other tumors
The cause of a decrease in blood glucose levels can also be the proliferation of insulinomas - tumors that arise in the body of the animal's pancreas. These tumors, becoming larger, begin to produce insulin in excess quantities, which causes a lack of sugar in the blood. In addition, other insulin-producing tumors can develop in the dog’s body, which can also cause the development of a pathological condition.
Unfortunately, cancer can cause an increase in insulin in a dog.
Liver pathologies
Some serious pathological processes affecting the liver, at certain stages, can also cause a decrease in the level of glucose in the dog’s blood.
Portosystemic shunts
The presence of portosystemic shunts in a dog's body can also cause a sharp drop in glucose levels. A portosystemic shunt is, in essence, a malformed vessel that most often passes inside or outside the liver, connecting the portal vein and the systemic venous circulation, bypassing the organ itself. Sometimes there are two shunts instead of one.
Various hereditary diseases
Some hereditary diseases in dogs can also cause the development of hypoglycemia, for example, a disease that is associated with the accumulation of glycogen in the body.
Sepsis
The development of septic processes in the dog’s body can also cause a decrease in blood glucose levels. Sepsis is an infection of bacterial etiology, and its consequences can affect not only sugar levels, but also other aspects of the body.
Sepsis can lead not only to hypoglycemia, but also to more serious consequences
Prevention measures
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. This fully applies to hypoglycemia. It is possible to prevent pathology, but to do this you need to take responsibility for keeping and feeding your pet. Many owners feed their dog food from their table, do not control food intake, and abuse treats.
Under no circumstances should you give your pet sweets (sweets, cookies, sugar). Such products cause great harm to the health of the animal. They cause hypoglycemia and create dangerous preconditions for the development of diabetes mellitus.
The owner is required to create the most comfortable living conditions for the dog and try to reduce the amount of stress. Emotional stress can be caused by anything - from a change of residence to a visit to the veterinary clinic.
If a newborn puppy does not gain weight or lags behind its peers in physical development, then this is a reason for the owner to be wary and seek advice from a veterinarian. Responsible breeders will never sell such a baby to people who do not have sufficient experience in keeping pets.
The puppy is under observation for at least 4 months; upon reaching this age, attacks of hypoglycemia, as a rule, are eliminated.
To prevent hypoglycemia in newborn dogs, preventive measures are also taken for pregnant bitches. The dog must eat well and receive the required amount of vitamins and microelements. Great importance is attached to quality care and hygiene.
In no case should you neglect routine examinations at the veterinary clinic. Thus, the most common cause of hypoglycemia is liver pathology. The sooner the problem is identified, the higher the chances of avoiding serious consequences for the health of your pet.
source
Clinical picture of hypoglycemia
Although hypoglycemia can only be definitively determined by a veterinarian's blood test and examination of the animal, there are some common symptoms that can tell you if your blood sugar is low before you visit the veterinarian. We are talking about such manifestations as:
- decreased appetite;
- apathy and lethargy;
- muscle tremors;
- convulsions;
- weak condition;
- any other manifestations of deviant behavior;
- deterioration of vision up to blindness;
- coma.
Apathy is one of the symptoms of the disease
As you can see, low blood glucose levels are actually quite difficult to confuse with anything else, so even if you are not a veterinarian, you will be able to recognize in time that your pet needs help.
How to diagnose hypoglycemia in dogs?
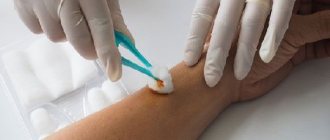
To diagnose a disease in a dog, the veterinarian, as we have already said, must measure your pet’s blood sugar level using a special device - a glucometer. To make a diagnosis, your pet will have a small puncture in the ear or have blood drawn in some other way. The biological fluid taken from the animal is collected and applied to a special measuring strip of the mentioned apparatus. Literally in moments the device will show the result of the examination.
A glucometer will help diagnose the disease at home.
This way you can tell if your dog is suffering from hypoglycemia. If there is a positive result, it is necessary to identify the cause of hypoglycemia in order to eliminate it. For this, other diagnostic tests are performed, such as:
- OAC, with the help of which processes of inflammatory etiology and anemia are detected;
- blood biochemistry, which allows you to assess the functioning of the internal systems of the body, for example, urinary, immune, endocrine, etc.;
- a general urine test, which detects the release of glucose, evaluates kidney function, etc.;
- testing for Addison's disease based on the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone;
- determining the amplitude of fluctuations in the level of gallbladder acid to exclude the presence of portosystemic shunts in the liver or within it;
- testing for insulin concentration levels commensurate with a certain amount of glucose present in the blood in order to exclude insulinoma;
- X-rays of the chest and abdomen to detect cancer in any way associated with hypoglycemia;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs to assess their structure and exclude cancer.
Tests can make your dog nervous and worried, so try to support him every minute so that your pet’s condition does not worsen.
Diagnosis of pathology
To make an accurate diagnosis, the veterinarian needs to collect an anamnesis, as well as conduct a series of clinical and laboratory tests. The main diagnostic method for hypoglycemia is to determine the blood glucose level. The lower limit is 3.4 mmol/l, hyperglycemic states occur when the value is above 6.2 mmol/l.
The treatment regimen is developed individually in each case, depending on the dog’s health condition. To do this, the specialist conducts an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test, and a bacterioscopic examination of the discharge (to exclude infection and urolithiasis).
How to treat hypoglycemia in dogs?
As we mentioned above, in order to finally understand hypoglycemia, you need to find out what exactly is causing it and, based on the information received, choose treatment. However, to quickly eliminate pathologically acute hypoglycemia, your pet urgently needs to inject a glucose solution directly into the bloodstream, through a vein. This measure will help instantly alleviate the dog’s well-being, transferring it from an acute condition to a stable one. Additionally, since dogs with hypoglycemia often have a low body temperature, the animal should be kept warm at all times using:
- blankets;
- heating pads with water.
A dropper with a glucose solution will help bring the animal out of a serious condition.
Animals whose condition is characterized as serious should remain at the veterinary clinic to receive treatment in a hospital setting. Feeding animals with hypoglycemia is also part of the therapy, as it is carried out according to a special schedule. So, food is given to dogs:
- in small portions;
- every few hours (3-4).
In this case, feeding should be carried out only with balanced and high-quality food.
All physical activity for a sick dog is limited, leaving only short walks, during which the dog simply defecates. Those animals whose hypoglycemia is caused by the development of tumors should begin taking glucocorticosteroid drugs.
Prognosis for dogs with hypoglycemia
Let's see what prognosis is relevant for dogs with the disease we are interested in, depending on what disease caused it.
The prognosis for hypoglycemic dogs may vary.
Table. Forecasts for the disease in question, depending on the cause of the disease
| Positive outlook | Negative Outlook |
| Juvenile hypoglycemia has an extremely positive prognosis, provided that you get your bearings in time and take the animal for examination to a veterinarian | A veterinarian will probably give a bad prognosis for a dog with insulinoma, since this tumor is not benign, and most likely, at the time of its discovery, there may already be metastases in the animal’s lungs |
| Hypoglycemia associated with malnutrition is also quickly eliminated, since its treatment only requires proper feeding and nutritious food, which will improve the dog’s health | A negative or unclear prognosis will be indicated for an animal that is suffering from any severe or moderate illness that causes the development of hypoglycemia, for example, liver pathology, impaired intestinal absorption of nutrients, sepsis. She may have portosystemic shunts or hereditary diseases. In this situation, the forecast will depend on:
|
| Hypoglycemia associated with increased physical activity is also considered harmless, since to restore the desired level of sugar in a dog’s blood, it is usually enough just to reduce the animal’s activity and help it with medication in the first stages |
You will be able to defeat the disease if you react to it in a timely manner
Symptoms
Symptoms of hypoglycemia vary depending on the specific form of the disease. In the normal course of the disease, the following signs indicate hypoglycemia:
- increased secretion of saliva;
- lethargy, apathy, drowsiness;
- sudden loss of appetite for no obvious reason;
- inactivity;
- digestive disorders;
- chills.
Acute hypoglycemia is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- loss of consciousness;
- severe cramps;
- coma (in the most severe cases);
- paralysis.
Dog owners should be aware that although an episode of acute hypoglycemia can be very frightening, it can be controlled with fairly simple measures. To do this, you need to give the dog an injection of glucose or give the dog a drink of water in which sugar is dissolved in large quantities. If the dog actively resists, you should try to open its mouth and forcefully pour water into it. But caution is necessary, since in this case there is a risk that the animal will choke.