Symptoms of inflammation of the glands
Dogs that live in unfavorable environments may develop the problem of blocked anal glands. At the same time, the animal is not able to free itself from the secretion, which greatly affects the well-being and mood of the pet.
During secretion stagnation, the animal constantly suffers from:
- pain in the anus;
- constant itching and discomfort.
Blockage of the paraanal glands is easily noticed by an attentive owner, because the dog becomes restless and behaves accordingly.
This problem can be identified by the following symptoms:
- The animal constantly chews or scratches in the area of the hind legs and under the tail;
- The animal sits on its hind legs and drags them along the ground, as if it has worms;
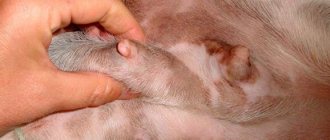
- When palpating the dog's glands, a thickening is felt.
Prevention
Preventive measures to avoid the development of the disease are extremely simple:
- proper, balanced and healthy nutrition for your pet;
- regular and long walks with active games and jumping;
- timely treatment of the intestines;
- Regular visits to the veterinarian to examine the anus;
- getting rid of helminths.
Obviously, it is always much easier to prevent the occurrence and development of a disease than to treat it later. Take care of your pet's health, walk it well and feed it properly, and also carefully care for your pet and may illness never befall you.
Many owners do not fully know the anatomy of their pets. Usually only veterinarians and breeders are aware of all the characteristics of animals. Let's look at what inflammation of the paraanal glands is in dogs, the symptoms and treatment of this pathology. It is important to know the intricacies of how your pet’s body works in order to identify signs of disease. This problem often confuses people.
Blockage of the paraanal glands leads to extremely unpleasant consequences. Owners should be aware of the symptoms of the problem and know how to clean it. Inflammation occurs due to the accumulation of secretion in the anal sacs, and its inability to come out naturally. If it is neglected, the pet may suffer from an abscess, self-injury, baldness, and nervousness. The list of possible consequences is incomplete, so there is no need to neglect this knowledge.
Cleansing the glands
If a dog has these symptoms, urgent cleaning of the paraanal glands (sanitation) is necessary. This procedure cannot be called pleasant, so squeamish people should not undertake it. It is better to immediately contact a veterinarian, who will cope with this task much faster and better. If the dog's owner can easily tolerate the strong and unpleasant odor of the secretion, then he can clean the glands on his own. This cleaning can be done by two methods, which require the presence of 2 people (one to carry out the manipulations, and the second to hold the dog in a certain position).
- First, you need to fix the dog in the basin, holding the muzzle with one hand and the body of the animal with the other;
- The second person should put on sterile gloves and carefully lift the animal by the tail with one hand;
- With your second hand you need to press on the sides on the anal glands, and the secretion will come out.
- The dog is fixed as in the first point of the previous method;
- The second person puts on gloves and lubricates his finger with Vaseline ointment;
- The finger is carefully inserted into the dog's anus;
- The person feels the gland with his finger and squeezes the liquid out of it.
Cleaning with this method is used exclusively for large breed dogs.
At the end of the manipulations, the animal is washed to get rid of the specific odor. An ichthyol suppository will help remove residual liquid. The frequency of the procedure is selected individually for the individual pet, depending on the rate of gland blockage.
Treatment of paraanal glands
At the initial stage, cleaning the anal glands can eliminate the problem. By eliminating the accumulated secretion from the glands, the cause of inflammation is eliminated. The remaining traces are cured by using specific medications.
The doctor cleans the outlet of the gland, if necessary, additionally rinses the cavities, injects an antibiotic solution and prescribes this medicine for severe purulent inflammatory process. Anti-inflammatory medications for dogs usually also have an analgesic effect.
If the animal has an abscess, it must be punctured, the contents released, and a deep cleaning performed. Additionally, antibiotics and other drugs are administered as prescribed by the doctor. If you just need to clean the formations, there is no need for anesthesia, but to treat inflammation, anesthesia is mandatory.
If the abscess has not yet matured, the dog is given a course of wet warm compresses to speed up the heating, and then the cavity is cleaned. Suppositories for dogs for inflammation of the paraanal glands in dogs are used at this stage and suppositories are chosen containing ichthyol. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for dogs are also used for treatment, which can effectively cope with the disease.
In general, treatment can take from 5 days to 2 weeks, but if there are no complications. If the formation of suppuration occurs frequently and cleansing must be carried out every 5-7 days, while the animal develops fistulas and obvious malaise, it is worth resorting to radical measures. In this case, the anal glands are surgically removed. This operation is considered simple, but it is performed extremely rarely. After all, the operation can disrupt the mental and emotional state of the animal. The animal loses its means of self-identification and may not be recognized by other dogs.
In addition to mechanical cleansing, the doctor may recommend:
- if your pet feels severe pain, the doctor may use a novocaine blockade;
- if there are purulent formations, the doctor prescribes fast-acting antibiotics. This allows you to quickly slow down the formation of pus and remove the bacteria that caused it;
- the use of antiseptics when washing the glands. These can be products with a natural composition or products to eliminate bacteria. Such drugs should be prescribed by a doctor after taking tests. This is due to the fact that antiseptics very often cause allergic reactions in animals.
Carrying out cleaning
You can clean the glands at home for therapeutic or preventive purposes. This procedure is not entirely pleasant and squeamish people should not do it. It is better to contact a veterinarian who can handle the task. But, if you still decide to carry out the procedure in the conditions familiar to the dog, you can use these most popular methods. For this procedure, you will need an assistant to hold the dog.
- First you need to secure the dog in a basin or bathtub, hold the muzzle with one hand, and the body with the other. If the dog breaks out and might bite, it is better to use a muzzle. The second person puts on sterile gloves and gently lifts the animal by the tail with one hand. With your other hand you need to lightly press on the sides of the anal glands. During this process, the secretion should come out;
- Fix the dog as in the previous method. The second person puts on gloves and smears his finger with Vaseline. The finger must be carefully inserted into the animal's anus. Feel the gland with your finger and squeeze the liquid out of it.
Cleaning with this method is only suitable for large dogs. For small breeds, only the external cleaning method should be used. Using a napkin, you need to squeeze the anal area and remove the contents that are released. The procedure should be carried out in the bathroom. Keep valuables away, as the secretion has a very unpleasant odor that is difficult to remove.
After you have completed the procedure, you should wash the animal with warm water and soap. This will eliminate the entire secret. To avoid inflammation or infection after the procedure, the dog can be given an anti-inflammatory suppository. This can be purchased at a pet store or veterinary pharmacy.
Complications
If the dogs’ paraanal glands under the tail are not cleaned in time, the treatment will be long and complicated, because there is a risk of complications.
The first problem that can arise from improper care of your pet is inflammation of the paraanal glands in dogs. It appears as a result of excessive accumulation of secretion in the anal sacs, which is influenced by bacteria and begins to rot.
In this case, the following are added to the main signs of inflammation of the glands:
- swelling in the anus area;
- redness of the anus;
- baldness around the base of the tail.
If the first symptoms of the disease appear, to exclude inflammation, it is necessary to contact a specialist in time, who can clean the dog’s glands and prescribe appropriate treatment. In addition, the doctor may prescribe the use of special suppositories, which are carefully inserted into the animal's anus. If the candle is intended for a small individual, it must be cut lengthwise into two parts. This treatment is quite effective.
The appearance of an abscess and fistula
If you don’t help your pet at this stage, then as a result of inflammation, the festering paraanal glands in dogs provoke the appearance of an abscess - an open wound under the tail on the animal’s skin through which pus comes out. An abscess forms as a result of the accumulation of pus in the anal sac. In this case, the symptoms of the disease become much more serious. Among them are loss of appetite, fever, and inactivity. Since the wound hurts, the animal constantly gnaws on the sore spot, thereby making it even worse. In this case, you should immediately contact a specialist, since cleaning the glands alone will not help.
Symptoms of malfunction of the paraanal glands
The owner can suspect a pathology in a pet by detecting the following clinical signs:
- The animal shows excessive interest in the anus - tries to bite the base of the tail, constantly licks the anus.
- The accumulated secretion causes irritation of the mucous membrane, which is accompanied by itching. The dog begins to fidget and “ride” on the floor at the fifth point, experiencing discomfort.
- The anal area swells, there is redness, rash, and scratching.
- The fur at the base of the tail has a sloppy appearance - wet and dull, with bald spots.
When the process is complicated by pathogenic microflora, the symptoms of inflammation of the paraanal glands in dogs are accompanied by a fetid odor of the secretion. In some cases, the pet experiences hyperthermia.
Treatment of complications
If the doctor has diagnosed an abscess or fistula in a dog, then the treatment should be comprehensive.
An abscess involves treatment in several stages:
- If the abscess does not have time to open on its own, the doctor may prescribe the use of compresses and, after a few days, open the suppuration on its own;
- Getting rid of pus and cleaning the paraanal gland under the tail;
- Antiseptic wound treatment;
- The use of suppositories, injections, tablets and preparations for local treatment of wounds;
- Use of antibiotics;
- Following recommendations to improve the animal’s diet, adding additional vegetables to the menu to improve intestinal function;
- In the most advanced cases, removal of the anal glands is indicated.
If a fistula is discovered in a pet, this is a reason to contact a veterinarian urgently, because eliminating this problem does not eliminate the need for surgical intervention. If after recovery the fistula reopens, a blood transfusion may be prescribed to the animal. After a course of treatment or removal of the source of suppuration, you need to properly conduct a recovery period using vitamins, a comfortable environment and quality nutrition.
Factors contributing to inflammation
The tendency to blockage of the anal sacs in felines develops regardless of their gender or breed. According to statistics, inflammation of the anus in cats diagnosed in young pets that are obese and do not move much.
Veterinarians tend to identify the following causes of inflammation of the paraanal glands in cats :
- physical inactivity;
- metabolic disorders in the animal and hormonal imbalance;
- helminthic infestation;
- frequent diarrhea;
- soft and liquid food in the animal’s daily diet;
- traumatic lesions of the anal area;
- bacterial infections;
- immunodeficiency states and hypovitaminosis.
Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory help - suppositories with Ichthyol
Last summer my dog developed an inflammation of the anal gland. There was severe swelling, fever, the dog was lethargic and warm. Her husband took her to the city, took her to a veterinary clinic, where they gave her local anesthesia and cleaned everything out. The dog recovered quite quickly, I was very happy.
In the fall the problem repeated itself. I took her to the clinic again, she was given an injection, a rinse and was told that the problem was solved. After that, once every month or two, one or the other gland became inflamed. I solved the problem locally - I applied synthomycin and baneocin, but the sore kept coming back.
Also, in the fall and spring the dog had a very sluggish estrus, which needed to be stimulated with injections to prevent purulent inflammation of the uterus. The solution to the problem with the anal glands was postponed, but then the cat got sick and I decided not to wait for free time, but to help the dog’s butt, without waiting for all family members to fully recover. Thanks to my dog, I learned about this interesting medicine.
- Name - Ichthyol
- Release form: rectal suppositories. Sold without a prescription.
- .
Full box with product information.
- The instructions are printed on both sides of a small piece of paper.
- The storage conditions are quite unusual; I don’t know how to create a temperature from 12 to 15C in the apartment. I put the box in the refrigerator, away from the freezer, to keep it warmer.
Ichthyol (ichhtamol), water, emulsifier, solid fat Vitepsol, Supposir.
- Action of the medicine: anti-inflammatory and antiseptic. Contraindication is children's age.
- Side effects are possible in the form of allergic reactions.
- Directions for use: 1-2 times a day, after consultation with a doctor.
Because of Ichthyol, the candle is almost black, but there is no strong smell, apparently it will be felt if the composition melts a little.
- The veterinarian's prescription was the same as for humans: 2 times a day, after a walk, when the intestines are empty.
The duration of the course is 10 days.
- What happens to a dog's anal glands if the ducts are blocked?
The gland becomes inflamed and makes its way out, past the duct that leads to the rectum. A schematic drawing will help to visualize this problem.
Inflammation of the paraanal glands in dogs
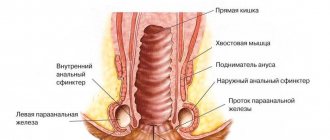
Under the dog's tail, on both sides of the anus, there are a pair of anal glands. If you visually draw a horizontal line through the center of the anal sphincter, the glands will be located below the horizontal on both sides of the anus.
Diagram of the paraanal glands of a dog.
Peculiarities
During defecation, the glands are emptied.
- The glands are subcutaneous and we cannot visually examine them, however, with a strong inflammatory process, during palpation we can feel the sealing tubercles.
- The ducts of a pair of anal glands exit into the rectum , into an area that is located almost at the sphincter itself.
- In their anatomical structure, they have something in common with the sweat and sebaceous glands . The secretion that is produced normally has a yellow color, liquid consistency and a specific smell.
- Such glands exist in the entire canine family , as well as some other mammals, for example, skunks.
- Emptying of the glands occurs during the act of defecation . The secret serves as a kind of odorous mark. With its help, animals “inform” their relatives about the ownership of the territory, and also attract individuals of the opposite sex.
Causes of inflammation and pathogenesis
Sometimes inflammation of a pair of anal glands occurs in dogs. There may be several reasons for this:
- anal sphincter injuries;
- genetic characteristics;
- weakened immunity as a result of stress;
- frequent constipation or diarrhea.
Stress can trigger inflammation of the anal glands.
Any of these reasons can lead to blockage of the outlet channel. As a result, the secretion accumulates in the glandular sacs and becomes concentrated.
By changing its biochemical composition, it becomes a medium for microflora. Opportunistic microorganisms acquire increased virulence and begin to multiply rapidly. The secretion becomes thick, dark brown in color and has a foul odor.
Sometimes, the contents of a pair of anal glands may contain:
- fibrin flakes - for fibrinous inflammation;
- blood - with serous inflammation;
- pus - with purulent inflammation.
If the pathogenic microflora develops intensively, and the animal is not helped, then the glands become overcrowded, their walls stretch and become thinner . As a result, a fistula can form either with an exit into the lumen of the rectum or with an exit out into the anal area.
Useful video
To learn how to wash a dog's anal glands, watch this video:
Similar articles
- Why does a dog smell (strongly like dog, fish, mice...)
The stench comes from the pet and with such a pathology as inflammation of the paraanal glands. ... Even the most expensive and high-quality food is not a guarantee that the dog is not allergic to the components of the mixture. Read more - Constipation in a dog - what to do, what will help best for...
Pathology of the paraanal glands. Inflammation and abscesses in the anal area lead to painful defecation and... Symptoms in dogs. A healthy adult dog should have bowel movements 1-2 times a day. Read more
- Inflammation of the dog's testicles: causes, symptoms, treatment
Causes of testicular inflammation in dogs and treatment. Author of the article: Lyubov Ilyina (veterinarian). Orchitis (epididymitis) is an inflammatory process that affects the male gonads - the testicles. Read more
- Boils in dogs: how to treat if they jump up on the nose...
Unpleasant boils in dogs: signs and treatment. Author of the article: Lyubov Ilyina (veterinarian). Focal inflammation of the sebaceous gland and hair follicle of a purulent nature in domestic animals is called a boil. Read more
- Inflammation of the salivary glands in a dog: symptoms, treatment
Causes of inflammation of the salivary glands in dogs. In dogs, according to their anatomical location, the parotid, submandibular, sublingual and zygomatic glands are distinguished. Read more
Symptoms of inflammation in a dog
Initially, the accumulation of contents in the glands does not cause concern to the animal and is not clinically manifested. After some time, you may notice the dog's anxiety and increased attention to the anal area.
When inflammation occurs, the dog develops itching in the anus area.
- The dog sits down, stands up, sits down again and tries to lick or bite the anus area . Sometimes the animal “rides” in a sitting position, trying to rub its tail zone against all possible objects.
- By carefully observing the animal, you can judge that this problem area is both itchy and painful for the dog.
- If the process is delayed and purulent exudate forms in the cavity of the sac, then the absorption of pathogenic microflora and waste products leads to an increase in body temperature . However, it is also not always possible to measure the temperature in the rectum, with septic inflammation in the anal area, because the animal shows excessive anxiety. In addition, the temperature will be increased at the site of inflammation, which will not make it possible to understand a clear picture of what is happening throughout the body.
- In this case, it is necessary to carefully observe the animal, and if during the act of defecation the animal experiences not just anxiety, but also pain, we will understand this by the dog’s reaction, then it is necessary to immediately contact a veterinarian.
- There are cases when a dog nevertheless violates the integrity of the skin (gnaws it, tears it against objects), the contents spill out and temporary relief occurs . The dog calms down, and so does the owner. However, the glands continue to function and secrete secretions. The wound surface is glued together with purulent masses and fibrin threads, and “imaginary” healing occurs. The problem is not solved, it is only getting worse.
Treatment
If you have already noticed all the signs of concern, it is better to consult a doctor. Because with such symptoms, you may have to resort to surgically opening the cavities with installing drainage, washing the cavity with disinfectants and administering antibiotics.
- If you discover a cavity on your own and there is no way to resort to medical help, then you need to put an ointment with a broad-spectrum antibiotic , for example, cephalexin or amoxicillin, into the sinus.
- The same antibiotics are used intramuscularly , the course duration is 6-8 days.
- If the cavities are not opened, then suppositories such as “ Proctosedyl ”, “ Ichthyol ” can be placed rectally (into the lumen of the anus).
- If the dog’s condition is severe and medical assistance does not lead to recovery, removal of a pair of anal sinuses (sacculectomy) is prescribed.
Ichthyol suppositories are used rectally.
Prevention
If your dog is genetically predisposed to blockage of the excretory ducts of a pair of anal glands, your doctor may recommend that you carry out the debridement procedure yourself.
Twice a month you need to wash your dogs anus.
Cleansing, releasing the glands, is carried out mechanically and regularly. The interval between manipulations can be within 3-9 months, and is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the animal’s body. As a rule, sanitation is combined with bathing the dog.
Sometimes, sanitation is not even required; it is enough to carry out water procedures in the anus area with warm soapy water 2 times a month with light massaging of the anus area.
Pet treatment methods
It is important to note that you can treat your dog yourself only if it is not possible to see a doctor at the moment. To alleviate the suffering of the animal, you can use rectal suppositories with ichthyol. It is also possible to use broad-spectrum antibiotic ointments, which include amoxicillin. In addition, intramuscular injections with similar antibiotics can be given. If there are regular relapses of inflammation, veterinarians recommend cleaning the glands at home or removing them altogether.
Mechanical cleaning and antibacterial treatment
Sanitation can be carried out in two ways: external and internal.
External cleaning
You can simply and painlessly clean your dog's anal glands using an ordinary napkin and Vaseline. The animal should be placed in the bathtub and its tail raised up towards its back. This position of the tail leads to relaxation of the muscles, the ducts open, which makes cleaning as comfortable as possible. Place a napkin on the sphincter area, gently press on both sides and wipe off the released secretion with the napkin. After the procedure, the anus should be lubricated with Vaseline. Then place ichthyol suppositories for three days.
Cleaning the dog's anal gland at home
Let's look at several cleaning methods.
There are two ways to clean the anal gland.
Method 1
- If the procedure is combined with bathing, then the animal is placed in the bathtub. With one hand, we lift the dog’s tail as much as possible and move it to the back (up, not to the side), the anatomical feature is such that at this moment the muscles relax and the ducts open.
- Place a napkin on the anal area and gently squeeze lightly on both sides of the anal sphincter. In this case, the released secret remains in the napkin. Next, we start bathing the dog. At the end of the procedure, lubricate the anus area with Vaseline.
- If during the procedure the animal’s anxiety, pain reaction, or damage in the sphincter area (cracks, redness) is noticeable, lubricate the anus area with syntomycin liniment (ointment), and place rectal ichthyol suppositories for 3-4 days.
After the bathing procedure, you need to lubricate the anus with Vaseline.
Method 2
As a rule, doctors use this method because it allows one to simultaneously palpate the area of the pair of anal glands for diagnostic purposes.
It is imperative to use personal protective equipment, in this case wear a rubber glove. Lubricate the anus area and fingers with Vaseline oil.
- The index finger is inserted into the rectum, and the thumb grasps the fold of skin around the sphincter. Apply pressure alternately on both sides with light massaging movements.
- The manipulation site is treated with a cloth moistened with chlorhexidine. We insert rectal ichthyol suppositories into the lumen of the anus for 3-4 days, preferably after the dog has defecated.
- For problem animals, it is advisable to wipe the anal area with a chlorhexidine wipe after each bowel movement. The procedure is simple and is an excellent prevention of inflammatory processes.
Before the procedure, you should wear rubber gloves.
conclusions
Before using one method or another, consult your doctor; perhaps the anatomical features of your dog will be a contraindication and the doctor will give individual advice.
The veterinarian will provide recommendations for effective treatment.
Each organism has individual characteristics, and if in your dog they are associated with a violation of the outflow of secretions, then you need to perceive this as part of caring for the animal. Proper feeding, walking, bathing and sanitation are necessary procedures that make the four-legged life healthy and prosperous.